






//创建 Stream方式一:通过集合 @Test public void test1(){ List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployees(); // default Stream<E> stream() : 返回一个顺序流 Stream<Employee> stream = employees.stream(); // default Stream<E> parallelStream() : 返回一个并行流 Stream<Employee> parallelStream = employees.parallelStream(); } //创建 Stream方式二:通过数组 @Test public void test2(){ int[] arr = new int[]{1,2,3,4,5,6}; //调用Arrays类的static <T> Stream<T> stream(T[] array): 返回一个流 IntStream stream = Arrays.stream(arr); Employee e1 = new Employee(1001,"Tom"); Employee e2 = new Employee(1002,"Jerry"); Employee[] arr1 = new Employee[]{e1,e2}; Stream<Employee> stream1 = Arrays.stream(arr1); } //创建 Stream方式三:通过Stream的of() @Test public void test3(){ Stream<Integer> stream = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6); } //创建 Stream方式四:创建无限流 @Test public void test4(){ // 迭代 // public static<T> Stream<T> iterate(final T seed, final UnaryOperator<T> f) //遍历前10个偶数 Stream.iterate(0, t -> t + 2).limit(10).forEach(System.out::println); // 生成 // public static<T> Stream<T> generate(Supplier<T> s) Stream.generate(Math::random).limit(10).forEach(System.out::println); }


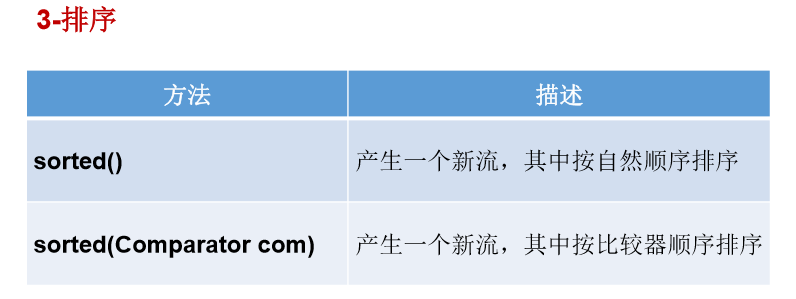
//1-筛选与切片 @Test public void test1(){ List<Employee> list = EmployeeData.getEmployees(); // filter(Predicate p)——接收 Lambda , 从流中排除某些元素。 Stream<Employee> stream = list.stream(); //练习:查询员工表中薪资大于7000的员工信息 stream.filter(e -> e.getSalary() > 7000).forEach(System.out::println); System.out.println(); // limit(n)——截断流,使其元素不超过给定数量。 list.stream().limit(3).forEach(System.out::println); System.out.println(); // skip(n) —— 跳过元素,返回一个扔掉了前 n 个元素的流。若流中元素不足 n 个,则返回一个空流。与 limit(n) 互补 list.stream().skip(3).forEach(System.out::println); System.out.println(); // distinct()——筛选,通过流所生成元素的 hashCode() 和 equals() 去除重复元素 list.add(new Employee(1010,"刘强东",40,8000)); list.add(new Employee(1010,"刘强东",41,8000)); list.add(new Employee(1010,"刘强东",40,8000)); list.add(new Employee(1010,"刘强东",40,8000)); list.add(new Employee(1010,"刘强东",40,8000)); // System.out.println(list); list.stream().distinct().forEach(System.out::println); } //映射 @Test public void test2(){ // map(Function f)——接收一个函数作为参数,将元素转换成其他形式或提取信息,该函数会被应用到每个元素上,并将其映射成一个新的元素。 List<String> list = Arrays.asList("aa", "bb", "cc", "dd"); list.stream().map(str -> str.toUpperCase()).forEach(System.out::println); // 练习1:获取员工姓名长度大于3的员工的姓名。 List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployees(); Stream<String> namesStream = employees.stream().map(Employee::getName); namesStream.filter(name -> name.length() > 3).forEach(System.out::println); System.out.println(); //练习2: Stream<Stream<Character>> streamStream = list.stream().map(StreamAPITest1::fromStringToStream); streamStream.forEach(s ->{ s.forEach(System.out::println); }); System.out.println(); // flatMap(Function f)——接收一个函数作为参数,将流中的每个值都换成另一个流,然后把所有流连接成一个流。 Stream<Character> characterStream = list.stream().flatMap(StreamAPITest1::fromStringToStream); characterStream.forEach(System.out::println); } //将字符串中的多个字符构成的集合转换为对应的Stream的实例 public static Stream<Character> fromStringToStream(String str){//aa ArrayList<Character> list = new ArrayList<>(); for(Character c : str.toCharArray()){ list.add(c); } return list.stream(); } //3-排序 @Test public void test4(){ // sorted()——自然排序 List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(12, 43, 65, 34, 87, 0, -98, 7); list.stream().sorted().forEach(System.out::println); //抛异常,原因:Employee没有实现Comparable接口 // List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployees(); // employees.stream().sorted().forEach(System.out::println); // sorted(Comparator com)——定制排序 List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployees(); employees.stream().sorted( (e1,e2) -> { int ageValue = Integer.compare(e1.getAge(),e2.getAge()); if(ageValue != 0){ return ageValue; }else{ return -Double.compare(e1.getSalary(),e2.getSalary()); } }).forEach(System.out::println); }


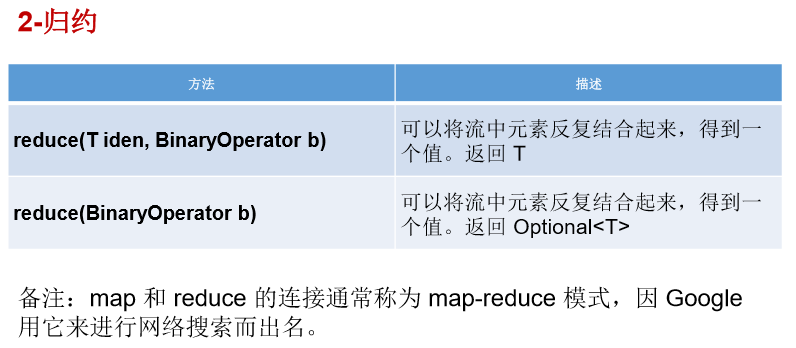
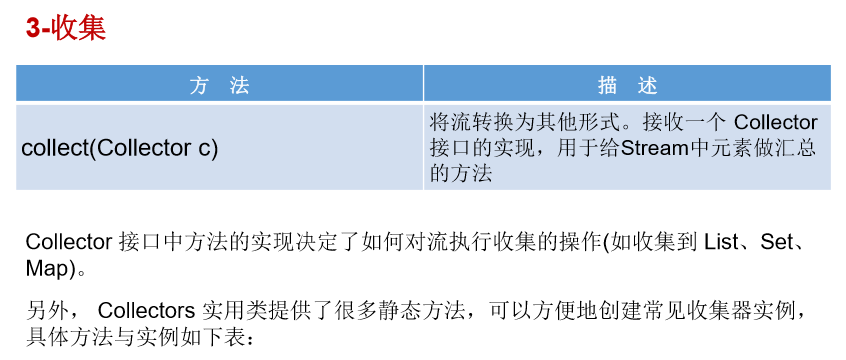
//1-匹配与查找 @Test public void test1(){ List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployees(); // allMatch(Predicate p)——检查是否匹配所有元素。 // 练习:是否所有的员工的年龄都大于18 boolean allMatch = employees.stream().allMatch(e -> e.getAge() > 18); System.out.println(allMatch); // anyMatch(Predicate p)——检查是否至少匹配一个元素。 // 练习:是否存在员工的工资大于 10000 boolean anyMatch = employees.stream().anyMatch(e -> e.getSalary() > 10000); System.out.println(anyMatch); // noneMatch(Predicate p)——检查是否没有匹配的元素。 // 练习:是否存在员工姓“雷” boolean noneMatch = employees.stream().noneMatch(e -> e.getName().startsWith("雷")); System.out.println(noneMatch); // findFirst——返回第一个元素 Optional<Employee> employee = employees.stream().findFirst(); System.out.println(employee); // findAny——返回当前流中的任意元素 Optional<Employee> employee1 = employees.parallelStream().findAny(); System.out.println(employee1); } @Test public void test2(){ List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployees(); // count——返回流中元素的总个数 long count = employees.stream().filter(e -> e.getSalary() > 5000).count(); System.out.println(count); // max(Comparator c)——返回流中最大值 // 练习:返回最高的工资: Stream<Double> salaryStream = employees.stream().map(e -> e.getSalary()); Optional<Double> maxSalary = salaryStream.max(Double::compare); System.out.println(maxSalary); // min(Comparator c)——返回流中最小值 // 练习:返回最低工资的员工 Optional<Employee> employee = employees.stream().min((e1, e2) -> Double.compare(e1.getSalary(), e2.getSalary())); System.out.println(employee); System.out.println(); // forEach(Consumer c)——内部迭代 employees.stream().forEach(System.out::println); //使用集合的遍历操作 employees.forEach(System.out::println); } //2-归约 @Test public void test3(){ // reduce(T identity, BinaryOperator)——可以将流中元素反复结合起来,得到一个值。返回 T // 练习1:计算1-10的自然数的和 List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10); Integer sum = list.stream().reduce(0, Integer::sum); System.out.println(sum); // reduce(BinaryOperator) ——可以将流中元素反复结合起来,得到一个值。返回 Optional<T> // 练习2:计算公司所有员工工资的总和 List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployees(); Stream<Double> salaryStream = employees.stream().map(Employee::getSalary); // Optional<Double> sumMoney = salaryStream.reduce(Double::sum); Optional<Double> sumMoney = salaryStream.reduce((d1,d2) -> d1 + d2); System.out.println(sumMoney.get()); } //3-收集 @Test public void test4(){ // collect(Collector c)——将流转换为其他形式。接收一个 Collector接口的实现,用于给Stream中元素做汇总的方法 // 练习1:查找工资大于6000的员工,结果返回为一个List或Set List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployees(); List<Employee> employeeList = employees.stream().filter(e -> e.getSalary() > 6000).collect(Collectors.toList()); employeeList.forEach(System.out::println); System.out.println(); Set<Employee> employeeSet = employees.stream().filter(e -> e.getSalary() > 6000).collect(Collectors.toSet()); employeeSet.forEach(System.out::println); }