前面两篇文章和读者聊了Spring Boot中最简单的数据持久化方案JdbcTemplate,JdbcTemplate虽然简单,但是用的并不多,因为它没有MyBatis方便,在Spring+SpringMVC中整合MyBatis步骤还是有点复杂的,要配置多个Bean,Spring Boot中对此做了进一步的简化,使MyBatis基本上可以做到开箱即用,本文就来看看在Spring Boot中MyBatis要如何使用。
工程创建
首先创建一个基本的Spring Boot工程,添加Web依赖,MyBatis依赖以及MySQL驱动依赖,如下:
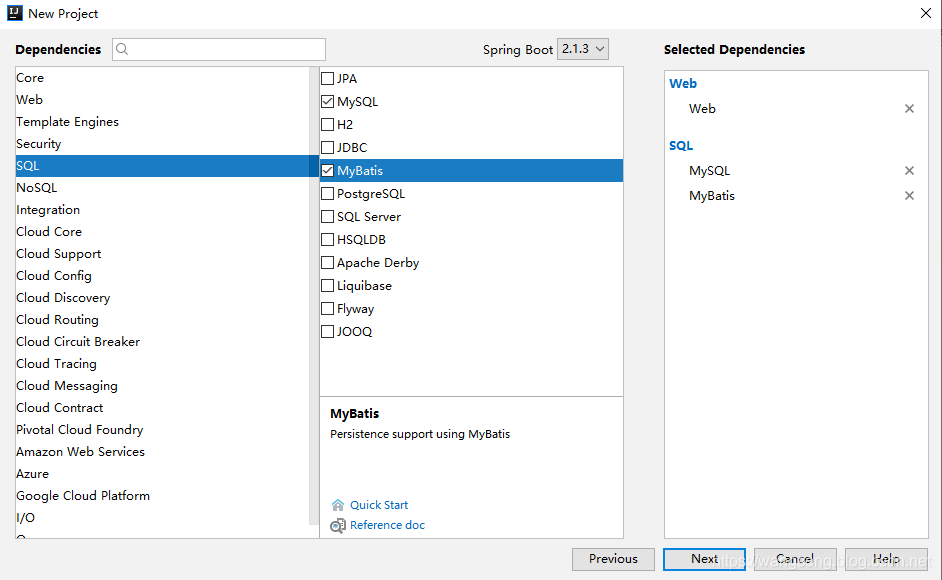
创建成功后,添加Druid依赖,并且锁定MySQL驱动版本,完整的依赖如下:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.0.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.1.10</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.28</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
如此,工程就算是创建成功了。读者注意,MyBatis和Druid依赖的命名和其他库的命名不太一样,是属于xxx-spring-boot-stater模式的,这表示该starter是由第三方提供的。
基本用法
MyBatis的使用和JdbcTemplate基本一致,首先也是在application.properties中配置数据库的基本信息:
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql:///test01?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=root
spring.datasource.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
配置完成后,MyBatis就可以创建Mapper来使用了,例如我这里直接创建一个UserMapper2,如下:
public interface UserMapper2 {
@Select("select * from user")
List<User> getAllUsers();
@Results({
@Result(property = "id", column = "id"),
@Result(property = "username", column = "u"),
@Result(property = "address", column = "a")
})
@Select("select username as u,address as a,id as id from user where id=#{id}")
User getUserById(Long id);
@Select("select * from user where username like concat('%',#{name},'%')")
List<User> getUsersByName(String name);
@Insert({"insert into user(username,address) values(#{username},#{address})"})
@SelectKey(statement = "select last_insert_id()", keyProperty = "id", before = false, resultType = Integer.class)
Integer addUser(User user);
@Update("update user set username=#{username},address=#{address} where id=#{id}")
Integer updateUserById(User user);
@Delete("delete from user where id=#{id}")
Integer deleteUserById(Integer id);
}
这里是通过全注解的方式来写SQL,不写XML文件,@Select、@Insert、@Update以及@Delete四个注解分别对应XML中的select、insert、update以及delete标签,@Results注解类似于XML中的ResultMap映射文件(getUserById方法给查询结果的字段取别名主要是向小伙伴们演示下@Results注解的用法),另外使用@SelectKey注解可以实现主键回填的功能,即当数据插入成功后,插入成功的数据id会赋值到user对象的id属性上。
UserMapper2创建好之后,还要配置mapper扫描,有两种方式,一种是直接在UserMapper2上面添加@Mapper注解,这种方式有一个弊端就是所有的Mapper都要手动添加,要是落下一个就会报错,还有一个一劳永逸的办法就是直接在启动类上添加Mapper扫描,如下:
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan(basePackages = "org.sang.mybatis.mapper")
public class MybatisApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MybatisApplication.class, args);
}
}
好了,做完这些工作就可以去测试Mapper的使用了。
mapper映射
当然,开发者也可以在XML中写SQL,例如创建一个UserMapper,如下:
public interface UserMapper {
List<User> getAllUser();
Integer addUser(User user);
Integer updateUserById(User user);
Integer deleteUserById(Integer id);
}
然后创建UserMapper.xml文件,如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="org.sang.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper">
<select id="getAllUser" resultType="org.sang.mybatis.model.User">
select * from t_user;
</select>
<insert id="addUser" parameterType="org.sang.mybatis.model.User">
insert into user (username,address) values (#{username},#{address});
</insert>
<update id="updateUserById" parameterType="org.sang.mybatis.model.User">
update user set username=#{username},address=#{address} where id=#{id}
</update>
<delete id="deleteUserById">
delete from user where id=#{id}
</delete>
</mapper>
将接口中方法对应的SQL直接写在XML文件中。
那么这个UserMapper.xml到底放在哪里呢?有两个位置可以放,第一个是直接放在UserMapper所在的包下面:
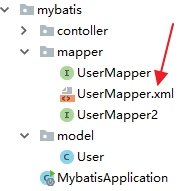
放在这里的UserMapper.xml会被自动扫描到,但是有另外一个Maven带来的问题,就是java目录下的xml资源在项目打包时会被忽略掉,所以,如果UserMapper.xml放在包下,需要在pom.xml文件中再添加如下配置,避免打包时java目录下的XML文件被自动忽略掉:
<build>
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/java</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
</includes>
</resource>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resources</directory>
</resource>
</resources>
</build>
当然,UserMapper.xml也可以直接放在resources目录下,这样就不用担心打包时被忽略了,但是放在resources目录下,又不能自动被扫描到,需要添加额外配置。例如我在resources目录下创建mapper目录用来放mapper文件,如下:
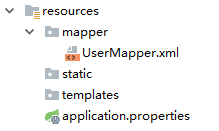
此时在application.properties中告诉mybatis去哪里扫描mapper:
mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:mapper/*.xml
如此配置之后,mapper就可以正常使用了。注意第二种方式不需要在pom.xml文件中配置文件过滤。
原理分析
在SSM整合中,开发者需要自己提供两个Bean,一个SqlSessionFactoryBean,还有一个是MapperScannerConfigurer,在Spring Boot中,这两个东西虽然不用开发者自己提供了,但是并不意味着这两个Bean不需要了,在org.mybatis.spring.boot.autoconfigure.MybatisAutoConfiguration类中,我们可以看到Spring Boot提供了这两个Bean,部分源码如下:
@org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass({ SqlSessionFactory.class, SqlSessionFactoryBean.class })
@ConditionalOnSingleCandidate(DataSource.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(MybatisProperties.class)
@AutoConfigureAfter(DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class)
public class MybatisAutoConfiguration implements InitializingBean {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory(DataSource dataSource) throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
factory.setDataSource(dataSource);
return factory.getObject();
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public SqlSessionTemplate sqlSessionTemplate(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) {
ExecutorType executorType = this.properties.getExecutorType();
if (executorType != null) {
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory, executorType);
} else {
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
@org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration
@Import({ AutoConfiguredMapperScannerRegistrar.class })
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(MapperFactoryBean.class)
public static class MapperScannerRegistrarNotFoundConfiguration implements InitializingBean {
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
logger.debug("No {} found.", MapperFactoryBean.class.getName());
}
}
}
从类上的注解可以看出,当当前类路径下存在SqlSessionFactory、 SqlSessionFactoryBean以及DataSource时,这里的配置才会生效,SqlSessionFactory和SqlTemplate都被提供了。为什么要看这段代码呢?下篇文章,松哥和大伙分享Spring Boot中MyBatis多数据源的配置时,这里将是一个重要的参考。
好了,本文就先说到这里,关于在Spring Boot中整合MyBatis,这里还有一个小小的视频教程,加入我的星球即可免费观看:

关于我的星球【Java达摩院】,大伙可以参考这篇文章推荐一个技术圈子,Java技能提升就靠它了.
