一、Github地址 课程项目要求 队友博客
二、具体分工
- 031602225 林煌伟 :负责C++部分主要功能函数的编写,算法的设计以及改进优化
- 031602230 卢恺翔 : 爬虫实现以及附加功能,代码框架设计,接口封装
三、psp表格 & 学习进度条
- psp表格
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 60 | 60 |
| · Estimate | · 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 30 | 30 |
| Development | 开发 | 1000 | 1160 |
| · Analysis | · 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 120 | 180 |
| · Design Spec | · 生成设计文档 | 10 | 10 |
| · Design Review | · 设计复审 | 10 | 10 |
| · Coding Standard | · 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 10 | 10 |
| · Design | · 具体设计 | 30 | 30 |
| · Coding | · 具体编码 | 780 | 900 |
| · Code Review | · 代码复审 | 20 | 20 |
| · Test | · 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 20 | 20 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 130 | 130 |
| · Test Repor | · 测试报告 | 60 | 60 |
| · Size Measurement | · 计算工作量 | 10 | 10 |
| · Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | · 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 60 | 60 |
| | 合计 | 1190|1350
- 学习进度条
| 第N周 | 新增代码(行) | 累计代码(行) | 本周学习耗时(小时) | 累计学习耗时(小时) | 重要成长 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 500 | 500 | 12 | 12 | 单元测试的编写 |
| 2 | 200 | 700 | 16 | 28 | Axure原型设计工具的使用、Python的文件读写 |
| 3 | 500 | 1200 | 20 | 48 | Python爬虫的编写、词云图的绘制和Python的文件读写 |
四、解题思路描述与设计实现说明 & 关键代码解释
-
爬虫使用
Attention!
爬虫的CVPR.py文件放在CVPR\_Python的根目录下。CVPR.exe文件放在
CVPR\_Python/dist/CVPR/CVPR.exe ,可以直接使用该文件来获取论文信息。
本次我们使用Python编写爬虫,利用requests库获取网页的html标签树,并用BeautifulSoup库对其进行解析。利用正则表达式或者BeautifulSoup类对象获取我们想要的信息。
#encoding: utf-8
import time
import requests
import multiprocessing
from multiprocessing import Queue,Process,Pool
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import re
import os
url = 'http://openaccess.thecvf.com/CVPR2018.py'
i = 0
href = Queue()
def get_url():
try:
r = requests.get(url,headers=req_header)
r.raise_for_status()
r.encoding = r.status_code
bsObj = BeautifulSoup(r.text,'lxml')
for dt in bsObj.find_all('dt'):
new_url = 'http://openaccess.thecvf.com/' + dt.a['href']
href.put(new_url)
except:
print("error")
通过上述函数来获取CVPR官网上所有的论文链接,并将他们放在一个队列中。每次获取论文的详细信息时,就从队列中拿出一个链接进行分析。
def get_message(myurl):
try:
global i
title, abstract, authors, pdflink = get_abstract(myurl)
with open('result.txt','a+',encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write(str(i) + '
')
f.write('Title: ' + title + '
')
f.write('Authors: ' + authors + '
')
f.write('Abstract: ' + abstract + '
')
f.write('PDF_LINK: '+ pdflink + '
')
f.write('
')
f.close()
i += 1
print("%s is crawled!" % myurl)
except:
print('error')
def get_abstract(newurl):
try:
r = requests.get(newurl,headers=req_header)
r.raise_for_status()
bsObj = BeautifulSoup(r.text,'lxml')
pattern = re.compile('(.*)</div>')
title = re.findall(pattern, r.text)
title = bsObj.find_all('div',{'id':'papertitle'})[0].text
abstract = bsObj.find_all('div',{'id':'abstract'})[0].text
pattern = re.compile('.*<i>(.*)</i>')
authors = re.findall(pattern, r.text)[0]
pattern = re.compile('.*<a href="(.*)">pdf')
pdflink = re.findall(pattern,r.text)[0].replace('../..','http://openaccess.thecvf.com')
return title.replace('
',''), abstract.replace('
',''), authors, pdflink
except:
print("error")
利用正则表达式或BeautifulSoup类对象来获取网页中我们需要的信息,如论文标题、作者、简介和论文的pdf链接。并将他们按照要求格式输入至result.txt之中。
if __name__ == '__main__':
if os.path.exists('result.txt'):
os.remove('result.txt')
get_url()
start = time.time()
while not href.empty():
get_message(href.get())
# process = []
# num_cpus = multiprocessing.cpu_count()
# print('将会启动进程数为:', num_cpus)
# while not href.empty():
# process.append(href.get())
# p = Pool()
# p.map(get_message, process)
# p.close()
# p.join()
end = time.time()
print("共计用时%.4f秒" %(end-start))
本来这里我想要用多进程来完成本次的爬虫,但是遇到2个问题,所以放弃了。
- 在使用多进程的时候,我的论文编号会保持在1个数字不动,直到所有进程全部完成,才会将论文编号+1 。
- 在使用pyinstaller对.py文件编译后的.exe文件,他会无限制地占用CPU资源,使得电脑死机。
希望如果懂得这些原理的大佬能够帮忙评论一下ORZ
-
代码组织与内部实现设计(类图)
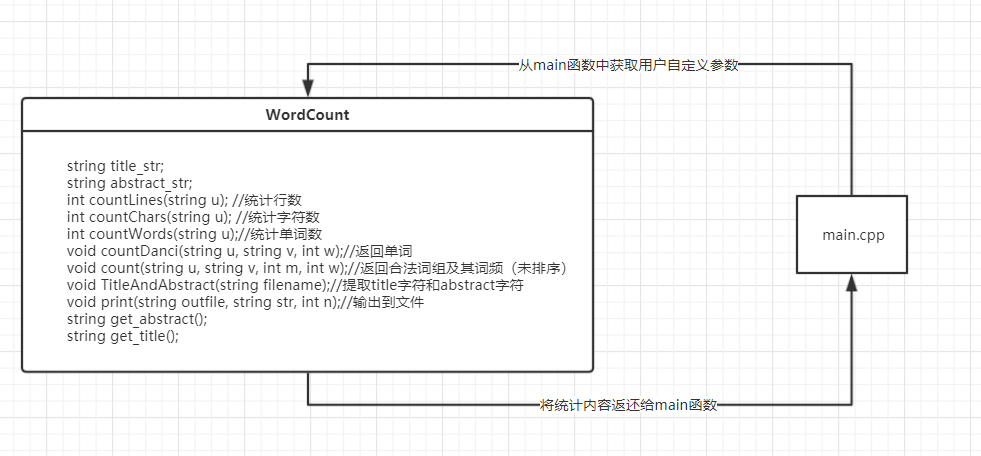
-
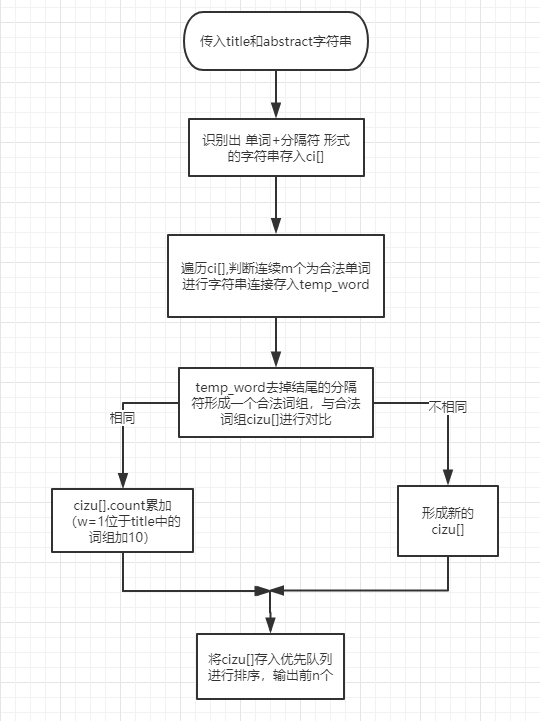
说明算法的关键与关键实现部分流程图
- 针对论文的格式,遍历一遍,提取出要求统计的字符,即 Title: 和 Abstract: 后面的所有字符;并且分成两个字符串string title 和 string abstract,以方便后面的权重分开计算
void MyCount::TitleAndAbstract(string filename)
{
char ch;
ifstream fin;
fin.open(filename);//打开文件
if (!fin)
{
cout << "can not open file" << endl;
}
while (!fin.eof())
{
ch = fin.get();
if (ch == '
')
{
ch = fin.get();
if (ch == 'T')
{
for (int i = 0; i <= 6; i++)
ch = fin.get();
while (ch != '
')
{
title_str += ch;
ch = fin.get();
}
title_str += ch;
}
}
if (ch == '
')
{
ch = fin.get();
if (ch == 'A')
{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
ch = fin.get();
while (ch != '
' && !fin.eof())
{
abstract_str += ch;
ch = fin.get();
}
if (ch == '
')
abstract_str += ch;
}
}
}
fin.close();
}
2.统计有效行数,字符数,以及单词数的算法思路和个人项目的相同,只不过给定的参数从文件名变成 title + abstract 的字符串,因为要去掉论文格式中不需要统计的部分;具体详见词频统计作业
3.词组统计思路:
- 将title字符串与abstract字符串传入函数,各自遍历一遍,识别出 单词+分隔符 的格式存入一个string数组 ci[] 中,并且换行符单独存;
for (int i = 0; i < le; i++)//存入所有的词和字符
{
if ((u[i] >= 'a'&&u[i] <= 'z') || (u[i] >= 'A'&&u[i] <= 'Z') || (u[i] >= '0'&&u[i] <= '9'))//第一个是字母或数字
{
while ((u[i] >= 'a'&&u[i] <= 'z') || (u[i] >= 'A'&&u[i] <= 'Z') || (u[i] >= '0'&&u[i] <= '9'))
{
if (u[i] >= 'A'&&u[i] <= 'Z')
u[i] += 32;
ci[k] += u[i];
i++;
}
while (!(u[i] >= 'a'&&u[i] <= 'z') && !(u[i] >= 'A'&&u[i] <= 'Z') && !(u[i] >= '0'&&u[i] <= '9') && u[i] != '
'&&i < le)
{
ci[k] += u[i];
i++;
}
if (u[i] == '
')ci[++k] = '
';//换行符单独存
i--;
k++;
}
else continue;
}
- 从头开始遍历 ci[] 组,以m为个数将符合单词规范的词连接起来,存入一个临时字符串word中,如m=3,则判断ci[0],ci[1],ci[2]是否为 合法单词+分隔符,是的话存入word,不是的话跳到该词的下一个继续遍历;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
int flag1 = 0;
int flag2 = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++)
{
if (!(ci[i][j] >= 'a'&& ci[i][j] <= 'z'))
{
flag2 = 1;//判断第一个是否符合单词规范
break;
}
}
if (flag2 == 0)//第一个符合
{
strcpy_s(temp_cizu.word, 500,ci[i].c_str()); //
temp_cizu.count = 1;
if (w == 1)temp_cizu.count += 9;
for (int j = 1; j < m; j++)
{
int flag3 = 0;
for (int f = 0; f < 4; f++)
{
if (!(ci[i + j][f] >= 'a'&& ci[i + j][f] <= 'z'))
{
flag3 = 1;//判断后几个是否符合单词规范
i = i + j;
break;
}
}
if (flag3 == 0)//后几个都合法
strcat_s(temp_cizu.word, 500, ci[i + j].c_str());//
else { flag1 = 1; break; }
}
- 将该临时字符串word的结尾的分隔符去掉,就是一个合法的需要统计的词组 ,拿去与合法词组一一对比,相同的权重个数(位于Title:中的权重加10)累加,都不相同则新增词组;
if (flag1 == 0) //插入
{
int a = strlen(temp_cizu.word) - 1;//去掉结尾的符号
while (!(temp_cizu.word[a] >= 'a'&&temp_cizu.word[a] <= 'z') && !(temp_cizu.word[a] >= '0'&&temp_cizu.word[a] <= '9'))
{
temp_cizu.word[a]='�';//
a--;
}
int h, j = t;
for (h = 0; h < j; h++)//相同的词个数累加
{
if (strcmp(temp_cizu.word,cizu[h].word) == 0)//
{
cizu[h].count++;
if (w == 1)cizu[h].count += 9;
break;
}
}
if (t == 0 || h == j)//新词生成新的空间
{
cizu[t] = temp_cizu;
t++;
}
}
- 将合法的词组放入优先队列中,自定义以频率数统计,相同的按字典序排列, 输出前n个词组及权重值
bool operator< (wo a, wo b)//自定义排序
{
//个数相同的单词按字典排序
if (a.count == b.count)
{
int i = -1;
do {
i++;
} while (a.word[i] == b.word[i]);
return a.word[i] > b.word[i];
}
//出现频率排序
else return a.count < b.count;
}
算法思路图如下:
4.接口参数
在命令行参数中如果遇到-i则argv[i+1]是输入文件名input_filename,同理-o对应的输出文件名output_filename、-w权重参数weight、-m词组词频统计参数m、-n词频统计输出参数n
stringstream ss;
string input_filename, output_filename;
int weight = 0;
int m = 1, n = 10;
for (int i = 1; i < argc; i++)
{
string s;
s = argv[i];
if (s == "-i")input_filename = argv[i + 1];
if (s == "-o")output_filename = argv[i + 1];
if (s == "-m")
{
s = argv[i + 1];
stringstream ss(s);
ss >> m;
}
if (s == "-n")
{
s = argv[i + 1];
stringstream ss(s);
ss >> n;
}
if (s == "-w")
{
s = argv[i + 1];
stringstream ss(s);
ss >> weight;
}
}
五、附加题设计与展示
- 将论文中的作者和pdf链接爬取到result.txt中,由于已经将该代码上传,所以这里不做展示。

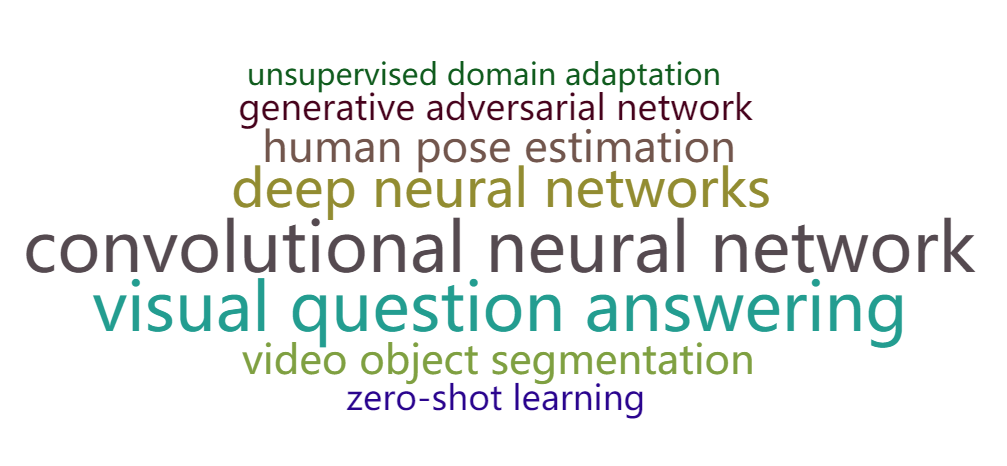
- 利用python的pyecharts库制作词云(将2014至2018年的论文爬取下来,进行统计后制作)
2014

2015

2016

2017

2018
附上代码
在使用pyecharts制作词云的时候,一定记得把频率转换成int型,否则会出现偏差!
from pyecharts import WordCloud
import re
def read_text(path):
with open(path,'r+',encoding='utf-8') as f:
text = f.read()
text = text.strip()
return text
for year in range(2018,2019):
txtpath = '%s.txt' %year
mystr = read_text(txtpath)
pattern = re.compile('<(.*)>')
phrase = re.findall(pattern, mystr) #获取热词
print(phrase)
pattern = re.compile(r'd{3}|d{2}|d{1}')
frequence = re.findall(pattern, mystr) #获取词频
new_frequence = []
for f in frequence:
new_frequence.append(int(f)) #将词频由str转为int型
print(new_frequence)
# print(frequence)
for i in range(len(phrase)):
myWordCloud = WordCloud(width=1500, height=820) #创建词云
myWordCloud.add('',phrase,new_frequence,word_size_range=[30,100],shape='diamond')
myWordCloud.render("%s.html"%str(year)) #绘制图片
六、性能分析与改进
用CVPR2018的979篇paper作为输入数据,参数为-i 1.txt -m 3 -n 10 -w 1 -o output.txt
运行完发现耗时四分钟多!我的天!调出查看性能分析:
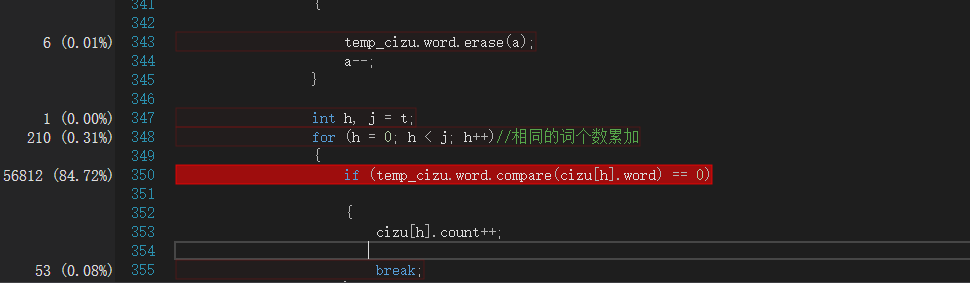
发现主要的耗时问题:两个string类型对比是否相同耗时达84%,想到之前个人项目的算法中是比较两个char数组,耗时很少,于是将string类型改为 char数组类型,运行完发现只需20秒
结果如下:

分析报告如下:
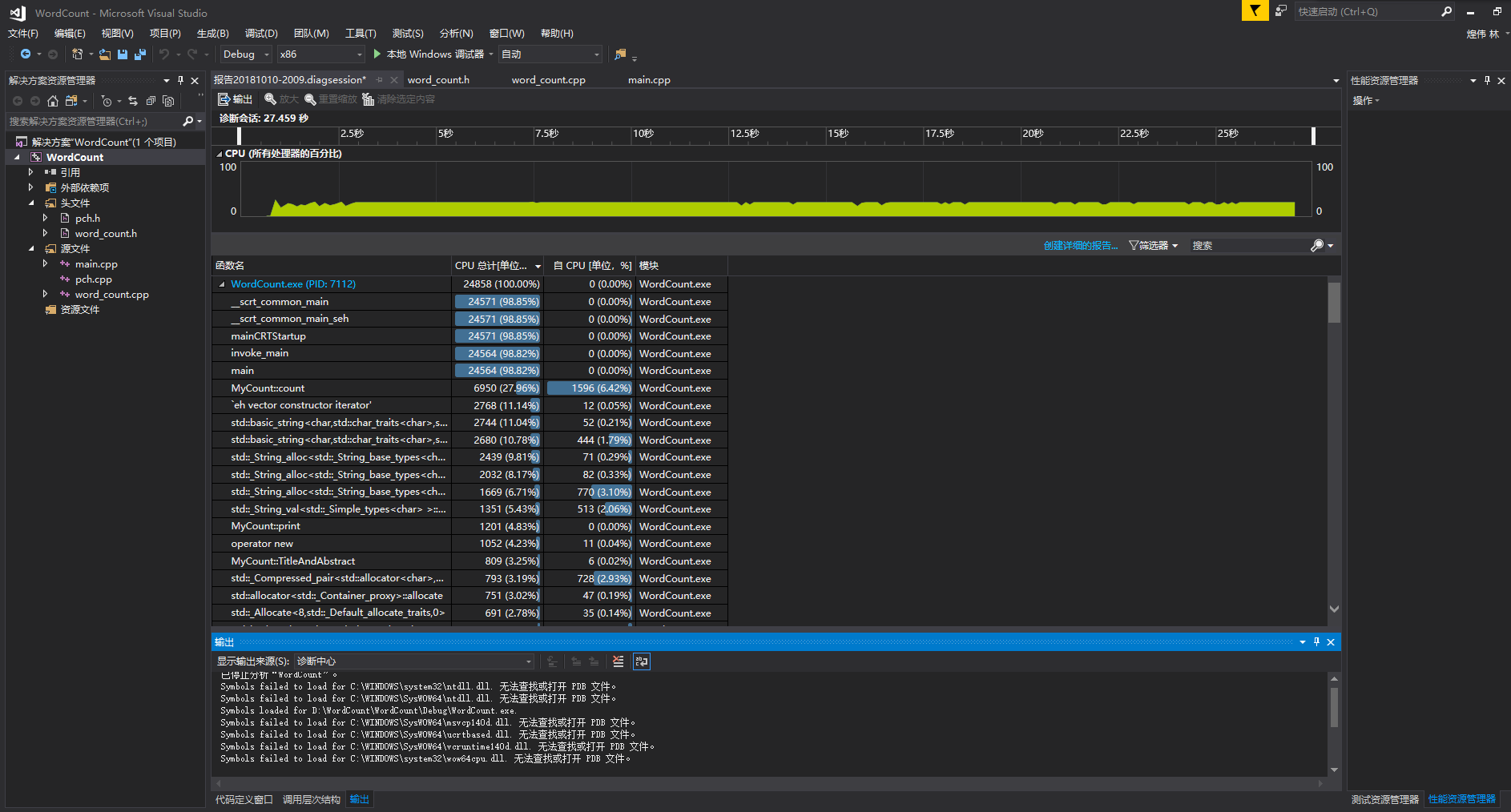
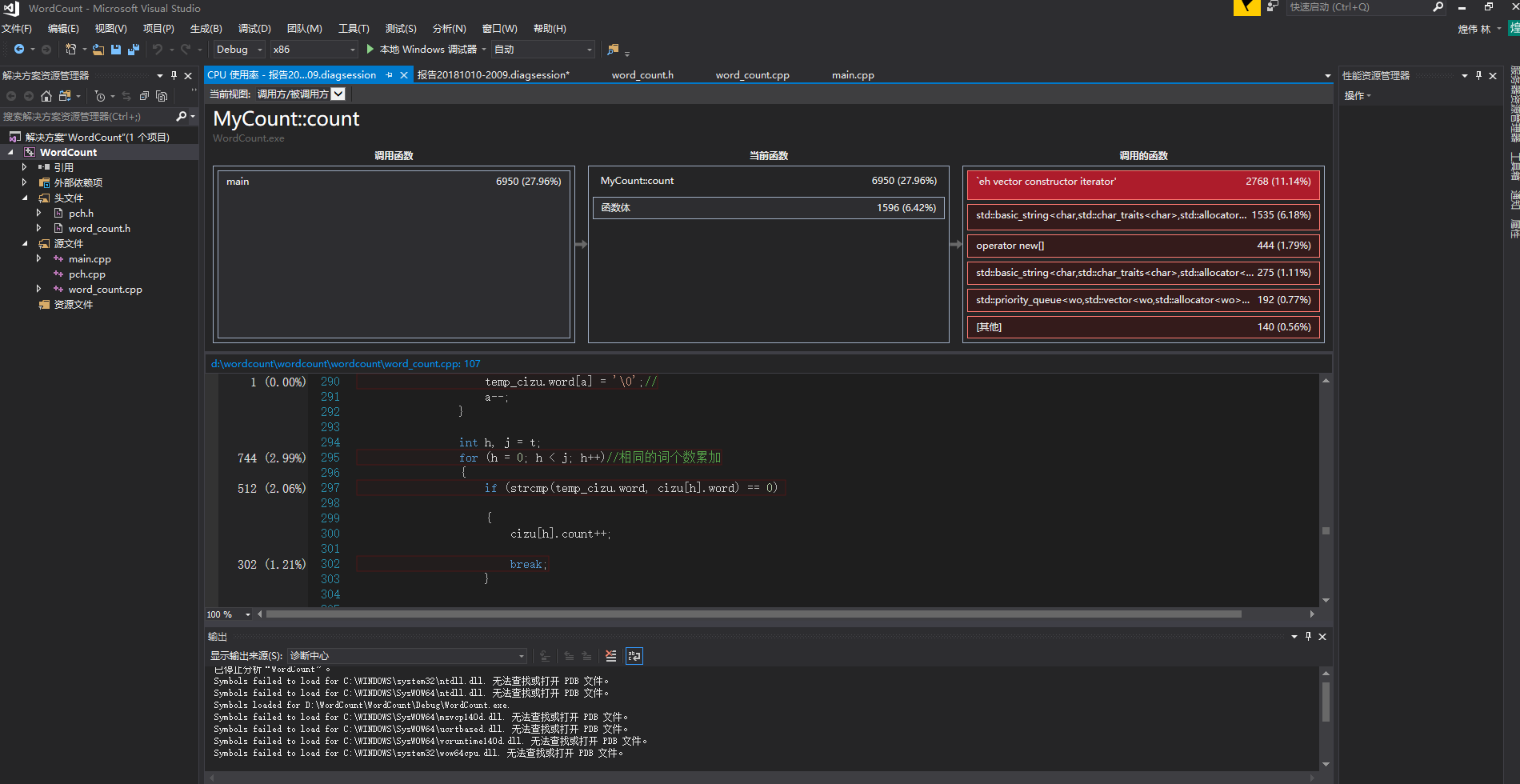
最耗时的是count函数,不过改进之后缩短了很多时间
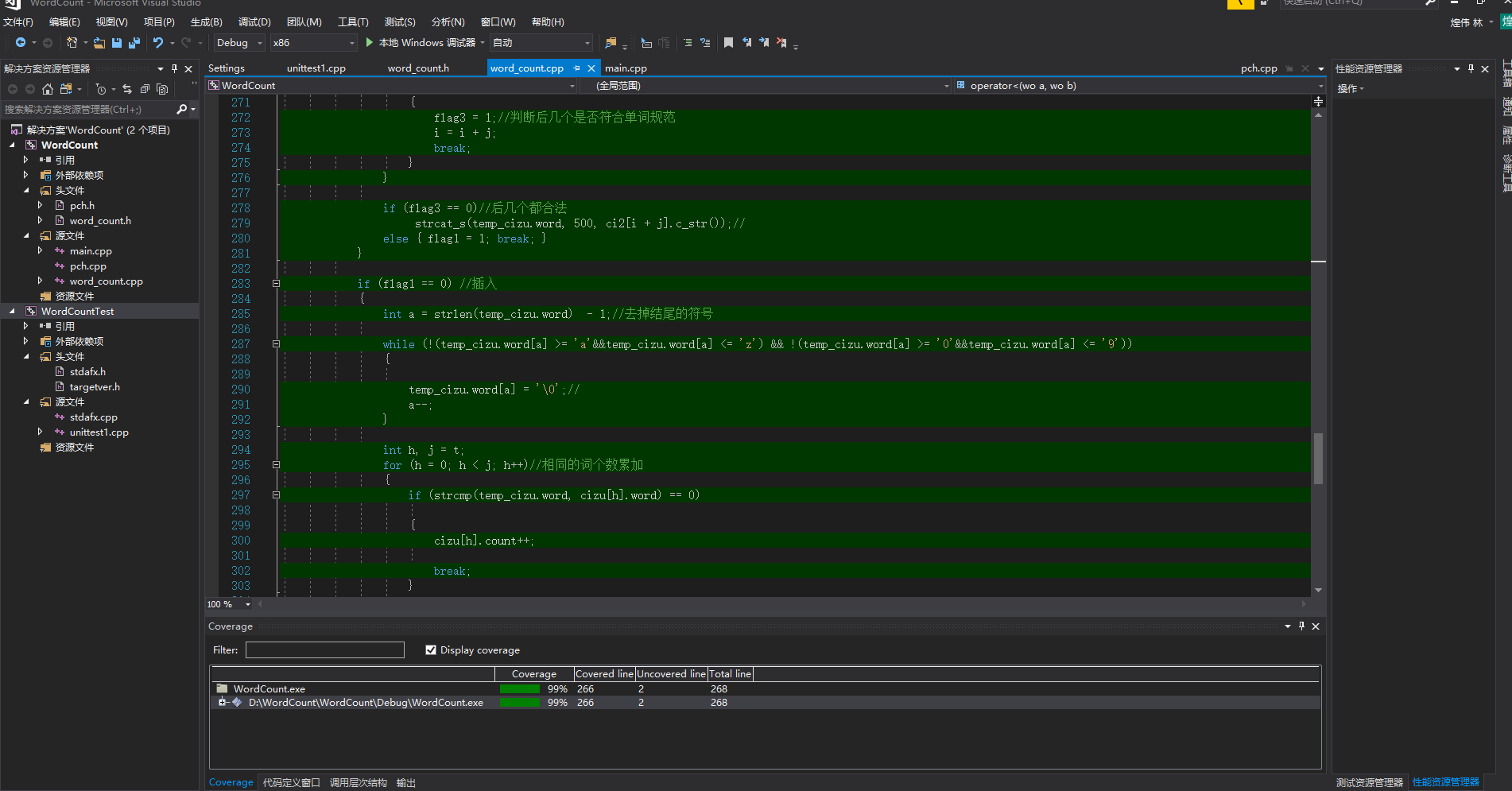
利用插件OpenCppCoverage,查看代码覆盖率:高达99%
七、单元测试
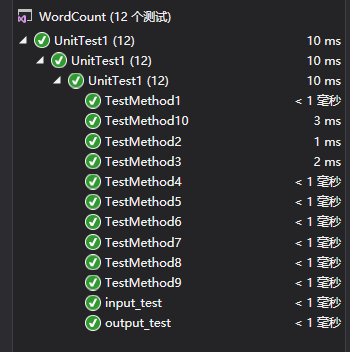
部分代码如下:
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "CppUnitTest.h"
#include "../WordCount/CountAscii.h"
#include "../WordCount/CountWords.h"
#include "../WordCount/File.h"
using namespace Microsoft::VisualStudio::CppUnitTestFramework;
namespace CountAsciiTest //用于对字符数量的统计
{
TEST_CLASS(UnitTest1)
{
public:
TEST_METHOD(TestMethod1)
{
// TODO: 在此输入测试代码
Ascii test_ascii;
int count = test_ascii.countAscii("countascii.txt");
Assert::IsTrue(count == 28);
}
};
}
namespace CountLineTest //用于测试对空白行的技术
{
TEST_CLASS(UnitTest1)
{
public:
TEST_METHOD(TestMethod2)
{
// TODO: 在此输入测试代码
Ascii test_ascii;
int count = test_ascii.countLine("countline.txt");
Assert::IsTrue(count == 0);
}
};
}
namespace FileTest //用于对空文件名的测试
{
TEST_CLASS(UnitTest1)
{
public:
TEST_METHOD(TestMethod3)
{
// TODO: 在此输入测试代码
Ascii test_ascii;
int count = test_ascii.countAscii("1.txt");
Assert::IsTrue(count == 0);
}
};
}
八、Github的代码签入记录
九、遇到的代码模块异常或结对困难及解决方法
-
问题描述
遇到的主要问题是词组统计的功能实现,不知道怎么设计数据结构,怎么设计算法,字符串怎么处理等问题
-
做过哪些尝试
想了挺多种思路,在网上查找了解决了很多问题,为了确保正确率,花了大量时间设计算法,在草稿纸上写了很多遍思路及其实现代码

-
是否解决
最后在规定时间内实现了功能,正确率也很高,解决了这个问题
-
有何收获
收获就是锻炼了自己的代码编写能力和算法优化能力,体会到了结对编程的过程,知道了怎么提高合作的效率,怎么更好的分工与整合。
十、评价你的队友
- 值得学习的地方
- 每天都能固定出一段时间来完成这个项目的事情。
- 逻辑思维都很清晰。
- 在我最需要他的时候伸出援手。
- 长得很帅。
- 需要改进的地方
- 注意自己的代码规范和命名方式!!!不要再用u、v、w来命名变量了!!!
- 请不要那么帅了,太耀眼了啊!!