哈夫曼编码过程记录
要实现的功能:
设有字符集:S={a,b,c,d,e,f,g,h,i,j,k,l,m,n.o.p.q,r,s,t,u,v,w,x,y,z}。
给定一个包含26个英文字母的文件,统计每个字符出现的概率,根据计算的概率构造一颗哈夫曼树。
并完成对英文文件的编码和解码。
要求:
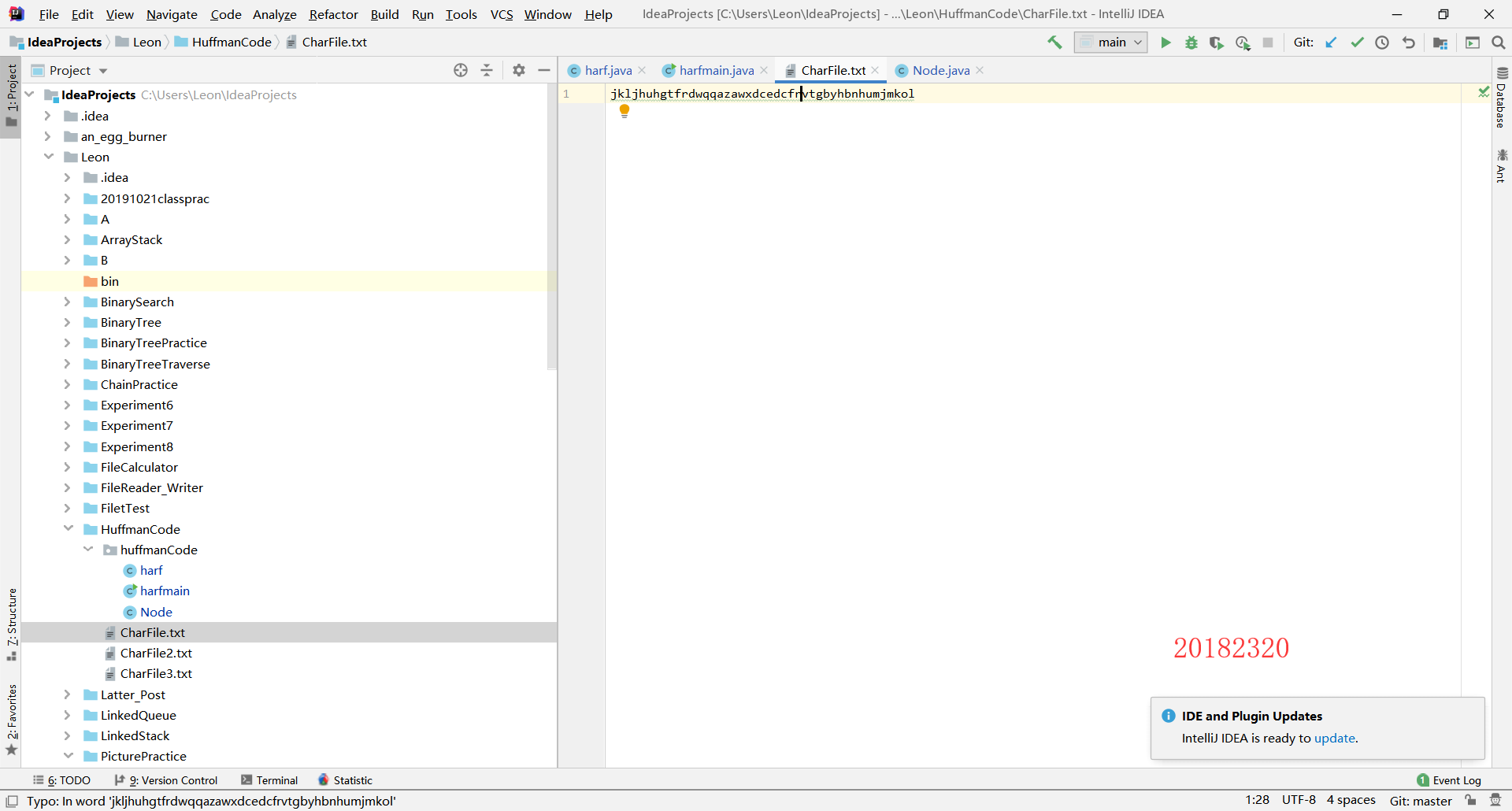
(1)准备一个包含26个英文字母的英文文件(可以不包含标点符号等),统计各个字符的概率
(2)构造哈夫曼树
(3)对英文文件进行编码,输出一个编码后的文件
(4)对编码文件进行解码,输出一个解码后的文件
实现过程:
1.编写主函数,实现每个字母出现次数的统计和文件读写
代码如下,详细请看注释:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//开出26个字母的数组
char[] S = new char[]{'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h', 'i', 'j', 'k', 'l', 'm', 'n', 'o', 'p', 'q', 'r', 's', 't', 'u', 'v', 'w', 'x', 'y', 'z'};
//开一个和26个字母对应的数组,拿来统计频数每个字母出现的
double[] sum = new double[26];
//count是记录所有字母出现总次数的
int count = 0;
//遍历第二个数组来初始化
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
sum[i] = 0;
}
//从CharFile.txt文件中读取出内容,存入String型的result变量中
File file = new File("C:\Users\Leon\IdeaProjects\Leon\HuffmanCode", "CharFile.txt");
Reader reader2 = new FileReader(file);
String result = "";
while (reader2.ready()) {
result += (char) reader2.read();
}
//将result中的字符串转换成一个个字符
char[] text = result.toCharArray();
//统计每个字母出现次数到第二个数组中
for (int j = 0; j < text.length; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < S.length; k++) {
if (text[j] == S[k] || text[j] == (S[k] - 32)) {
sum[k]++;
count++;
}
}
}
//将频数除总数成了频率,再存入第二个数组
for (int i = 0; i < sum.length; i++) {
sum[i] = sum[i] / count;
}
}
2.编写节点类
public class Node<E> {
E data;
public String code = "";
double weight;
Node leftChild;
Node rightChild;
public Node(E data, double weight) {
super();
this.data = data;
this.weight = weight;
}
}
3.编写构建哈夫曼树的类
public class harf {
//构造哈夫曼树的方法
Node createTree(List<Node> nodes) {
// 只要nodes数组中还有2个以上的节点
while (nodes.size() > 1) {
quickSort(nodes);
//获取权值最小的两个节点
Node left = nodes.get(nodes.size() - 1);
Node right = nodes.get(nodes.size() - 2);
//生成新节点,新节点的权值为两个子节点的权值之和
Node parent = new Node(null, left.weight + right.weight);
//让新节点作为两个权值最小节点的父节点
parent.leftChild = left;
parent.rightChild = right;
//删除权值最小的两个节点
nodes.remove(nodes.size() - 1);
nodes.remove(nodes.size() - 1);
//将新节点加入到集合中
nodes.add(parent);
}
return nodes.get(0);
}
//快速排序
public static void quickSort(List<Node> nodes) {
subSort(nodes, 0, nodes.size() - 1);
}
private static void subSort(List<Node> nodes, int start, int end) {
if (start < end) {
// 以第一个元素作为分界值
Node base = nodes.get(start);
// i从左边搜索,搜索大于分界值的元素的索引
int i = start;
// j从右边开始搜索,搜索小于分界值的元素的索引
int j = end + 1;
while (true) {
// 找到大于分界值的元素的索引,或者i已经到了end处
while (i < end && nodes.get(++i).weight >= base.weight)
;
// 找到小于分界值的元素的索引,或者j已经到了start处
while (j > start && nodes.get(--j).weight <= base.weight)
;
if (i < j) {
swap(nodes, i, j);
} else {
break;
}
}
swap(nodes, start, j);
//递归左边子序列
subSort(nodes, start, j - 1);
//递归右边子序列
subSort(nodes, j + 1, end);
}
}
//用于交换结点的方法
private static void swap(List<Node> nodes, int i, int j) {
Node tmp;
tmp = nodes.get(i);
nodes.set(i, nodes.get(j));
nodes.set(j, tmp);
}
//用递归给每个结点编码
public void setCode(Node root) {
if (root.leftChild != null) {
root.leftChild.code = root.code + "0";
setCode(root.leftChild);
}
if (root.rightChild != null) {
root.rightChild.code = root.code + "1";
setCode(root.rightChild);
}
}
//输出编码结果
public void output(Node root) {
if (root.leftChild == null && root.rightChild == null) {
System.out.println(root.data + ": " +root.code);
}
if (root.leftChild != null) {
output(root.leftChild);
}
if (root.rightChild != null) {
output(root.rightChild);
}
}
// 哈夫曼编码连接成的字符串
private String hfmCodeStr = "";
//编码
public String toHufmCode(String str,Node root) {
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
char c = str.charAt(i) ;
search(root, c);
}
return hfmCodeStr;
}
//匹配并拼接编码后的结果
private void search(Node root, char c) {
if (root.leftChild == null && root.rightChild == null) {
if (c == (char)root.data) {
hfmCodeStr += " "+root.code; // 找到字符,将其哈夫曼编码拼接到最终返回二进制字符串的后面
}
}
if (root.leftChild != null) {
search(root.leftChild, c);
}
if (root.rightChild != null) {
search(root.rightChild, c);
}
}
String result="";
boolean target = false; // 解码标记
//将编码转换成字符串
public String CodeToString(String codeStr,Node root) {
int start = 0;
int end = 1;
while(end <= codeStr.length()){
target = false;
String s = codeStr.substring(start, end);
matchCode(root, s); // 解码
// 每解码一个字符,start向后移
if(target){
start = end;
}
end++;
}
return result;
}
//匹配解码
private void matchCode(Node root, String code){
if (root.leftChild == null && root.rightChild == null) {
if (code.equals(root.code)) {
result += root.data; // 找到对应的字符,拼接到解码字符穿后
target = true; // 标志置为true
}
}
if (root.leftChild != null) {
matchCode(root.leftChild, code);
}
if (root.rightChild != null) {
matchCode(root.rightChild, code);
}
}
}
4.完善驱动类
在上面的驱动类主函数中添加如下代码:
//采用队列结构
List<Node> nodes = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < sum.length; i++) {
nodes.add(new Node(S[i], sum[i]));
}
harf h = new harf();
Node root = h.createTree(nodes);
h.setCode(root);
h.output(root);
String s = h.toHufmCode(result, root);
System.out.println(s);
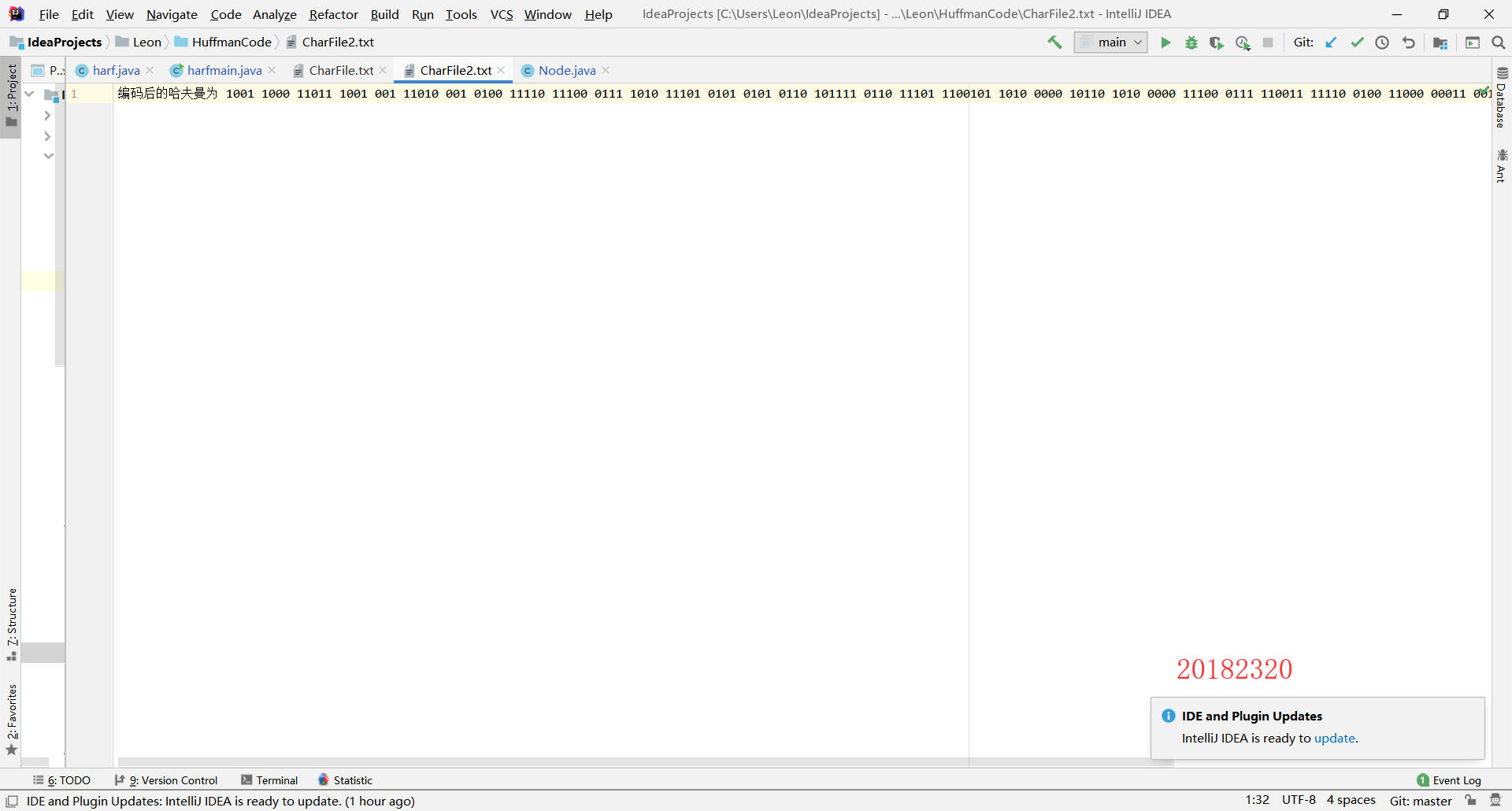
//将编码结果写入第二个文件
File file1 = new File("C:\Users\Leon\IdeaProjects\Leon\HuffmanCode", "CharFile2.txt");
Writer writer2 = new FileWriter(file1);
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(writer2);
bufferedWriter.write("编码后的哈夫曼为"+s, 0, s.length());
bufferedWriter.flush();
bufferedWriter.close();
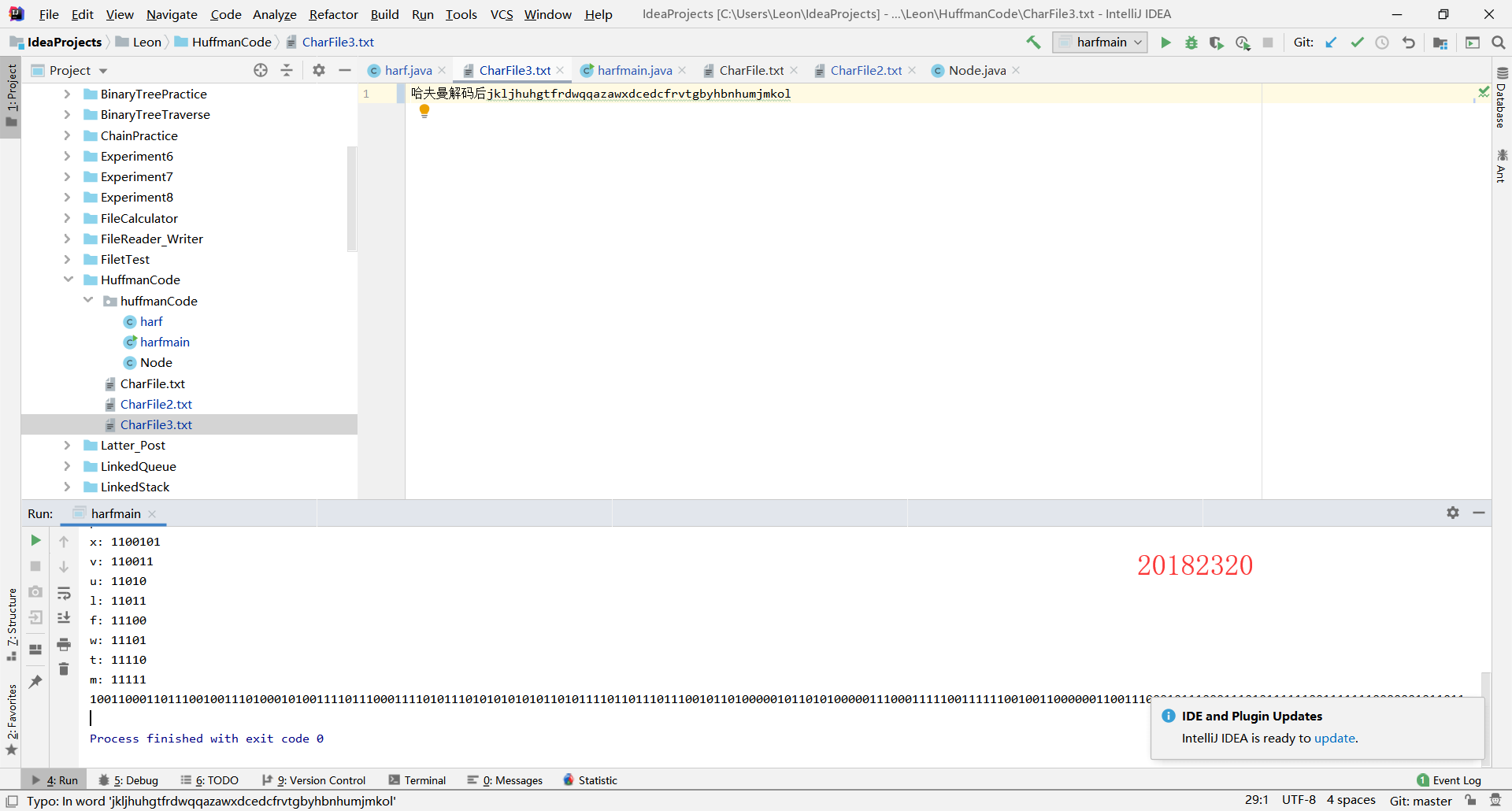
String a ="哈夫曼解码后"+h.CodeToString(s,root);
//将解码结果写入第三个文件
File file2 = new File("C:\Users\Leon\IdeaProjects\Leon\HuffmanCode", "CharFile3.txt");
Writer writer3 = new FileWriter(file2);
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter1 = new BufferedWriter(writer3);
bufferedWriter1.write(a, 0, a.length());
bufferedWriter1.flush();
bufferedWriter1.close();
运行结果: