new 、delete关键字的重载。

重载new关键字的时候,返回值必须是void *。
并且:第一个形参必须是:size_t .

new [] delete[] 关键字的重载,
注:new 的重载与new [] 的重载 并不等价。delete 与delete[] 的重载并不等价。
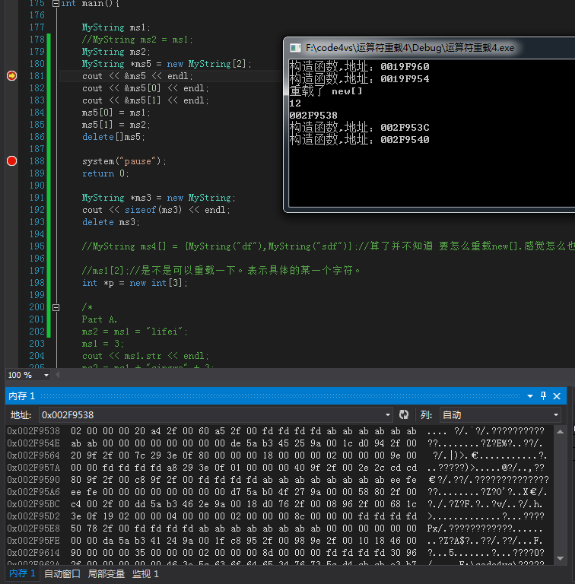

下图辅助理解,是之前某一次的运行结果。
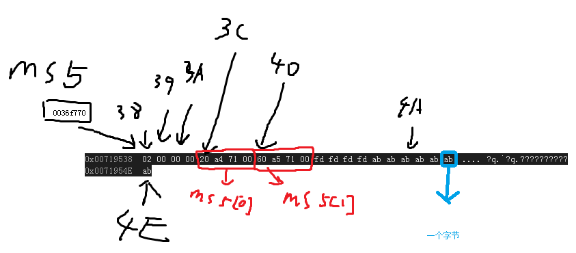
倒是没少删,多清空了一大块。
总之 就是 多写几遍巩固一下,运算符的重载。然后 new delete new[] delete[] 的重载一边比较少见。这个需要对内存掌握的比较充分才好。
然后对于++ 的重载。
Object++; 的重载写法是: 类名 &operator++(){}
++Object; 的重载写法是: 类名 &operator++(int){}
还有就是 如果没有区分前置后置,那么编译器就会都认为成是一个,但是并不知道别的编译器怎么处理,对于 vs来讲是这样的。
对于 反制的写法,也就是 我们常见的 对于类似“+” 的重载都是对象在前
写法为: 类名 &operator +(const char *s){}
但是 +应该满足交换律 也就是 如果 const 写在前面对象写在后面也应该支持:
其写法为:
friend 类名 &operator+(const char *s,类名 对象){}//再加上前面的友元关键字。
在写这个东西的时候,总觉得貌似可以把 friend去掉:

发现还真不行,还是需要加上的。
以下代码:
#include <iostream> #include <string.h> #pragma warning(disable:4996) using namespace std; class MyString{ public: char *str; MyString(){ cout << "构造函数,地址:" <<&str<< endl; str = new char[256]; memset(str, 0, 256);//内存置空。 } MyString(const char *s){ str = new char[256]; strcpy(str, s); } MyString(const MyString &mystr){ cout << "复制构造函数,地址:" << &str << endl; str = new char[256]; //memset(str, 0, 256); strcpy(str, mystr.str); } ~MyString(){ cout << "析构函数,地址:" << &str << endl; delete[]str; } /*注意他们的原型是: void operator =(const MyString &mystr){ strcpy(str, mystr.str); } void operator = (const char *s){ strcpy(str, s); } 为了 满足 ms2 = ms1 = "lifei" 这样的语法结构,所以给了他们一个返回值。以 赋值表达式成立。这个回头可以看下人家是怎么写的。或者 现在看吧。 */ MyString &operator =(const MyString &mystr){//加上这句话,下面的 ms2 = ms1 就不再出错了。 strcpy(str, mystr.str); return *this; } MyString &operator =(const char *s){ strcpy(str, s); return *this; } MyString &operator = (const int i){//重载了int 的内容。 sprintf(str, "%d", i); return *this; } /** 应该是一个字符串拼接。 */ MyString &operator +(const char *s){ sprintf(str, "%s%s", str, s); return *this; } MyString &operator +(const int i){ sprintf(str, "%s%i", str, i); return *this; } //对象应该也可以+对象, 要在考虑到颠倒的情况,也就是 友元重载。还没试过,怎么分出去写,待会儿试验一个。现在吧。 MyString &operator +(const MyString &mystr){ sprintf(str, "%s%s", str, mystr.str); return *this; } friend MyString operator +(const char *s, const MyString &mystr){//这样就可以不写在外面了。 //这里要重新建立一个对象。 MyString myString; char buf[1024] = { 0 }; sprintf(buf, "%s%s", s, mystr.str); myString = buf; return myString; } friend MyString operator +(const int i, const MyString &mystr){ MyString myString; char buf[1024] = { 0 }; sprintf(buf, "%d%s", i, mystr.str); myString = buf; return myString; } /* 这个也要重载int 和 char *的,到底要不要返回引用呢?,为了执行效率要不还是加上吧先。*/ MyString &operator +=(const MyString &mystr){ sprintf(str, "%s%s", str, mystr.str); return *this; } MyString &operator +=(const char *s){ sprintf(str, "%s%s", str, s); return *this; } MyString &operator +=(const int i){ sprintf(str, "%s%i", str, i);//其实开始这里我想到的是itoa。 return *this; } //ms1 << "lifei" MyString &operator <<(const char *s){//定义为赋值操作。 sprintf(str, "%s", s); return *this; } MyString &operator<<(const int i){ sprintf(str, "%d", i); return *this; } MyString &operator<<(const MyString &mystr){ sprintf(str, "%s", mystr.str); return *this; } //ms1++; MyString &operator++(){//我记得好像是 写上是一种操作方式,不写是另一种操作方式。 这样就重载了 前置 跟后置两种方式。这个是object++。 int i = 0; for (i = 0; i < strlen(str); i++){ str[i] = str[i]++; } return *this; } //++ms1;不过好像并实现不了,先赋值,还是先运算那种关系的。 MyString &operator++(int){//我记得好像是 写上是一种操作方式,不写是另一种操作方式。 这样就重载了 前置 跟后置两种方式。这个是 ++object。 int i = 0; for (i = 0; i < strlen(str); i++){ str[i] = str[i]--; } return *this; } //重载 new关键字 void *operator new(size_t i){//重载new关键字的时候返回值的类型必须是void /*int *p; cout << sizeof(p) << endl; 感觉貌似一个指针就是 4个字节。估计帮我屏蔽了底层了吧。 */ cout << i << endl;//这个的输出结果是4.所以就是一个指针的大小嘛!?~ MyString *myptr = (MyString *)malloc(i); //return NULL;//返回空的时候没有调用构造函数,当返回myptr的时候 调用了构造函数。。。这个东西感觉很复杂。 return myptr; } //重载delete的时候,返回值必须是void 并且 第一个参数 必须是 void* ,其实不记得也没有关系 ,只要使用某一个很智能的ide比如vs void operator delete(void *p){ free((MyString *)p);//还记得我们的为什么要如此指定么,应该记得,根据类型决定到内存中,释放多大的内存空间。 p = NULL; } // new 跟 new[] 是完全不同的,不要以为重载了new就是 重载了new[].这是两回事,要分开重载。 void *operator new[](size_t size){ cout << "重载了 new[]" << endl; cout << size << endl;//这个size的大小是 单个的 new 的 关键字里面的大小的数值乘以对象个数,最后+4.举例 本文中就是 4*2+4 = 12; MyString *myptr = (MyString *)malloc(size); memset(myptr, 0, size); cout << myptr << endl; return myptr; } void operator delete[](void *p){ cout << "我的delete[]" << endl; free((MyString *)p); p = NULL; } char &operator [](int index){ return str[index]; } }; int main(){ MyString ms1; //MyString ms2 = ms1; MyString ms2; MyString *ms5 = new MyString[2]; cout << &ms5 << endl; cout << &ms5[0] << endl; cout << &ms5[1] << endl; ms5[0] = ms1; ms5[1] = ms2; ms5[0] = "lifei"; cout << ms5[0][1] << endl;//重载一下。 ms5[1] = 3+ms5[0]; delete[]ms5; system("pause"); return 0; MyString *ms3 = new MyString; cout << sizeof(ms3) << endl; delete ms3; //MyString ms4[] = {MyString("df"),MyString("sdf")};//算了并不知道 要怎么重载new[].感觉怎么也写不出来,那个使用语句。 //ms1[2];//是不是可以重载一下[]。表示具体的某一个字符。 int *p = new int[3]; /* Part A. ms2 = ms1 = "lifei"; ms1 = 3; cout << ms1.str << endl; ms2 = ms1 + "qingwa" + 3; cout << ms2.str << endl; MyString ms3 = ms1 + ms2; cout << ms3.str << endl; memset(ms1.str, 0, 256); memset(ms2.str, 0, 256); ms1 = " come on!"; cout << ms1.str << endl; ms2 = "lifei" + ms1; cout << ms2.str << endl; ms1 = 3 + ms2; cout << ms1.str <<endl;*/ /* Part B. MyString ms3; ms1 = "li"; ms2 = "fei"; ms2 = ms1++; cout << ms1.str << endl; cout << ms2.str << endl; ms2 = ++ms1; cout << ms1.str << endl; cout << ms2.str << endl; ms3 = ms1 += ms2;//这个语法就比较复杂了 //我都不知道是不是我想要的结果了 MyString ms4 = ms3 + 5; cout << ms4.str << endl;//还是。。。 */ //用. 的话要这样写: strcpy(ms2.str,"lifei"); 要么别用。仔细想想 ms2.str 是个地址啊!地址怎么能给一个 //ms2.str = "asdf";倒是也让赋值了,不过结果就是不对。 system("pause"); return 0; }