这是剑指offer中关于二叉树重构的一道题。题目原型为:
输入某二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果,请重建出该二叉树。假设输入的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果中都不含重复的数字。例如输入前序遍历序列{1,2,4,7,3,5,6,8}和中序遍历序列{4,7,2,1,5,3,8,6},则重建二叉树并返回。
一、二叉树的数据结构
做题之前,我们先熟悉下二叉树的数据结构。其一,定义:二叉树是一个连通的无环图,并且每一个顶点的度不大于3。有根二叉树还要满足根结点的度不大于2。有了根结点之后,每个顶点定义了唯一的父结点,和最多2个子结点。然而,没有足够的信息来区分左结点和右结点。如果不考虑连通性,允许图中有多个连通分量,这样的结构叫做森林。(定义来自百度百科)
由定义可知,二叉树含有许多节点,而不同节点之间通过子父关系来连接。一般来说,二叉树的节点由结构体来定义,如下所示:
1 struct TreeNode { 2 int val; 3 TreeNode *left; 4 TreeNode *right; 5 TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} 6 ~TreeNode() { 7 cout << "TreeNode with value " << val << " has been destroyed." <<endl; 8 } 9 };
该结构体定义了节点的int型变量(当然也可以是其它类型),以及指向左右孩子的指针。在TreeNode中,我们还定义了构造函数和析构函数,其实可有可无,对本题来说没有多大意义。
二、二叉树的建立
二叉树的建立过程,就是不断扩展节点的过程。建立根节点,由根节点建立左右子节点,再递归的建立子节点的子节点。我们下面看看代码的实现过程:
1 void BiTree::createBiTree(struct TreeNode* &root) { 2 int val; 3 //cout << "Please input the tree node:" << endl; 4 cin >> val; 5 if (999 == val) { 6 root = NULL; 7 } 8 else { 9 //root = (struct TreeNode*) malloc(sizeof(TreeNode)); 10 root = new TreeNode(1); 11 if (root == NULL) 12 return; 13 root->val = val; 14 15 cout << "Please input the left child of " << val << ": "; 16 createBiTree(root->left); 17 18 cout << "Please input the right child of" << val << ": "; 19 createBiTree(root->right); 20 } 21 }
这里,我是把创建二叉树的方法createBiTree()作为了BiTree的成员函数(简单说明一下)。
1、首先,我们看参数 struct TreeNode* &root, 这是结构体指针的引用。为什么要传递引用呢,就是希望函数体外的指针变量能指向函数体内所新建的根节点。若只是指针传递,那么函数体内新建的节点和函数体外的指针变量是没有指向关系的。
2、然后就是新建节点,
//root = (struct TreeNode*) malloc(sizeof(TreeNode));
root = new TreeNode(1);
这两条语句的效果相同。如果创建成功,那么递归调用本方法,创建后续节点。
三、二叉树的遍历
二叉树有三种遍历方法:先序,中序,后序。即父前(父-左-右),父中(左-父-右),父后(左-右-父)。
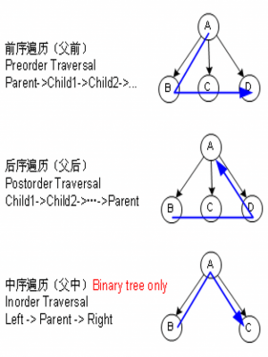
1、先序遍历
1 // 这里参数传递指针,或指针的引用都可以 2 void BiTree::preOrder(struct TreeNode* &root) { 3 if (root == NULL) 4 return; 5 cout << root->val << ' '; 6 preTrav.push_back(root->val); 7 preOrder(root->left); 8 preOrder(root->right); 9 }
其中,preTraa.push_back(root->val);我只是把先序遍历的结果存在了vector 中,方便重构二叉树时作为输入。下同。
2,、中序遍历
1 void BiTree::inOrder(struct TreeNode* root) { 2 if (root == NULL) 3 return; 4 inOrder(root->left); 5 cout << root->val << ' '; 6 inTrav.push_back(root->val); 7 inOrder(root->right); 8 }
3、后序遍历,就不贴代码了。
另外,值得说明一下的是。这里的遍历方法都是通过递归来实现的,还有遍历的非递归算法(日后再详细去探讨,这里先着重看这个题目,也不知日后是否会想起这个任务。。。囧)
三、已知先序遍历,中序遍历,重构二叉树
我们观察先序遍历和中序遍历的结果。先序遍历的第一个节点肯定是根节点,然后在中序遍历中找到此根节点,我们可以看到,中序遍历中根节点以左是二叉树的左子树,根节点以右是二叉树的右子树。然后,左右子女树又可以单独的看成一个独立的二叉树,然后再对其划分,如此递归,便可重构二叉树的结构。下面上代码:
1 struct TreeNode* reConstructBinaryTree(vector<int> pre, vector<int> in){ 2 //TreeNode* head = new TreeNode(pre[0]); 3 /* 注意上面这一条语句不能放在函数体的第一句。 4 * 因为此时还不能确定pre这个vector是否为空,如果不为空,那么访问pre[0]就是非法内存访问。此时若debug,会有 5 * Program received signal SIGSEGV, Segmentation fault.的错误信息。其中,SIG是signal的缩写,SEGV是segmentation violation(段违例)的缩写。详见维基百科 6 * 所以,此条语句放在return NULL;语句之后为宜,因为这个时候已经确定vector in不为空。但是好像没判断pre是否为空呢,这就可以了?? 7 */ 8 vector<int> left_pre, left_in, right_pre, right_in; 9 10 int pos = 0; 11 int length = in.size(); 12 13 if (length == 0) 14 return NULL; 15 16 TreeNode* head = new TreeNode(pre[0]); 17 18 for (int i = 0; i < length; ++i) { 19 if (pre[0] == in[i]) { 20 pos = i; 21 break; 22 } 23 } 24 25 for (int i = 1; i < pos + 1; ++i) { 26 left_pre.push_back(pre[i]); 27 left_in.push_back(in[i-1]); 28 } 29 30 for (int i = pos + 1; i < length; ++i) { 31 right_pre.push_back(pre[i]); 32 right_in.push_back(in[i]); 33 } 34 35 head->left = reConstructBinaryTree(left_pre, left_in); 36 head->right = reConstructBinaryTree(right_pre, right_in); 37 38 return head; 39 40 }
其实,关于这个重构函数,笔者还有一个问题,就如函数中注释中所诉。还请广大博友解答下(新手博客,都没人看,好忧伤~_~!)
四、重构验证
首先,贴上验证程序。验证程序综合了上述建立二叉树,遍历二叉树以及重构二叉树的相关实现。

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 // Definition for binary tree 6 struct TreeNode { 7 int val; 8 TreeNode *left; 9 TreeNode *right; 10 TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} 11 ~TreeNode() { 12 cout << "TreeNode with value " << val << " has been destroyed." <<endl; 13 } 14 }; 15 16 class BiTree { 17 public: 18 int flag; 19 vector<int> preTrav, inTrav; 20 21 BiTree(int _flag) : flag(_flag){ 22 cout << "Instance of Bitree with flag " << flag << " has been constructed." << endl; 23 } 24 ~BiTree() { 25 cout << "Instance of Bitree with flag " << flag << " has been destroyed." << endl; 26 } 27 28 /* createBiTree()注意这里传递的是指针的引用,因为函数体内部在不断的new,需要让传进来的根节点指向内部新开辟的空间, 29 * 不过这样的话,在main函数内,定义的mytree结构体的空间就浪费了,怎么去优化呢? 30 * struct TreeNode* tree = nullptr;此条语句解决上诉问题 31 */ 32 void createBiTree(struct TreeNode*&); 33 void preOrder(struct TreeNode*&); //这里传递指针或指针的引用都可以 34 void inOrder(struct TreeNode*); 35 }; 36 // Create the binary tree 37 void BiTree::createBiTree(struct TreeNode* &root) { 38 int val; 39 //cout << "Please input the tree node:" << endl; 40 cin >> val; 41 if (999 == val) { 42 root = NULL; 43 } 44 else { 45 //root = (struct TreeNode*) malloc(sizeof(TreeNode)); 46 root = new TreeNode(1); 47 if (root == NULL) 48 return; 49 root->val = val; 50 51 cout << "Please input the left child of " << val << ": "; 52 createBiTree(root->left); 53 54 cout << "Please input the right child of" << val << ": "; 55 createBiTree(root->right); 56 } 57 } 58 59 // pre order of binary tree 60 void BiTree::preOrder(struct TreeNode* &root) { 61 if (root == NULL) 62 return; 63 cout << root->val << ' '; 64 preTrav.push_back(root->val); 65 preOrder(root->left); 66 preOrder(root->right); 67 } 68 69 // in order of binary tree 70 void BiTree::inOrder(struct TreeNode* root) { 71 if (root == NULL) 72 return; 73 inOrder(root->left); 74 cout << root->val << ' '; 75 inTrav.push_back(root->val); 76 inOrder(root->right); 77 } 78 // 在类外部定义一个中序遍历,作调试用 79 void inOrder(struct TreeNode* &root) { 80 if (root == NULL) 81 return; 82 inOrder(root->left); 83 cout << root->val << ' '; 84 inOrder(root->right); 85 } 86 87 // Solution of reconstruct binary tree 88 class Soultion { 89 public: 90 int flag; 91 Soultion(int _flag) : flag(_flag) { 92 cout << "Instance of Solution with flag " << flag << " has been constructed." << endl; 93 } 94 ~Soultion() { 95 cout << "Instance of Solution with flag " << flag << " has been destroyed." << endl; 96 } 97 98 struct TreeNode* reConstructBinaryTree(vector<int> pre, vector<int> in){ 99 //TreeNode* head = new TreeNode(pre[0]); 100 /* 注意上面这一条语句不能放在函数体的第一句。 101 * 因为此时还不能确定pre这个vector是否为空,如果不为空,那么访问pre[0]就是非法内存访问。此时若debug,会有 102 * Program received signal SIGSEGV, Segmentation fault.的错误信息。其中,SIG是signal的缩写,SEGV是segmentation violation(段违例)的缩写。详见维基百科 103 * 所以,此条语句放在return NULL;语句之后为宜,因为这个时候已经确定vector in不为空。但是好像没判断pre是否为空呢,这就可以了?? 104 */ 105 vector<int> left_pre, left_in, right_pre, right_in; 106 107 int pos = 0; 108 int length = in.size(); 109 110 if (length == 0) 111 return NULL; 112 113 TreeNode* head = new TreeNode(pre[0]); 114 115 for (int i = 0; i < length; ++i) { 116 if (pre[0] == in[i]) { 117 pos = i; 118 break; 119 } 120 } 121 122 for (int i = 1; i < pos + 1; ++i) { 123 left_pre.push_back(pre[i]); 124 left_in.push_back(in[i-1]); 125 } 126 127 for (int i = pos + 1; i < length; ++i) { 128 right_pre.push_back(pre[i]); 129 right_in.push_back(in[i]); 130 } 131 132 head->left = reConstructBinaryTree(left_pre, left_in); 133 head->right = reConstructBinaryTree(right_pre, right_in); 134 135 return head; 136 137 } 138 // 在solution类中也定义个中序遍历,作调试用 139 void inOrder(struct TreeNode* &root) { 140 if (root == NULL) 141 return; 142 inOrder(root->left); 143 cout << root->val << ' '; 144 inOrder(root->right); 145 } 146 147 }; 148 149 int main() { 150 //struct TreeNode myTree(1); 151 //struct TreeNode* tree = &myTree; 152 struct TreeNode* tree = nullptr; 153 154 BiTree myBiTree(1); 155 cout << "Please input the head tree node: "; 156 myBiTree.createBiTree(tree); 157 158 cout << "Preorder of binary tree." << endl; 159 myBiTree.preOrder(tree); 160 161 cout << endl << "Inorder of binary tree." << endl; 162 myBiTree.inOrder(tree); 163 cout << endl; 164 165 Soultion mySolution(2); 166 cout << endl 167 << "refactor the binary tree based on preorder and inorder " 168 << "and print it with preorder" 169 << endl; 170 myBiTree.inOrder(mySolution.reConstructBinaryTree(myBiTree.preTrav, myBiTree.inTrav)); 171 cout << endl; 172 173 delete tree; 174 //struct TreeNode* refactor = mySolution.reConstructBinaryTree(myBiTree.preTrav, myBiTree.inTrav); 175 //myBiTree.inOrder(refactor); 176 //mySolution.inOrder(refactor); 177 178 //inOrder(refactor); 179 return 0; 180 }
下面我们看看程序结果。
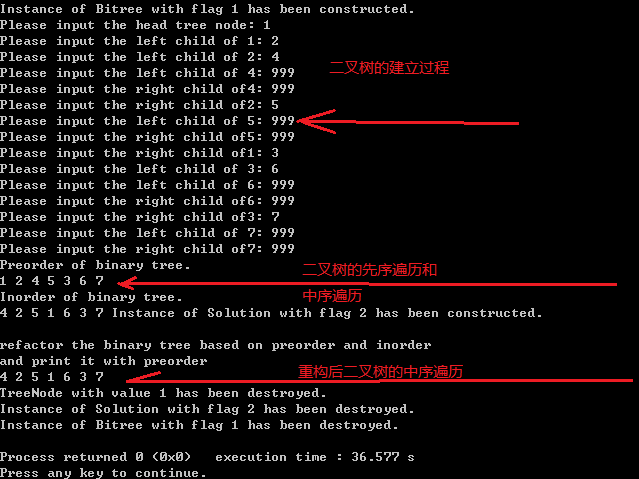
从结果中我们可以看见,重构后二叉树的中序遍历和我们输入的二叉树的中序遍历相同。我们还可以输出重构后的先序遍历,来确定我们的重构是正确的。
二叉树的重构暂且先探讨这。二叉树还有其它很多特性需要没我们去研究,择日再说。
