一、简单介绍
2.1. TaskExecutor---Spring异步线程池的接口类,其实质是java.util.concurrent.Executor
以下是官方已经实现的全部7个TaskExecuter。Spring宣称对于任何场景,这些TaskExecuter完全够用了:
| 名字 | 特点 |
|---|---|
| SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor | 每次请求新开线程,没有最大线程数设置.不是真的线程池,这个类不重用线程,每次调用都会创建一个新的线程。 --【1】 |
| SyncTaskExecutor | 不是异步的线程.同步可以用SyncTaskExecutor,但这个可以说不算一个线程池,因为还在原线程执行。这个类没有实现异步调用,只是一个同步操作。 |
| ConcurrentTaskExecutor | Executor的适配类,不推荐使用。如果ThreadPoolTaskExecutor不满足要求时,才用考虑使用这个类。 |
| SimpleThreadPoolTaskExecutor | 监听Spring’s lifecycle callbacks,并且可以和Quartz的Component兼容.是Quartz的SimpleThreadPool的类。线程池同时被quartz和非quartz使用,才需要使用此类。 |
| ThreadPoolTaskExecutor | 最常用。要求jdk版本大于等于5。可以在程序而不是xml里修改线程池的配置.其实质是对java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor的包装。 |
方式1:Executors new一个CachedThreadPool线程池。
private static final ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(new BasicThreadFactory.Builder() .namingPattern("create-card-thread-%d") .build()); CompletableFuture.runAsync(createCards(reqVO, buId), executorService) .whenComplete((Void v, Throwable t) -> { if (t == null) { log.info("create card complete.batchId={}", reqVO.getBatchId()); } else { log.error("create card failed.batchId={}", reqVO.getBatchId(), t); } try (ShardingCtx s = ShardingCtx.setShardingValue(buId)) { CustomerIntGencardLogPO updateLog = new CustomerIntGencardLogPO(); updateLog.setPk(gencardLogPO.getPk()) .setLastUpdated(LocalDateUtil.localDateTimeMinus8Hours(LocalDateTime.now())) .setGencardStatus(PROCESSED); customerIntGencardLogMapper.updateById(updateLog); } });
方式二:注入:@Autowire @Resource
@Service
public class AsyncService {
@Autowired //1.注入默认的线程池
@Resource("taskExecutor") //2.自定义的线程池
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor threadPoolTaskExecutor;
public void addEventLog(String buId, String status){
CustomerEventLogPO customerEventLog = new CustomerEventLogPO();
customerEventLog.setUuid(uuid);
customerEventLog.setStatus(status);
customerEventLog.setCreated(LocalDateTime.now());
customerEventLogMapper.insert(customerEventLog);
threadPoolTaskExecutor.submit(new Thread(()->{
customerEventLogMapper.insert(customerEventLog);
})); //submit有返回值
threadPoolTaskExecutor.execute(new Thread(()->{
customerEventLogMapper.insert(customerEventLog);
})); //execute无返回值
taskExecutor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// TODO
try {
studentscount = coursesService.getStudentCount(pd);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
}
方式三: 方法上直接加注解: @Async("taskExecutor") taskExecutor是自定义的bean或者默认的。
@Async("taskExecutor")
@DynamicDatasource
public void addEventLog(String buId, String uuid, String evenType, String eventData, Exception e, String status){
CustomerEventLogPO customerEventLog = new CustomerEventLogPO();
customerEventLog.setUuid(uuid);
customerEventLog.setEventType(evenType);
customerEventLog.setEventData(eventData);
customerEventLog.setStatus(status);
customerEventLog.setDescripe(e != null ? e.getMessage() : "");
customerEventLog.setCreated(LocalDateTime.now());
customerEventLogMapper.insert(customerEventLog);
}
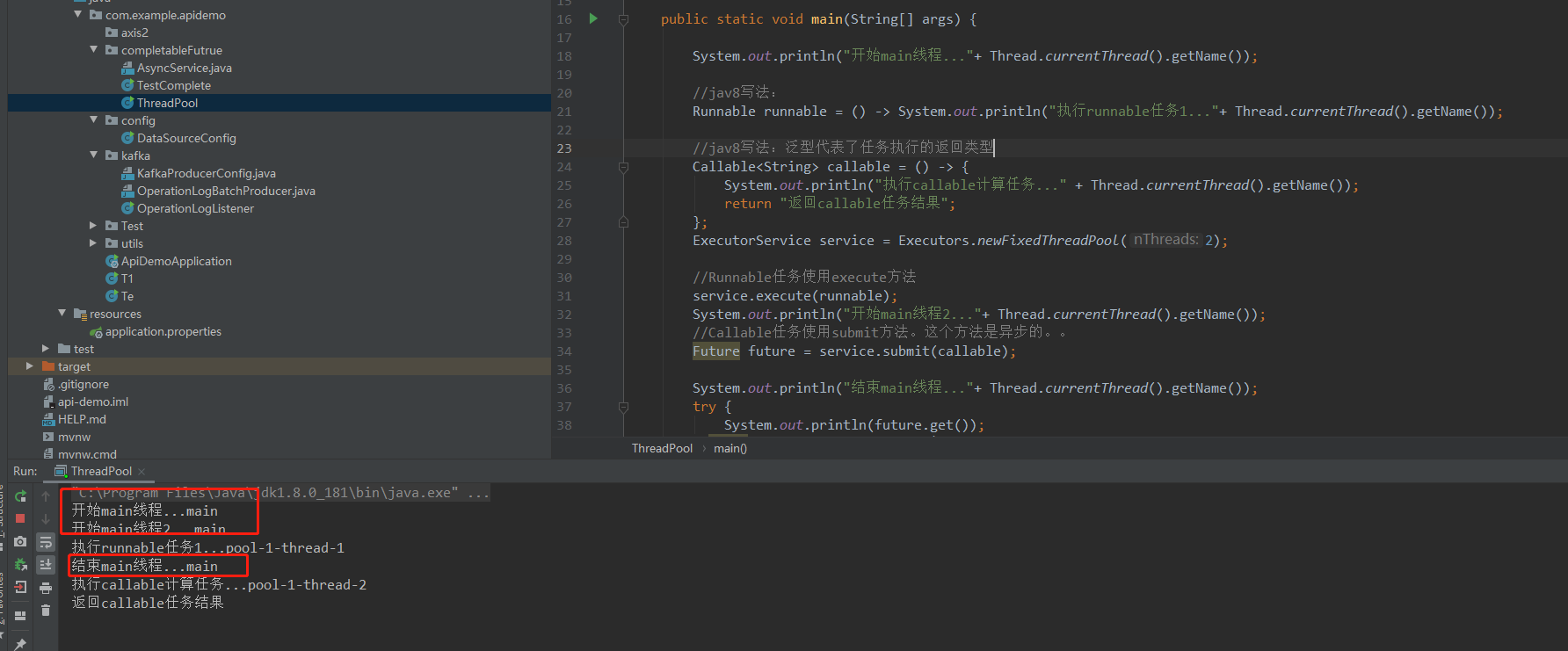
方式四:结论:在main方法里面的用线程池开多线程,不是按main方法执行顺序完再执行多线程,而是运行到新线程的地方,如果新线程先跑,那就在main方法之前
public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("开始main线程..."+ Thread.currentThread().getName()); //jav8写法: Runnable runnable = () -> System.out.println("执行runnable任务1..."+ Thread.currentThread().getName()); //jav8写法:泛型代表了任务执行的返回类型 Callable<String> callable = () -> { System.out.println("执行callable计算任务..." + Thread.currentThread().getName()); return "返回callable任务结果"; }; ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2); //Runnable任务使用execute方法 service.execute(runnable); System.out.println("开始main线程2..."+ Thread.currentThread().getName()); //Callable任务使用submit方法。这个方法是异步的。。 Future future = service.submit(callable); System.out.println("结束main线程..."+ Thread.currentThread().getName()); try { System.out.println(future.get()); } catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) { } // //老的写法: // Runnable runnable2 = new Runnable() { // @Override // public void run() { // System.out.println("执行任务1..."); // } // }; // //老的写法: 泛型代表了任务执行的返回类型 // Callable<String> callable = new Callable<String>() { // @Override // public String call() throws Exception { // System.out.println("执行计算任务2..."); // return "任务2结果"; // } // }; }