Secant 方法介绍
函数 Secant_Methods 简介
1.函数定义
[c, errColumn] = Secant_Method(f, a, b, N, convergence_type, tolerance)
2.输入
% f - function handle
% a - start position of interval bracket
% b - end position of interval bracket
% N [optional] - max iteration number
% convergence_type [optional] - [= 1] absolute error tolerances
% [= 0] relative error tolerances
% tolerance [optional] - [convergence_type = 1] absolute error tolerances
% [convergence_type = 0] relative error tolerances
%
3.输出
% c - approximation of root r ( f(r) = 0 )
% errColumn - the absolute/relative errors during the progress
% convergence_step - the number of steps taken, if the method doesn't
% convergence, [convergence_step = inf]
注意,errColumn 长度为 N,若在第k步收敛解后,剩余元素都与收敛步误差相同
4.代码
function [c, errColumn, convergence_step] = Secant_Method(f, a, b, N, convergence_type, tolerance)
% Use Secant Method to find roots of equation [f(x) = 0]
%
% Input:
% f - function handle
% a - start position of interval bracket
% b - end position of interval bracket
% N [optional] - max iteration number (default value: 10)
% convergence_type [optional] - [= 1] absolute error tolerances (default)
% [= 0] relative error tolerances
% tolerance [optional] - [convergence_type = 1] absolute error tolerances
% [convergence_type = 0] relative error tolerances
%
% Output:
% c - approximation of root r ( f(r) = 0 )
% errColumn - the absolute/relative errors during the progress
% convergence_step - the number of steps taken, if the method doesn't
% convergence, [convergence_step = inf]
% Usages:
%
% 1. use default value
% f = @(x) x^2 - 1
% c = false_position(f, 0, 2)
%
% 2. user set value
% c = false_position(f, 0, 2, 20, 0, 1e-5)
%
% Warnning:
% 1. if f(a) and f(b) have the same sign, the function returns an Nan.
% 2. if the false position lines outside the bracket interval, the
% function will throws an error.
% 3. After N times iteration, if the method does not converge, an message
% will be printed on the command window and return the current vaule.
%% check input parameters
% check the interval is really a bracket
if (a > b)
error('please check the bracket!');
end
% check that that neither end-point is a root
% if f(a) and f(b) have the same sign, throw an Nan.
if( f(a) == 0 )
c = a;
return;
elseif ( f(b) == 0 )
c = b;
return;
elseif ( f(a) * f(b) > 0 )
c = Nan;
return;
end
% check max iteration number exits
% default value is 10
if ~exist('N', 'var')
N = 10;
end% if
% check choice of error tolerances
% default value is 1
if ~exist('convergence_type', 'var')
convergence_type = 1;
tolerance = 1e-6;
end% if
% check the tolerances is positive
if tolerance <= 0
error('the tolerances should be positive!');
end
% relative error tolerances
errColumn = zeros(N, 1);
%% iteration
% iterate at most N times
c_old = a;
convergence_step = inf;
for k = 1:N
%% find the false position
% c = (a*f(b) + b*f(a))/(f(b) - f(a));
c = ( b*f(a) - a*f(b) )/(f(a) - f(b));
% check c lies within the bracketing interval
if (c < a) || (c > b)
error('convergence problem occurs! please reset bracket interval.')
end
%% reset bracketing interval
% Check if c is a root
if ( f(c) == 0 )
% return c
return;
elseif ( f(c)*f(a) < 0 )
% if f(a) and f(c) have opposite signs
% set [a, c] as the new bracketing interval
b = c;
else
% if f(b) and f(c) have opposite signs
% set [c, b] as the new bracketing interval
a = c;
end
%% cal the absolute/relative errors
switch convergence_type
case 0 % relative error
errColumn(k) = abs( (c - c_old)/c_old );
if errColumn(k) < tolerance
convergence_step = k;
errColumn(k:end) = errColumn(k);
% set convergence step
% set the remaining step errors
return;
end
case 1 % absolute error
errColumn(k) = abs( f(c) );
if errColumn(k) < tolerance
% set convergence step
% set the remaining step errors
convergence_step = k;
errColumn(k:end) = errColumn(k);
return;
end
end% switch
c_old = c;
end
fprintf( 'the method did not converge
' );
end
算例 Q1.m
find all roots of (1000000x^3 − 111000x^2 + 1110x = 1)
-
绘制函数函数图像,寻找方程根所在区间
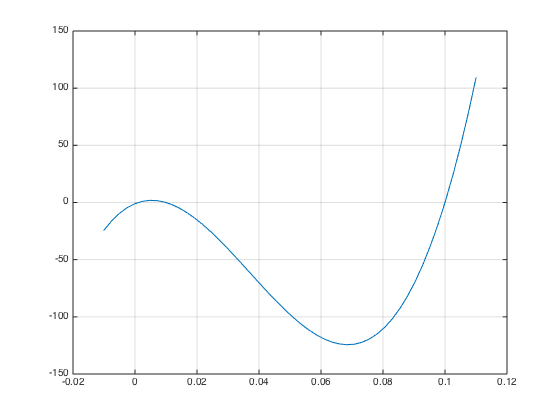
-
选取区间
选取3个区间分别为 ([-0.01, 0.005], [0.005, 0.06], [0.06, 0.11])。 -
计算
第一个区间 ([-0.01, 0.005]) 为例,选择绝对误差为 (10^{-6}),迭代40次。得到误差随迭代次数变化关系为
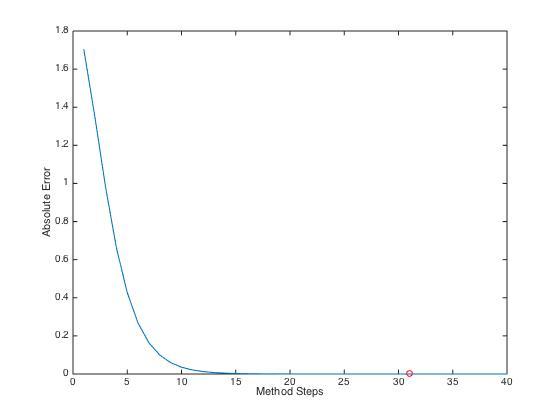
其中红色点代表第31步方法收敛位置。 -
结果
最终得到方程三个根为
r =
0.0010
0.0100
0.1000
- 脚本
%% Q1
f = @(x) 1000000*x.^3 - 111000*x.^2 + 1110*x - 1;
% plot function
x = linspace(-0.01, 0.11, 50);
y = f(x);
figure; plot(x,y); grid on;
% set interval bracket
a(1) = -0.01; a(2) = 0.005; a(3) = 0.06; a(4) = 0.11;
% cal roots in a loop
r = zeros(3,1);
for ib = 1:3
[r(ib), errColumn, con_step] = Secant_Method(f, a(ib), a(ib+1), 40);
if ib == 1
figure; plot(errColumn); hold on;
plot(con_step, errColumn(con_step), 'ro');
xlabel('Method Steps'); ylabel('Absolute Error')
end% if
end% for