React是个技术栈,单单使用React很难构建复杂的Web应用程序,很多情况下我们需要引入其他相关的技术
React Router是React的路由库,保持相关页面部件与URL间的同步
下面就来简单介绍其基础使用,更全面的可参考 指南
1. 它看起来像是这样
在页面文件中
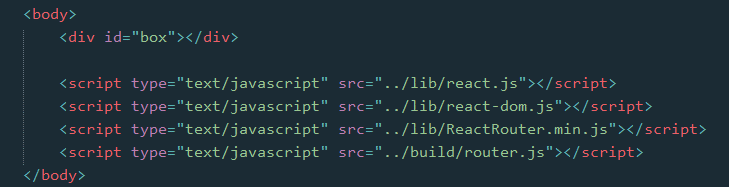
在外部脚本文件中
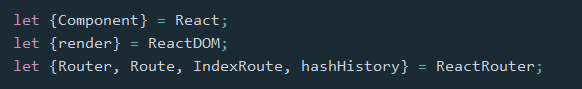
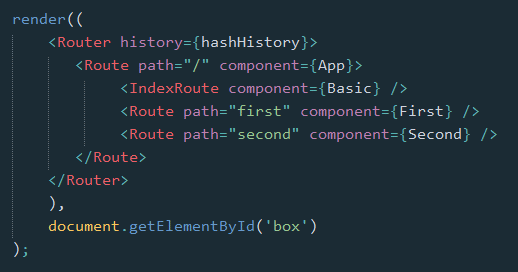
2. 库的引入
React Router库的引入,有两种方式
2.1 浏览器直接引入
可以引用 这里 的浏览器版本,或者下载之后引入
然后就可以直接使用 ReactRouter 这个对象了,我们可能会使用到其中的几个属性
let {Router, Route, IndexRoute, Redirect, IndexRedirect, Link, IndexLink, hashHistory, browserHistory} = ReactRouter;
2.2 npm 安装,通过构建工具编译引入
npm install --save react-router
安装好路由库之后,在脚本文件中引入相关属性
import {Router, Route, IndexRoute, Redirect, IndexRedirect, Link, IndexLink, hashHistory, browserHistory} from 'react-router';
因浏览器目前还不能支持import与export命令,且babel工具不会将require命令编译,所以我们还得需要如Webpack等构建工具编译引入
库引入之后,在ReactDOM的render方法中,就可以使用相关的组件了
3. 路由简单使用
最基本的,通过URL判断进入哪个页面(组件部件)
class First extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
}
render() {
return <p>First</p>
}
}
class Second extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
}
render() {
return <p>Second</p>
}
}
class App extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
}
render() {
return <div></div>
}
}
render((
<Router history={hashHistory}>
<Route path="/" component={App} />
<Route path="first" component={First} />
<Route path="second" component={Second} />
</Router>
),
document.getElementById('box')
);
首先,Router是一个容器,history属性定义了是用何种方式处理页面的URL
有三种:
- browserHistory:通过URL的变化改变路由,是推荐的一种方式,但是需要在服务器端需要做一些配置(窝目前还不知怎么配)
- hashHistory:通过#/ ,其实就像是单页面应用中常见的hashbang方式,example.com/#/path/path.. (使用简单,这里暂且就用这种方式)
- createMemoryHistory:Memory history 并不会从地址栏中操作或是读取,它能够帮助我们完成服务器端的渲染,我们得手动创建history对象
然后,在容器中使用Route组件定义各个路由,通过path指定路径(可以看到,是不区分大小写的),通过component指定该路径使用的组件
也可以直接在Router容器上直接用routes属性定义各个路由,如
let routes =
<div>
<Route path="/" component={App} />
<Route path="first" component={First} />
<Route path="second" component={Second} />
</div>;
render(<Router routes={routes} history={hashHistory}></Router>, document.getElementById('box'));
需要注意的是{routes}中只能有一个父级,所以这里加了<div>标签
另外,路由Route也可以嵌套,在上面的例子中,嵌套起来可能更符合实际情况
需要注意的是,这里的App在父级,为了获取子级的First与Second组件,需要在App组件中添加 this.props.children 获取
class App extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
}
render() {
return <div>{this.props.children}</div>
}
}
render((
<Router history={hashHistory}>
<Route path="/" component={App}>
<Route path="first" component={First} />
<Route path="second" component={Second} />
</Route>
</Router>
),
document.getElementById('box')
);
同样的,可以直接在Router中用routes属性定义路由
let routes =
<Route path="/" component={App}>
<Route path="first" component={First} />
<Route path="second" component={Second} />
</Route>;
render(<Router routes={routes} history={hashHistory}></Router>, document.getElementById('box'));
4. 路由的其他组件
除了基本的Route之外,IndexRoute、Redirect、IndexRedirect、Link、IndexLink等,顾名思义
- IndexRoute: 在主页面会用到,如上个例子中,在路径"/"下我们看到的是空白页面,可以添加默认的页面组件用于导航
- Link: 可以认为它是<a>标签在React中的实现,使用to属性定义路径,还可以通过activeClass或activeStyle定义active的样式
- IndexLink: 类似Link,推荐用来定义指向主页面的链接,当然也可以随意定义
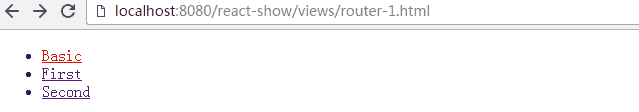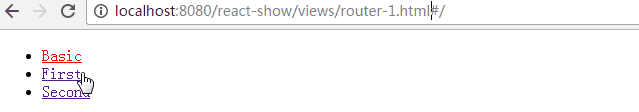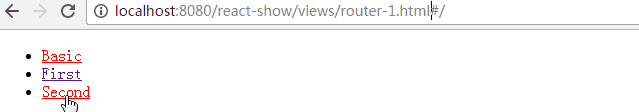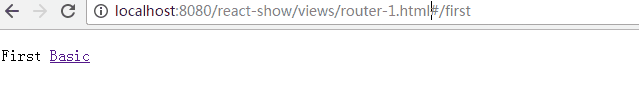
class First extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
}
render() {
return (
<p>First
<IndexLink to="/" activeStyle={{color: 'red'}}>Basic</IndexLink>
</p>
)
}
}
class Second extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
}
render() {
return <p>Second</p>
}
}
class Basic extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
}
render() {
return (
<ul role="nav">
<li><IndexLink to="/" activeStyle={{color: 'red'}}>Basic</IndexLink></li>
<li><Link to="/first" activeStyle={{color: 'red'}}>First</Link></li>
<li><Link to="/Second" activeClass="active">Second</Link></li>
</ul>
)
}
}
class App extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
}
render() {
return <div>
{this.props.children}
</div>
}
}
render((
<Router history={hashHistory}>
<Route path="/" component={App}>
<IndexRoute component={Basic} />
<Route path="first" component={First} />
<Route path="second" component={Second} />
</Route>
</Router>
),
document.getElementById('box')
);
- Redirect: 从from路径重定向到to路径
- IndexRedirect: 在主页面,直接重定向到to路径
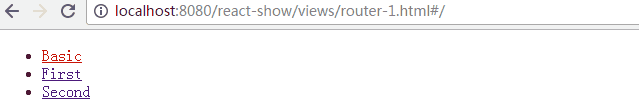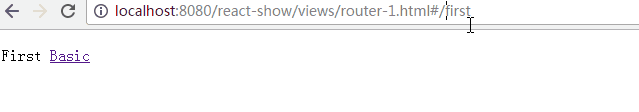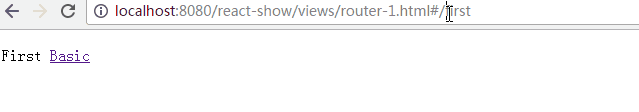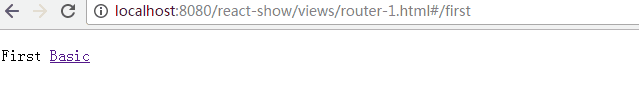
render((
<Router history={hashHistory}>
<Route path="/" component={App}>
<IndexRoute component={Basic} />
<IndexRedirect to="first" />
<Redirect from="second" to="first" />
<Route path="first" component={First} />
<Route path="second" component={Second} />
</Route>
</Router>
),
document.getElementById('box')
);
5. 路由的path规则
path定义的路由的路径,在hashHistory中,它的主页路径是#/
自定义Route路由通过与父Route的path进行合并,在与主页路径合并,得到最终的路径
- :paramName 匹配 URL 的一个部分,直到遇到下一个/、?、#
- () 表示URL的这个部分是可选的
- * 匹配任意字符(非贪婪模式),直到模式里面的下一个字符为止
- ** 匹配任意字符(贪婪模式),直到下一个/、?、#为止
<Route path="/hello/:name"> // 匹配 /hello/michael 和 /hello/ryan <Route path="/hello(/:name)"> // 匹配 /hello, /hello/michael, 和 /hello/ryan <Route path="/files/*.*"> // 匹配 /files/hello.jpg 和 /files/hello.html <Route path="/**/*.jpg"> // 匹配 /files/hello.jpg 和 /files/path/to/file.jpg
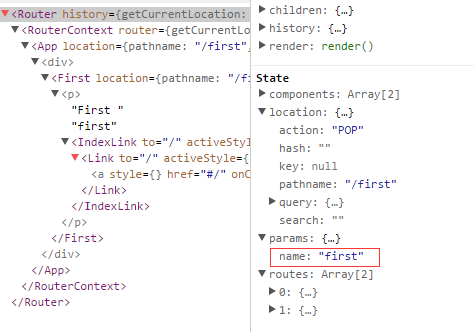
而:name可以通过 this.props.params 中取到
class First extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
}
render() {
return (
<p>First {this.props.params.name}
<IndexLink to="/" activeStyle={{color: 'red'}}>Basic</IndexLink>
</p>
)
}
}
.
.
<Route path="/:name" component={First} />
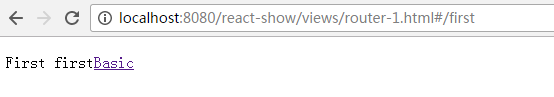
通过React Dev Tool也可以看到组件的相关数据
6. 路由的onEnter、onLeave钩子
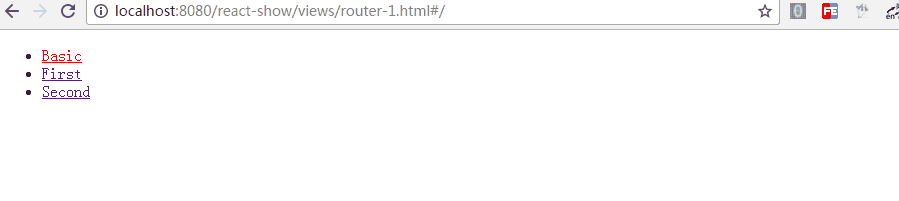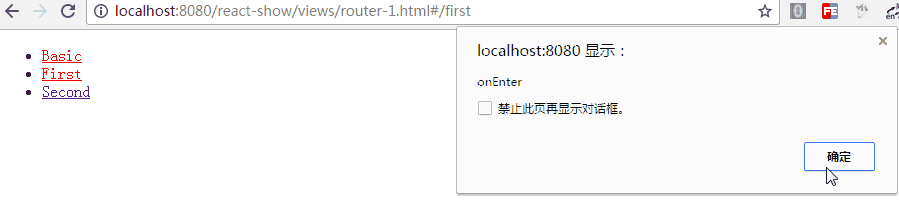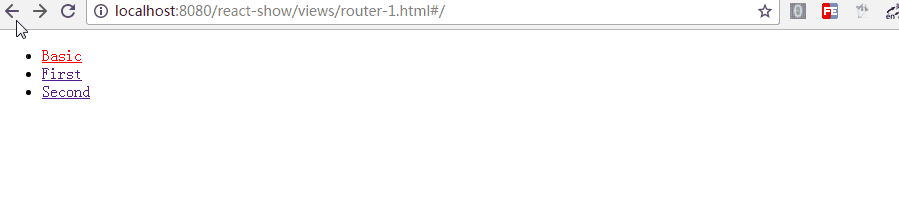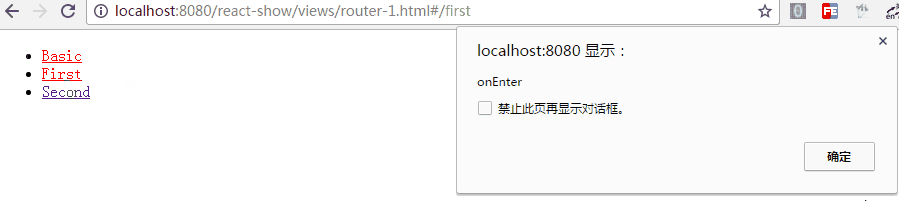
在路由的跳转中,我们可能需要在进入页面或离开页面的时候做一些特殊操作,Route 通过 onEnter 与 onLeave 定义了这两个行为
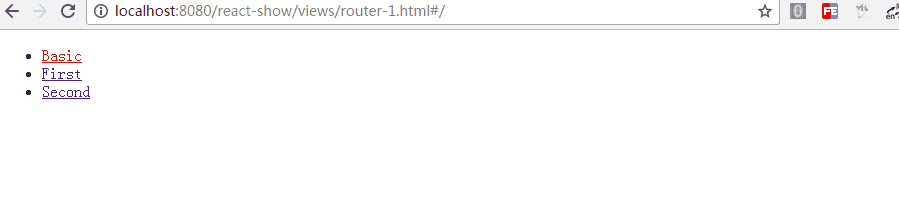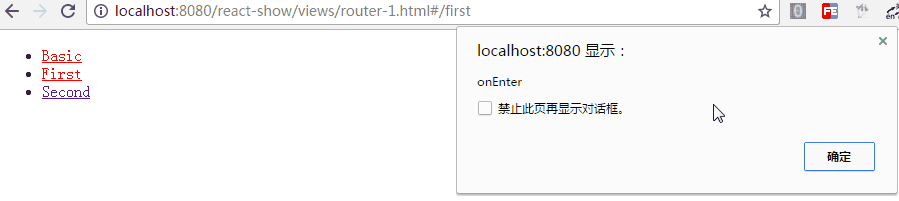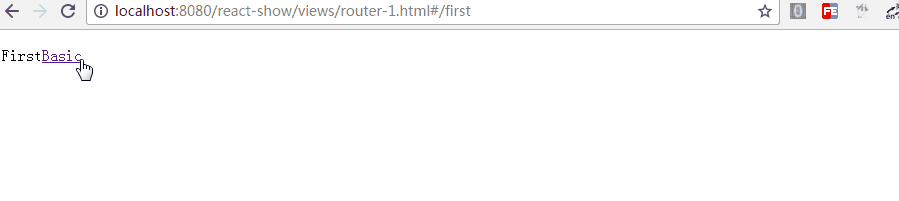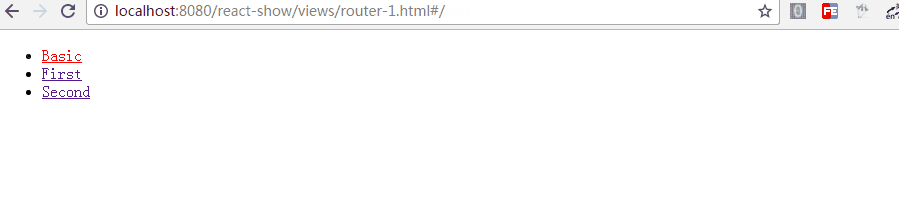
<Route path="first" component={First} onEnter={(nextState, replace) => {
console.log(nextState);
alert('onEnter');
// replace('second');
}} onLeave={() => {
alert('onLeave');
}}/>
如上,带两个参数,通过 replace 可以更新路径,把注释去掉后,进入"/first"时立马跳转值"/second",这在检测登录时应该比较有用
更多的使用参见 指南
