引言
最经关于基础C开发框架基本都搭建好了. 在研究githup,准备传上去. 可惜的是两会连githup 都登陆不进去.
三观很正的我也觉得, 这样不好. 双向标准, 共x党不是一个代表穷苦大众的党.当然我也恒感谢党国, 给我选举权,每次都是
人大代表帮我投了,好人. 谢谢了!
后面可能没办法, 继续上传到 csdn 上. 会把使用手册,注意事项写清楚.这个框架,适合新手参考吧.大多库还是很复杂的
内力不足看多了容易走火入魔.我这里提供都比较浅显易懂. 适合使用. 感受简单,高效,能用,实在的设计.
杀死那个石家庄人 http://music.163.com/#/song?id=386844
前言
同样先介绍一写,这节要将的精华.首先说一下大白文,将读取文件的内容直到全部.
/* * 简单的文件帮助类,会读取完毕这个文件内容返回,失败返回NULL. * 需要事后使用 tstring_destroy(&ret); 销毁这个字符串对象 * path : 文件路径 * ret : 返回创建好的字符串内容,返回NULL表示读取失败 */ tstring file_malloc_readend(const char* path) { int c; tstring tstr; FILE* txt = fopen(path, "r"); if (NULL == txt) { SL_NOTICE("fopen r path = '%s' error!", path); return NULL; } //这里创建文件对象,创建失败直接返回 if ((tstr = tstring_create(NULL)) == NULL) { fclose(txt); return NULL; } //这里读取文本内容 while ((c = fgetc(txt))!=EOF) if (_RT_OK != tstring_append(tstr, c)){ //出错了就直接销毁已经存在的内容 tstring_destroy(&tstr); break; } fclose(txt);//很重要创建了就要释放,否则会出现隐藏的句柄bug return tstr; }
一个细节是 加了字符串数据 返回判断,如果内存分配失败直接返回.
还有一个值得学习的细节是 只能在堆上分配的内存结构
/* * 这里是一个解析 csv 文件的 简单解析器. * 它能够帮助我们切分文件内容,保存在数组中. */ struct sccsv { //内存只能在堆上 int rlen; //数据行数,索引[0, rlen) int clen; //数据列数,索引[0, clen) const char* data[]; //保存数据一维数组,希望他是二维的 rlen*clen }; typedef struct sccsv* sccsv_t;
上面是新语法, 以前的做法是data[0], data[1]等. 在结构体中声明可变数组.这种结构是不完全结构无法 直接 struct sccsv 在堆上声明.
这里基本上就是我们说的. 再扯一点当你使用inline语法在C中的时候. 一种是static inline 内联.一种如下内联声明
/* * 获取某个位置的对象内容,这个函数 推荐声明为内联的, window上不支持 * csv : sccsv_t 对象, new返回的 * ri : 查找的行索引 [0, csv->rlen) * ci : 查找的列索引 [0, csv->clen) * : 返回这一项中内容,后面可以用 atoi, atof, str_dup 等处理了... */ extern inline const char* sccsv_get(sccsv_t csv, int ri, int ci);
到这里基本C基础普及就这样了,等一下分析正文.
正文
那就开始正题描述吧.首先什么是csv文件. 对比显差异.预览图
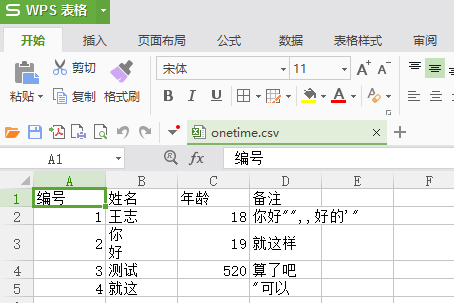
再看看实际的编码图
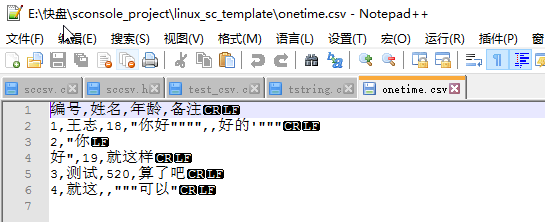
通过这个看应该就知道csv文件的编码规则了吧. 总结如下
1.用 , 分割
2.如果出现 , " 这种特殊字符, 会被用 "" 包裹起来, 并且 "" 表示一个 " 号
3.每行用 结束
这样语法问题都已经解决了.
再分析我们今天的 接口内容 sccsv.h
#ifndef _H_SCCSV #define _H_SCCSV /* * 这里是一个解析 csv 文件的 简单解析器. * 它能够帮助我们切分文件内容,保存在数组中. */ struct sccsv { //内存只能在堆上 int rlen; //数据行数,索引[0, rlen) int clen; //数据列数,索引[0, clen) const char* data[]; //保存数据一维数组,希望他是二维的 rlen*clen }; typedef struct sccsv* sccsv_t; /* * 从文件中构建csv对象, 最后需要调用 sccsv_die 释放 * path : csv文件内容 * : 返回构建好的 sccsv_t 对象 */ extern sccsv_t sccsv_new(const char* path); /* * 释放由sccsv_new构建的对象 * pcsv : 由sccsv_new 返回对象 */ extern void sccsv_die(sccsv_t* pcsv); /* * 获取某个位置的对象内容,这个函数 推荐声明为内联的, window上不支持 * csv : sccsv_t 对象, new返回的 * ri : 查找的行索引 [0, csv->rlen) * ci : 查找的列索引 [0, csv->clen) * : 返回这一项中内容,后面可以用 atoi, atof, str_dup 等处理了... */ extern inline const char* sccsv_get(sccsv_t csv, int ri, int ci); #endif // !_H_SCCSV
构建销毁获得指定内容. 很容易理解.
现在我们展示一下运行的结果, 测试代码是
#include <schead.h> #include <sclog.h> #include <sccsv.h> #define _STR_PATH "onetime.csv" // 解析 csv文件内容 int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { sccsv_t csv; int i, j; int rlen, clen; INIT_PAUSE(); sl_start(); // 这里得到 csv 对象 csv = sccsv_new(_STR_PATH); if (NULL == csv) CERR_EXIT("open " _STR_PATH " is error!"); //这里打印数据 rlen = csv->rlen; clen = csv->clen; for (i = 0; i < rlen; ++i) { for (j = 0; j < clen; ++j) { printf("<%d, %d> => [%s] ", i, j, sccsv_get(csv, i, j)); } } //开心 测试圆满成功 sccsv_die(&csv); return 0; }
最后运行的预览图

运行起来可能复杂一点点, 这里摘录一下编译图,还是看代码吧,你自己找其中关于 test_csv.c 文件的编译过程吧

C = gcc DEBUG = -g -Wall -D_DEBUG #指定pthread线程库 LIB = -lpthread -lm #指定一些目录 DIR = -I./module/schead/include -I./module/struct/include #具体运行函数 RUN = $(CC) $(DEBUG) -o $@ $^ $(LIB) $(DIR) RUNO = $(CC) $(DEBUG) -c -o $@ $^ $(DIR) # 主要生成的产品 all:test_cjson_write.out test_csjon.out test_csv.out test_json_read.out test_log.out test_scconf.out test_tstring.out #挨个生产的产品 test_cjson_write.out:test_cjson_write.o schead.o sclog.o tstring.o cjson.o $(RUN) test_csjon.out:test_csjon.o schead.o sclog.o tstring.o cjson.o $(RUN) test_csv.out:test_csv.o schead.o sclog.o sccsv.o tstring.o $(RUN) test_json_read.out:test_json_read.o schead.o sclog.o sccsv.o tstring.o cjson.o $(RUN) test_log.out:test_log.o schead.o sclog.o $(RUN) test_scconf.out:test_scconf.o schead.o scconf.o tree.o tstring.o sclog.o $(RUN) test_tstring.out:test_tstring.o tstring.o sclog.o schead.o $(RUN) #产品主要的待链接文件 test_cjson_write.o:./main/test_cjson_write.c $(RUNO) test_csjon.o:./main/test_csjon.c $(RUNO) test_csv.o:./main/test_csv.c $(RUNO) test_json_read.o:./main/test_json_read.c $(RUNO) test_log.o:./main/test_log.c $(RUNO) -std=c99 test_scconf.o:./main/test_scconf.c $(RUNO) test_tstring.o:./main/test_tstring.c $(RUNO) #工具集机械码,待别人链接 schead.o:./module/schead/schead.c $(RUNO) sclog.o:./module/schead/sclog.c $(RUNO) sccsv.o:./module/schead/sccsv.c $(RUNO) tstring.o:./module/struct/tstring.c $(RUNO) cjson.o:./module/schead/cjson.c $(RUNO) scconf.o:./module/schead/scconf.c $(RUNO) tree.o:./module/struct/tree.c $(RUNO) #删除命令 clean: rm -rf *.i *.s *.o *.out __* log ; ls -hl .PHONY:clean
最后展示 实现的代码
#include <schead.h> #include <sccsv.h> #include <sclog.h> #include <tstring.h> //从文件中读取 csv文件内容 char* __get_csv(FILE* txt, int* prl, int* pcl) { int c, n; int cl = 0, rl = 0; TSTRING_CREATE(ts); while((c=fgetc(txt))!=EOF){ if('"' == c){ //处理这里数据 while((c=fgetc(txt))!=EOF){ if('"' == c) { if((n=fgetc(txt)) == EOF) { //判断下一个字符 SL_WARNING("The CSV file is invalid one!"); free(ts.str); return NULL; } if(n != '"'){ //有效字符再次压入栈 ungetc(n, txt); break; } } //都是合法字符 保存起来 if (_RT_OK != tstring_append(&ts, c)) { free(ts.str); return NULL; } } //继续判断,只有是c == '"' 才会下来,否则都是错的 if('"' != c){ SL_WARNING("The CSV file is invalid two!"); free(ts.str); return NULL; } } else if(',' == c){ if (_RT_OK != tstring_append(&ts, '�')) { free(ts.str); return NULL; } ++cl; } else if(' ' == c) continue; else if(' ' == c){ if (_RT_OK != tstring_append(&ts, '�')) { free(ts.str); return NULL; } ++cl; ++rl; } else {//其它所有情况只添加数据就可以了 if (_RT_OK != tstring_append(&ts, c)) { free(ts.str); return NULL; } } } if(cl % rl){ //检测 , 号是个数是否正常 SL_WARNING("now csv file is illegal! need check!"); return NULL; } // 返回最终内容 *prl = rl; *pcl = cl; return ts.str; } // 将 __get_csv 得到的数据重新构建返回, 执行这个函数认为语法检测都正确了 sccsv_t __get_csv_new(const char* cstr, int rl, int cl) { int i = 0; sccsv_t csv = malloc(sizeof(struct sccsv) + sizeof(char*)*cl); if(NULL == csv){ SL_FATAL("malloc is error one !"); return NULL; } // 这里开始构建内容了 csv->rlen = rl; csv->clen = cl / rl; do { csv->data[i] = cstr; while(*cstr++) //找到下一个位置处 ; }while(++i<cl); return csv; } /* * 从文件中构建csv对象, 最后需要调用 sccsv_die 释放 * path : csv文件内容 * : 返回构建好的 sccsv_t 对象 */ sccsv_t sccsv_new(const char* path) { FILE* txt; char* cstr; int rl, cl; DEBUG_CODE({ if(!path || !*path){ SL_WARNING("params is check !path || !*path ."); return NULL; } }); // 打开文件内容 if((txt=fopen(path, "r")) == NULL){ SL_WARNING("fopen %s r is error!", path); return NULL; } // 如果解析 csv 文件内容失败直接返回 cstr = __get_csv(txt, &rl, &cl); fclose(txt); // 返回最终结果 return cstr ? __get_csv_new(cstr, rl, cl) : NULL; } /* * 释放由sccsv_new构建的对象 * pcsv : 由sccsv_new 返回对象 */ void sccsv_die(sccsv_t* pcsv) { if (pcsv && *pcsv) { // 这里 开始释放 free(*pcsv); *pcsv = NULL; } } /* * 获取某个位置的对象内容 * csv : sccsv_t 对象, new返回的 * ri : 查找的行索引 [0, csv->rlen) * ci : 查找的列索引 [0, csv->clen) * : 返回这一项中内容,后面可以用 atoi, atof, str_dup 等处理了... */ inline const char* sccsv_get(sccsv_t csv, int ri, int ci) { DEBUG_CODE({ if(!csv || ri<0 || ri>=csv->rlen || ci<0 || ci >= csv->clen){ SL_WARNING("params is csv:%p, ri:%d, ci:%d.", csv, ri, ci); return NULL; } }); // 返回最终结果 return csv->data[ri*csv->clen + ci]; }
到这里原本要结束了,但是再扯一点,上面采用的内存模型是整体内存模型, 一共分配两次,一次为了所有字符.一次
为了保存分割串内容. 可以细细品味上面 new那段代码,还是很有意思的.
到这里简单的基础库的各个细节都已经实现完毕. 下一次会详细介绍怎么使用这个框架.再试试githup. 实在
不行再采用菜一点的做法.
后记
错误是难免的,欢迎吐槽.... 以科幻的图结束吧 -------------------------------未来是不可知的---------------------------------

