引言
做一个老实人挺好的,至少还觉得自己挺老实的.

再分享一首 自己喜欢的诗人的一首 情景诗. 每个人总会有问题,至少喜欢就好,

本文 参照
http 协议 http://www.cnblogs.com/rayray/p/3729533.html
html格式 http://blog.csdn.net/allenjy123/article/details/7375029
tinyhttpd 源码 https://github.com/EZLippi/Tinyhttpd
附录 本文最后完稿的资源
httpd 源码打包 http://download.csdn.net/detail/wangzhione/9461441
通过本文练习, 至少会学会 Linux上fork用法, pipe管道用法0读1写, pthread用法等.
其它的都是业务解析内容.
前言
讲的不好望见谅, 因为很多东西需要自己去写一写就有感悟了. 看懂源码和会改源码是两码事. 和 会优化更不同了.
凡事多练习. 不懂也都懂了. 我们先说一下总的结构.
client.c 是一个简易的 测试 http请求的客户端
httpd.c 使我们重点要说的 小型简易的Linux上的http服务器
index.html 测试网页 是client.c 想请求的网页
Makefile 编译文件.
这里先总的展示一下 httpd.c
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <stdint.h> #include <errno.h> #include <pthread.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <sys/wait.h> #include <sys/socket.h> #include <arpa/inet.h> #include <netinet/in.h> // --------------------------------------- 辅助参数宏 ---------------------------------------------- /* * c 如果是空白字符返回 true, 否则返回false * c : 必须是 int 值,最好是 char 范围 */ #define sh_isspace(c) ((c==' ')||(c>=' '&&c<=' ')) //4.0 控制台打印错误信息, fmt必须是双引号括起来的宏 #define CERR(fmt, ...) fprintf(stderr,"[%s:%s:%d][error %d:%s]" fmt " ", __FILE__, __func__, __LINE__, errno, strerror(errno),##__VA_ARGS__) //4.1 控制台打印错误信息并退出, t同样fmt必须是 ""括起来的字符串常量 #define CERR_EXIT(fmt,...) CERR(fmt,##__VA_ARGS__),exit(EXIT_FAILURE) //4.3 if 的 代码检测 #define IF_CHECK(code) if((code) < 0) CERR_EXIT(#code) // --------------------------------------- 辅助变量宏 和 声明 ------------------------------------------ // char[]缓冲区大小 #define _INT_BUF (1024) // listen监听队列的大小 #define _INT_LIS (7) /* * 读取文件描述符 fd 一行的内容,保存在buf中,返回读取内容长度 * fd : 文件描述符 * buf : 保存的内容 * sz : buf 的大小 * : 返回读取的长度 */ int getfdline(int fd, char buf[], int sz); // 返回400 请求解析失败,客户端代码错误 extern inline void response_400(int cfd); // 返回404 文件内容, 请求文件没有找见 extern inline void response_404(int cfd); // 返回501 错误, 不支持的请求 extern inline void response_501(int cfd); // 服务器内部错误,无法处理等 extern inline void response_500(int cfd); // 返回200 请求成功 内容, 后面可以加上其它参数,处理文件输出 extern inline void response_200(int cfd); /* * 将文件 发送给客户端 * cfd : 客户端文件描述符 * path : 发送的文件路径 */ void response_file(int cfd, const char* path); /* * 返回启动的服务器描述符(句柄), 这里没有采用8080端口,防止冲突,用了随机端口 * pport : 输出参数和输出参数, 如果传入NULL,将不返回自动分配的端口 * : 返回 启动的文件描述符 */ int serstart(uint16_t* pport); /* * 在客户端链接过来,多线程处理的函数 * arg : 传入的参数, 客户端文件描述符 (int)arg * : 返回处理结果,这里默认返回 NULL */ void* request_accept(void* arg); /* * 处理客户端的http请求. * cfd : 客户端文件描述符 * path : 请求的文件路径 * type : 请求类型,默认是POST,其它是GET * query : 请求发送的过来的数据, url ? 后面那些数据 */ void request_cgi(int cfd, const char* path, const char* type, const char* query); /* * 主逻辑,启动服务,可以做成守护进程. * 具体的实现逻辑, 启动小型玩乐级别的httpd 服务 */ int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { pthread_attr_t attr; uint16_t port = 0; int sfd = serstart(&port); printf("httpd running on port %u. ", port); // 初始化线程属性 pthread_attr_init(&attr); pthread_attr_setdetachstate(&attr, PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED); for(;;){ pthread_t tid; struct sockaddr_in caddr; socklen_t clen = sizeof caddr; int cfd = accept(sfd, (struct sockaddr*)&caddr, &clen); if(cfd < 0){ CERR("accept sfd = %d is error!", sfd); break; } if(pthread_create(&tid, &attr, request_accept, (void*)cfd) < 0) CERR("pthread_create run is error!"); } // 销毁吧, 一切都结束了 pthread_attr_destroy(&attr); close(sfd); return 0; } // ----------------------------------------- 具体的函数实现过程 ------------------------------------------------ /* * 读取文件描述符 fd 一行的内容,保存在buf中,返回读取内容长度 * fd : 文件描述符 * buf : 保存的内容 * sz : buf 的大小 * : 返回读取的长度 */ int getfdline(int fd, char buf[], int sz) { char* tp = buf; char c; --sz; while((tp-buf)<sz){ if(read(fd, &c, 1) <= 0) //伪造结束条件 break; if(c == ' '){ //全部以 分割 if(recv(fd, &c, 1, MSG_PEEK)>0 && c == ' ') read(fd, &c, 1); else //意外的结束,填充 结束读取 *tp++ = ' '; break; } *tp++ = c; } *tp = '�'; return tp - buf; } // 返回400 请求解析失败,客户端代码错误 inline void response_400(int cfd) { const char* estr = "HTTP/1.0 400 BAD REQUEST " "Server: wz simple httpd 1.0 " "Content-Type: text/html " " " "<p>你的请求有问题,请检查语法!</p> "; write(cfd, estr, strlen(estr)); } // 返回404 文件内容, 请求文件没有找见 inline void response_404(int cfd) { const char* estr = "HTTP/1.0 404 NOT FOUND " "Server: wz simple httpd 1.0 " "Content-Type: text/html " " " "<html>" "<head><title>你请求的界面被查水表了!</title></head> " "<body><p>404: 估计是回不来了</p></body>" "</html>"; //开始发送数据 write(cfd, estr, strlen(estr)); } // 返回501 错误, 请求解析失败,不支持的请求 inline void response_501(int cfd) { const char* estr = "HTTP/1.0 501 Method Not Implemented " "Server: wz simple httpd 1.0 " "Content-Type: text/html " " " "<html>" "<head><title>小伙子不要乱请求</title></head> " "<body><p>too young too simple, 年轻人别总想弄出个大新闻.</p></body>" "</html>"; //这里还有一个好的做法是将这些内容定义在文件中输出文件 write(cfd, estr, strlen(estr)); } // 服务器内部错误,无法处理等 inline void response_500(int cfd) { const char* estr = "HTTP/1.0 500 Internal Server Error " "Server: wz simple httpd 1.0 " "Content-Type: text/html " " " "<html>" "<head><title>Sorry </title></head> " "<body><p>最近有点方了!</p></body>" "</html>"; write(cfd, estr, strlen(estr)); } // 返回200 请求成功 内容, 后面可以加上其它参数,处理文件输出 inline void response_200(int cfd) { // 打印返回200的报文头 const char* str = "HTTP/1.0 200 OK " "Server: wz simple httpd 1.0 " "Content-Type: text/html " " "; write(cfd, str, strlen(str)); } /* * 将文件 发送给客户端 * cfd : 客户端文件描述符 * path : 发送的文件路径 */ void response_file(int cfd, const char* path) { FILE* txt; char buf[_INT_BUF]; // 读取报文头,就是过滤 while(getfdline(cfd, buf, sizeof buf)>0 && strcmp(" ", buf)) ; // 这里开始处理 文件内容 if((txt = fopen(path, "r")) == NULL) //文件解析错误,给它个404 response_404(cfd); else{ response_200(cfd); //发送给200的报文头过去 // 先判断文件内容存在 while(!feof(txt) && fgets(buf, sizeof buf, txt)) write(cfd, buf, strlen(buf)); } fclose(txt); } /* * 返回启动的服务器描述符(句柄) * pport : 输出参数和输出参数, 如果传入NULL,将不返回自动分配的端口 * : 返回 启动的文件描述符 */ int serstart(uint16_t* pport) { int sfd; struct sockaddr_in saddr = { AF_INET }; IF_CHECK(sfd = socket(PF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0)); saddr.sin_port = !pport || !*pport ? 0 : htons(*pport); saddr.sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY; // 绑定一下端口信息 IF_CHECK(bind(sfd, (struct sockaddr*)&saddr, sizeof saddr)); if(pport && !*pport){ socklen_t clen = sizeof saddr; IF_CHECK(getsockname(sfd, (struct sockaddr*)&saddr, &clen)); *pport = ntohs(saddr.sin_port); } // 开启监听任务 IF_CHECK(listen(sfd, _INT_LIS)); return sfd; } /* * 在客户端链接过来,多线程处理的函数 * arg : 传入的参数, 客户端文件描述符 (int)arg * : 返回处理结果,这里默认返回 NULL */ void* request_accept(void* arg) { char buf[_INT_BUF], path[_INT_BUF>>1], type[_INT_BUF>>5]; char *lt, *rt, *query, *nb = buf; struct stat st; int iscgi, cfd = (int)arg; if(getfdline(cfd, buf, sizeof buf) <= 0){ //请求错误 response_501(cfd); close(cfd); return NULL; } // 合法请求处理 for(lt=type, rt=nb; !sh_isspace(*rt) && (lt-type)< sizeof type - 1; *lt++ = *rt++) ; *lt = '�'; //已经将 buf中开始不为empty 部分塞入了 type 中 //同样处理合法与否判断, 出错了直接返回错误结果 if((iscgi = strcasecmp(type, "POST")) && strcasecmp(type, "GET")){ response_501(cfd); close(cfd); return NULL; } // 在buf中 去掉空字符 while(*rt && sh_isspace(*rt)) ++rt; // 这里得到路径信息 *path = '.'; for(lt = path + 1; (lt-path)<sizeof path - 1 && !sh_isspace(*rt); *lt++ = *rt++) ; *lt = '�'; //query url路径就拼接好了 //单独处理 get 获取 ? 后面数据, 不是POST那就是GET if(iscgi != 0){ for(query = path; *query && *query != '?'; ++query) ; if(*query == '?'){ iscgi = 0; *query++ = '�'; } } // type , path 和 query 已经构建好了 if(stat(path, &st) < 0){ while(getfdline(cfd, buf, sizeof buf)>0 && strcmp(" ", buf))// 读取内容直到结束 ; response_404(cfd); close(cfd); return NULL; } // 合法情况, 执行,写入,读取权限 if ((st.st_mode & S_IXUSR) ||(st.st_mode & S_IXGRP) ||(st.st_mode & S_IXOTH)) iscgi = 0; if(iscgi) //没有cgi response_file(cfd, path); else request_cgi(cfd, path, type, query); close(cfd); return NULL; } /* * 处理客户端的http请求. * cfd : 客户端文件描述符 * path : 请求的文件路径 * type : 请求类型,默认是POST,其它是GET * query : 请求发送的过来的数据, url ? 后面那些数据 */ void request_cgi(int cfd, const char* path, const char* type, const char* query) { char buf[_INT_BUF]; int pocgi[2], picgi[2]; pid_t pid; int contlen = -1; //报文长度 char c; if(strcasecmp(type, "POST") == 0){ while(getfdline(cfd, buf, sizeof buf)>0 && strcmp(" ", buf)){ buf[15] = '�'; if(!strcasecmp(buf, "Content-Length:")) contlen = atoi(buf + 16); } if(contlen == -1){ //错误的报文,直接返回错误结果 response_400(cfd); return; } } else{ // 读取报文头,就是过滤, 后面就假定是 GET while(getfdline(cfd, buf, sizeof buf)>0 && strcmp(" ", buf)) ; } //这里处理请求内容, 先处理错误信息 if(pipe(pocgi) < 0){ response_500(cfd); return; } if(pipe(picgi) < 0){ //管道 是 0读取, 1写入 close(pocgi[0]), close(pocgi[1]); response_500(cfd); return; } if((pid = fork())<0){ close(pocgi[0]), close(pocgi[1]); close(picgi[0]), close(picgi[1]); response_500(cfd); return; } // 这里就是多进程处理了, 先处理子进程 if(pid == 0) { // dup2 让 前者共享后者同样的文件表 dup2(pocgi[1], STDOUT_FILENO); //标准输出算作 pocgi管道 的写入端 dup2(picgi[0], STDIN_FILENO); //标准输入做为picgif管道的读取端 close(pocgi[0]); close(pocgi[1]); // 添加环境变量,用于当前会话中 sprintf(buf, "REQUEST_METHOD=%s", type); putenv(buf); // 继续凑环境变量串,放到当前会话种 if(strcasecmp(buf, "POST") == 0) sprintf(buf, "CONTENT_LENGTH=%d", contlen); else sprintf(buf, "QUERY_STRING=%s", query); putenv(buf); // 成功的话调到 新的执行体上 execl(path, path, NULL); // 这行代码原本是不用的, 但是防止 execl执行失败, 子进程没有退出.妙招 exit(EXIT_SUCCESS); } // 父进程, 为所欲为了,先发送个OK write(cfd, "HTTP/1.0 200 OK ", 17); close(pocgi[1]); close(picgi[0]); if(strcasecmp(type, "POST") == 0){ int i; //将数据都写入到 picgi 管道中, 让子进程在 picgi[0]中读取 => STDIN_FILENO for(i=0; i<contlen; ++i){ read(cfd, &c, 1); write(picgi[1], &c, 1); } } //从子进程中 读取数据 发送给客户端, 多线程跨进程阻塞模型 while(read(pocgi[0], &c, 1) > 0) write(cfd, &c, 1); close(pocgi[0]); close(picgi[1]); //等待子进程结束 waitpid(pid, NULL, 0); }
我们看见 上面 函数 解释的很清楚, 对于 response_* 响应部分占了大头的一半.其实本质也就200行左右. 很适合临摹一下.
正文
现在到了正文,说的很水. 再扯一点. 自己学习反人类的库libuv, 就是note.js 底层通信的那套网络库. 也就是看官方的demo
一个个的临摹. 了解的. 也就会用. 后面也就简易的看看源码. 也就懂了. 最经看的深入之后还是觉得,越简单越直白越好.封装太多了,
容易绕晕自己,而且很多功能用不上,遇到bug了又得查看繁琐的万行源码.
总结就是, 学好基础 问题, 走到哪里都容易, 至少能做. 做的好不好, 以后再说.
那我们分析了. 第一个 看下面函数声明
// 返回400 请求解析失败,客户端代码错误 extern inline void response_400(int cfd);
这里使用了C的内联函数, 内联函数声明必须要有inline.否则编译器解析 函数名称会不一致找不见. 再扯一点对于
strcasecmp 其实是 linux上提供的函数 , window上使用需要做额外配置. 说白了就是不跨平台. 下面一种跨平台的实现如下
/* * 这是个不区分大小写的比较函数 * ls : 左边比较字符串 * rs : 右边比较字符串 * : 返回 ls>rs => >0 ; ls = rs => 0 ; ls<rs => <0 */ int str_icmp(const char* ls, const char* rs) { int l, r; if(!ls || !rs) return (int)(ls - rs); do { if((l=*ls++)>='a' && l<='z') l -= 'a' - 'A'; if((r=*rs++)>='a' && r<='z') r -= 'a' - 'A'; } while(l && l==r); return l-r; }
参照编译器源码给的一种实现. 性能方面基本上还可以. 这里再扯一点. 为什么C中常说用指针速度快.
分析如下 普通的 a[6] ,访问过程是 先取a首地址,再取a+6地址后面 取*(a+6)的值.
而如果直接用 ptr = a, ++ => ptr -> a+6 那就省略了一步 a+6的问题. 所以快一点.
再扯一点 a[6]其实就是语法糖, 本质也就是 *(a + 6), 通过这个推广, a[-1] 也合法 等价于 *(a - 1).
后面再简单分析一下 细节
我们总的思路是 服务器httpd 采用多线程接收客户端请求. 再分析报文, 主要是分get请求和post请求.
get请求直接请求, 如果get 后面有? 或post请求 走 cgi 动态处理界面.
说白都很简单, http 是在tcp 基础上添加了 http报文的基础解析内容. 本质是业务逻辑的处理.
这里继续说一说 本文中采用的管道细节
//这里处理请求内容, 先处理错误信息 if(pipe(pocgi) < 0){ response_500(cfd); return; } if(pipe(picgi) < 0){ //管道 是 0读取, 1写入 close(pocgi[0]), close(pocgi[1]); response_500(cfd); return; } if((pid = fork())<0){ close(pocgi[0]), close(pocgi[1]); close(picgi[0]), close(picgi[1]); response_500(cfd); return; }
这里是请求失败会相应释放打开的端口. 理论上在exit之后系统会自动回收打开的端口.但是不及时.
对于上面管道 是 子进程充定向管道为标准输入输出. 父进程向管道中写入给子进程标准输入输出. 这就是传说的cgi.
最后说明一段代码
/* * 主逻辑,启动服务,可以做成守护进程. * 具体的实现逻辑, 启动小型玩乐级别的httpd 服务 */ int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { pthread_attr_t attr; uint16_t port = 0; int sfd = serstart(&port); printf("httpd running on port %u. ", port); // 初始化线程属性 pthread_attr_init(&attr); pthread_attr_setdetachstate(&attr, PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED); for(;;){ pthread_t tid; struct sockaddr_in caddr; socklen_t clen = sizeof caddr; int cfd = accept(sfd, (struct sockaddr*)&caddr, &clen); if(cfd < 0){ CERR("accept sfd = %d is error!", sfd); break; } if(pthread_create(&tid, &attr, request_accept, (void*)cfd) < 0) CERR("pthread_create run is error!"); } // 销毁吧, 一切都结束了 pthread_attr_destroy(&attr); close(sfd); return 0; }
这是主业务, 亮点在于 pthread_attr 这块, 添加了线程分离属性, 自己回收. 不需要内核继续保存线程尸体.
最后记得释放.
到这里基本细节我们都说完了. 对于 serstart 中采用了随机端口, 是为了不合 服务器可能的http服务8080端口冲突, 就来个随机端口.
对于socket 采用0端口,意思就是操作系统随机分配.
测试
下面我们开始测试测试 的 client.c 代码
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <errno.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/socket.h> #include <netinet/in.h> #include <arpa/inet.h> //4.0 控制台打印错误信息, fmt必须是双引号括起来的宏 #define CERR(fmt, ...) fprintf(stderr,"[%s:%s:%d][error %d:%s]" fmt " ", __FILE__, __func__, __LINE__, errno, strerror(errno),##__VA_ARGS__) //4.1 控制台打印错误信息并退出, t同样fmt必须是 ""括起来的字符串常量 #define CERR_EXIT(fmt,...) CERR(fmt,##__VA_ARGS__),exit(EXIT_FAILURE) //4.3 if 的 代码检测 #define IF_CHECK(code) if((code) < 0) CERR_EXIT(#code) //待拼接的字符串 #define _STR_HTTP_1 "GET /index.html HTTP/1.0 User-Agent: Happy is good. Host: 127.0.0.1:" #define _STR_HTTP_3 " Connection: close " // 简单请求一下 int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { char buf[1024]; int sfd; struct sockaddr_in saddr = { AF_INET }; int len, port; // argc 默认为1 第一个参数 就是 执行程序串 if((argc != 2) || (port=atoi(argv[1])) <= 0 ) CERR_EXIT("Usage: %s [port]", argv[0]); // 开始了,就这样了 IF_CHECK(sfd = socket(PF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0)); saddr.sin_port = htons(port); saddr.sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY; IF_CHECK(connect(sfd, (struct sockaddr*)&saddr, sizeof saddr)); //开始发送请求 strcpy(buf, _STR_HTTP_1); strcat(buf, argv[1]); strcat(buf, _STR_HTTP_3); write(sfd, buf, strlen(buf)); //读取所哟内容 while((len = read(sfd, buf, sizeof buf - 1))){ buf[len] = '�'; printf("%s", buf); } putchar(' '); close(sfd); return 0; }
这里就简单向httpd 发送get 请求 index.html界面. 这里再扯一点, 这个httpd 许多细节没有考虑,容错性不是那么健全.
这些都好做,只要理解了实现思路和详细了解HTTP协议就可以写出好的HTTP知识,当然TCP的功底不可或缺,这点也很有挑战.
对于index.html 界面如下
<html> <head> <title> 有意思 </title> </head> <body> <p> 只有野兽不会欺骗 <p> </body> </html>
最后上 Makefile
all:httpd.out client.out
httpd.out:httpd.c
gcc -g -Wall -o $@ $^ -lpthread
client.out:client.c
gcc -g -Wall -o $@ $^
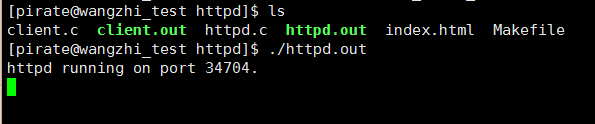
最后执行结果示意图图如下,先启动 httpd服务器
后面开启http测试机, 需要输入端口34704 如下
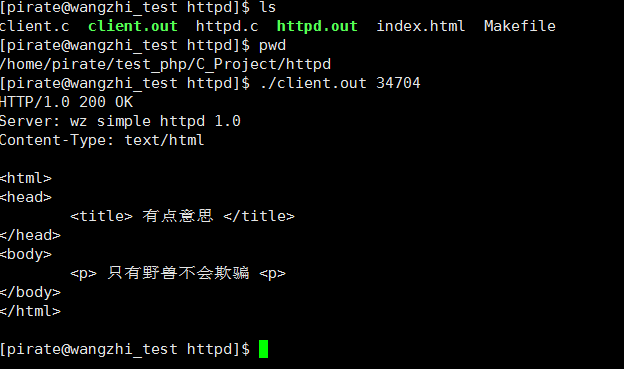
到这里我们至少简单测试都过了.
一切都是那么自然而然. 前提你要个节奏,这个你能坚持. 节奏很重要, 装逼是次要的.下次有机会再分享
开发中需要用到的一些开发模型和细节. 或者分享简单高效的网络库知识. 最后扯一点, 都是从不懂,一点都不懂
坚持临摹开始的.后面就懂了, 只有不懂和痛苦,恶心才会有点意思.哈哈.
后记
错误是难免的, 欢迎交流, 拜~~~
