1首先来回顾C的强制转换
大家都知道,在编译C语言中的强制转换时,编译器不会检查转换是否成功,都会编译正确.
比如:
#include "stdio.h" struct Position { int x; int y; }; int main() { int i; struct Position *p; i=0x123456; p=(struct Position *)i; printf("px=%d,py=%d ",p->x,p->y); }
输出结果如下图所示:
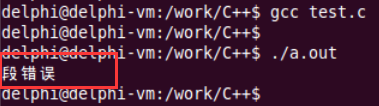
从上图可以看到,只有当运行代码时,才会出现段错误问题.
当C代码上千行时,若出现这种问题,是非常难找的.
2.C++的新型类型转换
所以在C++中,便引入了4种强制类型转换
2.1 static_cast(静态类型转换)
- 用于基本数据类型以及对象之间的转换(char,int,const int等)
- 不能用于基本数据类型指针之间的转换(char *,int *等)
- 用于有继承关系类对象指针之间的转换
- 用于类指针之间的转换
示例-基本数据:
int i = 0x45; char c = 'c'; c = static_cast<char>(i); //char* pc = static_cast<char*>(&i); //此行错误,不能用于基本指针之间转换
示例-基本数据与对象转换:
class Test{ public: explicit Test(int i) //只能显示调用 { cout<<i<<endl; } }; int main() { Test t = static_cast<Test>(3.55); //等价于 : Test t(3); }
示例-有继承关系的类对象指针转换:
class Parent { public: int mm; Parent(int i) { mm=i; cout<<"Parent:"<<i<<endl; } }; class Child : public Parent { public: int mval; Child(int i):Parent(i) { mval=i; cout<<"Child:"<<i<<endl; } }; int main() { Parent *p =new Parent(3); //会调用父类构造函数 Child *c = static_cast <Child *> (p) ; //并不会调用子类构造函数,此时的mval成员为随机值 c->mval=100; cout<<"mval:"<<c->mval<<endl;
cout<<"mm:"<<c->mm<<endl; //此时的c->mm指向的对象就是p->mm
c->mm=100; //修改c->mm 等价于修改p->mm
cout<<"mm:"<<p->mm<<endl;
}
运行打印:
Parent:3 mval:100
mm:3
mm:100
2.2 const_cast(去常类型转换)
- 常用于去除const类对象的只读属性
- 且强制转换的类型必须是指针*或引用&
示例1:
const int x =1; //const:定义一个常量x const int& j =2; //const引用:定义一个只读变量j int& p1= const_cast<int&>(x); //强制转换int & int *p2 = const_cast<int*>(&j); //强制转换int* //int p3 = const_cast<int>(j); //此行错误,不能转换普通数据型 p1=3; *p2=4; printf("x=%d, j=%d ",x,j); printf("p1=%d *p2=%d ",p1,*p2);
输出结果:
x=1 j=4 p1=3 *p2=4
从输出结果,可以看出修改p1,p2,只有j内容变换了,是因为变量j用const引用定义的,所以是个只读变量.
示例2-去除const类对象的只读属性
class Test { public: int mval; Test():mval(10) { } }; int main() { const Test n1; //n1.mval = 100; //error,不能直接修改常量对象的成员 Test *n2 = const_cast<Test *>(&n1); //通过指针*转换 Test &n3 = const_cast<Test &>(n1); //通过引用&转换 n2->mval = 20; cout<<n1.mval<<endl; //打印20 n3.mval = 30; cout<<n1.mval<<endl; //打印30 }
2.3 dynamic_cast(动态类型转换)
- 用于有继承关系的类指针(引用)间的转换
- 用于有交叉关系的类指针(引用)间的转换
- 具有类型检查的功能,编译时会去检查使用的方法是否正确,转换是否成功只有在程序运行时才能知道
- 类中必须有虚函数的支持
- 不能用于基本数据类型指针之间的转换(char *,int *等)
-当转换为指针时:
- 转换成功 : 得到目标类型的指针
- 转换失败 : 得到一个空指针
-当转换为引用时:
- 转换成功 : 得到目标类型的引用
- 转换失败 : 得到一个异常操作信息
示例-通过子类指针去指向父类:
#include <iostream> using namespace std; class Base { public: Base() { cout << "Base::Base()" << endl; } virtual ~Base() { cout << "Base::~Base()" << endl; } }; class Derived : public Base { }; int main() { Base* p = new Base; //初始化父类指针 Derived* pd = dynamic_cast<Derived*>(p); //由于父类指针指向的是父类,没有子类虚函数表,所以转换失败 cout << "pd = " << pd << endl; //转换失败,打印 0
delete p; p = new Derived; pd = dynamic_cast<Derived*>(p); //由于父类指针指向的是子类,所以有子类虚函数表 cout <<"pd = " << pd <<endl; //转换成功,打印地址值 delete p; return 0; }
示例-通过多重继承下的类指针转换:
class BaseA { public: virtual void funcA() { cout<<"BaseA: funcA()"<<endl; } };
class BaseB { public: virtual void funcB() { cout<<"BaseB: funcB()"<<endl; } };
class Derived : public BaseA,public BaseB { };
int main() { Derived d; BaseA *pa=&d; pa->funcA(); //打印 BaseA: funcA() /*通过强制转换执行*/ BaseB *pb=(BaseB *)pa; pb->funcB(); //还是打印 BaseA: funcA(), 因为pb还是指向pa,执行的还是pa的虚函数表 /*通过dynamic_cast执行*/ pb = dynamic_cast<BaseB *>(pa); pb->funcB(); //打印 BaseB: funcB() //编译器会去检测pa所在的地址,发现有多个虚函数表,然后根据 <BaseB *>来修正指针pb return 0; }
2.4 reinterpret_ cast(解读类型转换)
- 用于所有指针的强制转换
(解读是指:对要转换的数据进行重新的解读)
例如:
int i = 0; char j='c'; int *p1=reinterpret_cast<int *>(&i); char *p2=reinterpret_cast<char *>(&j); //int p3=reinterpret_cast<int >i; //此行错误,不能转换普通数据型