A.POJ_1321
考查DFS的一个循环中递归调用


1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstring> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 char a[10][10]; //记录棋盘位置 6 int book[10]; //记录一列是否已经放过棋子 7 int n, k; // k 为 需要放入的棋子数 8 int total, m; //total 是放棋子的方案数 ,m是已放入棋盘的棋子数目 9 10 void DFS(int cur) 11 { 12 if (k == m) { 13 total++; 14 return; 15 } 16 if (cur >= n) //边界 17 return; 18 for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) 19 if (book[j] == 0 && a[cur][j] == '#'){ //判断条件(为#才能在该处下棋) 20 book[j] = 1; //标记 21 m++; 22 DFS(cur + 1); //到下一行 23 book[j] = 0; //改回来方便下一行的判断 24 m--; 25 } 26 DFS(cur + 1); //到下一行 27 } 28 29 int main() 30 { 31 int i; 32 while ((cin >> n >> k) && n != -1 && k != -1){ 33 total = 0; 34 m = 0; 35 for (i = 0; i < n; i++) 36 cin >> a[i]; 37 // 以上内容都是输入 38 memset(book, 0, sizeof(book)); // 对于每一组处理完了数据进行数组的清空 39 DFS(0); // 进行搜索 40 cout << total << endl; 41 } 42 return 0; 43 }
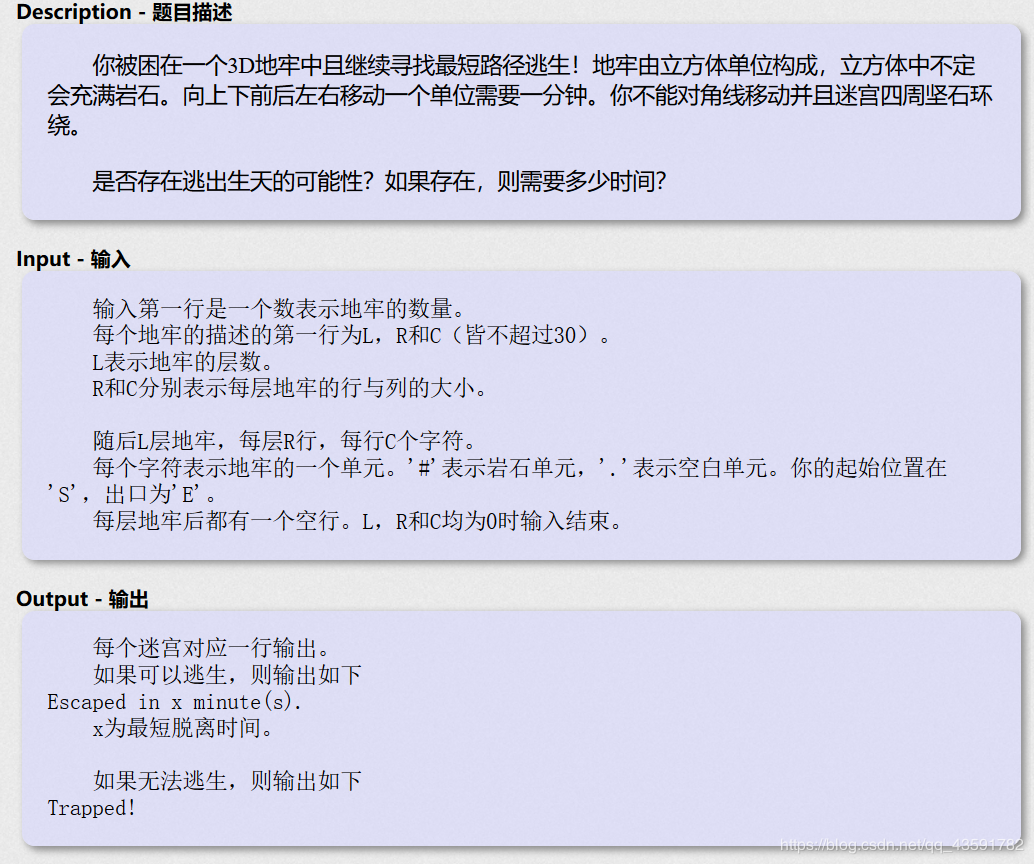
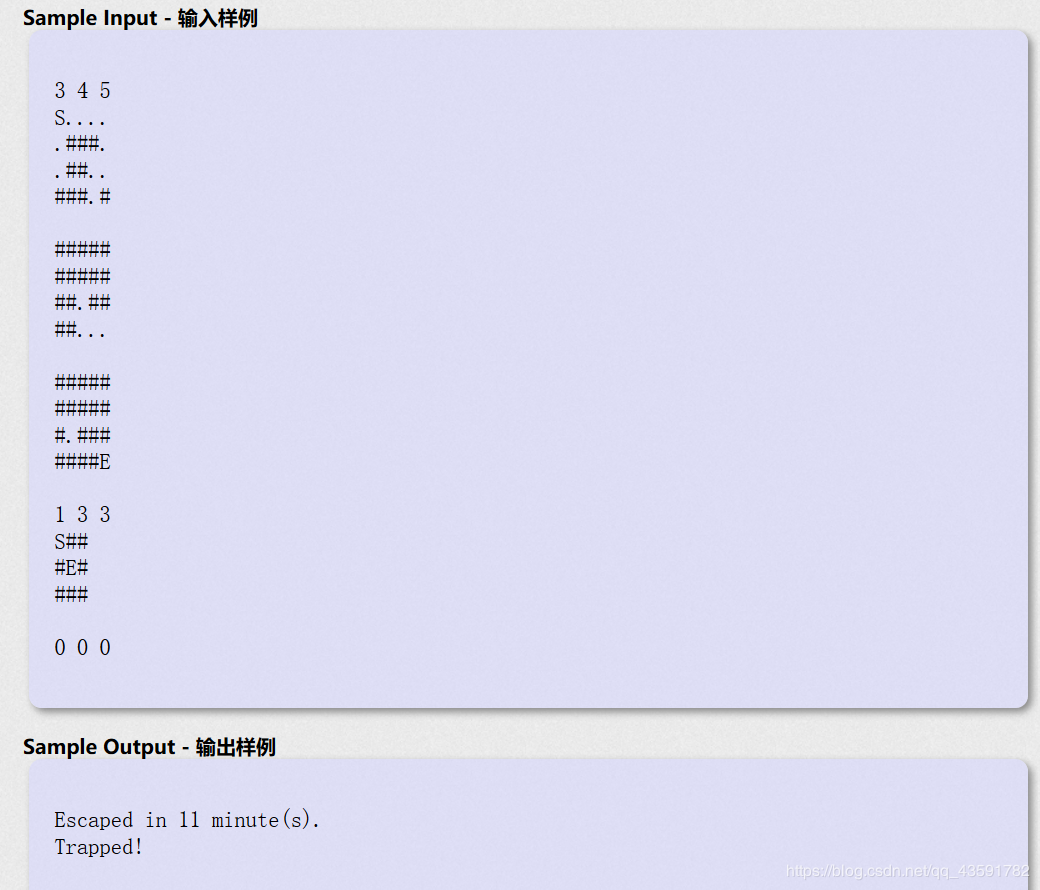
B.POJ_2251
PS:六个方向的BFS题
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <queue> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 //bfs对于每一层的搜索都是很详细的可以扫完所有 7 using namespace std; 8 9 char map[35][35][35]; // 用于建图 10 int vis[35][35][35]; // 查询数组 判断该点是否被访问了 11 int k, n, m, sx, sy, sz, ex, ey, ez; //k , n, m,题干要求量; sx, sy, sz,开始坐标值;ex, ey, ez终点坐标值 12 int to[6][3] = { {1,0,0},{-1,0,0},{0,1,0},{0,-1,0},{0,0,1},{0,0,-1} }; // 方向向量坐标 13 // 前后左右上下不存在顺序限制 14 15 struct node{ // 定义一个结构体 16 int x, y, z, step; // x,y,z 表示 node 声明出来的点的 三个坐标的值 和 该点下的是第几步 17 }; 18 19 int check(int x, int y, int z){ 20 // 若 1.越界 2.是障碍物 3.查询过 该函数的返回值是 1 否则 则是 0; 21 if (x < 0 || y < 0 || z < 0 || x >= k || y >= n || z >= m) 22 return 1; 23 else if (map[x][y][z] == '#') 24 return 1; 25 else if (vis[x][y][z]) 26 return 1; 27 return 0; 28 } 29 30 int bfs(){ 31 int i; 32 node a, next; 33 queue<node> Q; 34 a.x = sx, a.y = sy, a.z = sz; // 从起点开始扫 35 a.step = 0; 36 vis[sx][sy][sz] = 1; 37 Q.push(a); // 把元素压入队列中 38 while (!Q.empty()){ // 如果队列q为空就证明没找到可以通过的路径 39 a = Q.front(); // 取出队列第一个元素 40 Q.pop(); // 删去靠前元素 41 if (a.x == ex && a.y == ey && a.z == ez) 42 return a.step; // 如果扫到的该点与目标点相同则返回该点对应的步数 43 for (i = 0; i < 6; i++){ 44 cout << "a"; 45 cout << a.x << a.y << a.z << endl; 46 next = a; 47 next.x = a.x + to[i][0]; 48 next.y = a.y + to[i][1]; 49 next.z = a.z + to[i][2]; 50 // 通过方向向量值改变 51 cout << "next"; 52 cout << next.x << next.y << next.z << endl; 53 if (check(next.x, next.y, next.z)) 54 continue; // 如果下一步的点不和规范就不执行下面步骤 55 cout << "标记next"; 56 cout << next.x << next.y << next.z << endl; 57 vis[next.x][next.y][next.z] = 1; 58 next.step = a.step + 1; 59 Q.push(next); 60 } 61 } 62 return 0; 63 } 64 65 int main(){ 66 int i, j, r; 67 while (cin >> k >> n >> m, n + m + k){ // k为牢房个数n,m代表n行m列 68 for (i = 0; i < k; i++){ 69 for (j = 0; j < n; j++){ 70 cin >> map[i][j]; // 建图 71 for (r = 0; r < m; r++){ // 扫一遍图 找出起点与终点 72 if (map[i][j][r] == 'S'){ 73 sx = i, sy = j, sz = r; 74 } 75 else if (map[i][j][r] == 'E'){ 76 ex = i, ey = j, ez = r; 77 } 78 } 79 } 80 } 81 memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis)); 82 int ans; 83 ans = bfs(); 84 if (ans) 85 cout << "Escaped in " << ans << " minute(s)." << endl; 86 else 87 cout << "Trapped!" << endl; 88 } 89 return 0; 90 }