题目描述
给定两个非空二叉树 s 和 t,检验 s 中是否包含和 t 具有相同结构和节点值的子树。s 的一个子树包括 s 的一个节点和这个节点的所有子孙。s 也可以看做它自身的一棵子树。
示例 1:
给定的树 s:
3
/
4 5
/
1 2
给定的树 t:
4
/
1 2
返回 true,因为 t 与 s 的一个子树拥有相同的结构和节点值。
示例 2:
给定的树 s:
3
/
4 5
/
1 2
/
0
给定的树 t:
4
/
1 2
返回 false。
测试用例
// 树中结点含有分叉,树B是树A的子结构
// 8 8
// / /
// 8 7 9 2
// /
// 9 2
// /
// 4 7
void Test1()
{
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeA1 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(8);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeA2 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(8);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeA3 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(7);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeA4 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(9);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeA5 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(2);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeA6 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(4);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeA7 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(7);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNodeA1, pNodeA2, pNodeA3);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNodeA2, pNodeA4, pNodeA5);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNodeA5, pNodeA6, pNodeA7);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeB1 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(8);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeB2 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(9);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeB3 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(2);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNodeB1, pNodeB2, pNodeB3);
Test("Test1", pNodeA1, pNodeB1, true);
DestroyTree(pNodeA1);
DestroyTree(pNodeB1);
}
// 树中结点含有分叉,树B不是树A的子结构
// 8 8
// / /
// 8 7 9 2
// /
// 9 3
// /
// 4 7
void Test2()
{
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeA1 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(8);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeA2 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(8);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeA3 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(7);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeA4 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(9);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeA5 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(3);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeA6 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(4);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeA7 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(7);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNodeA1, pNodeA2, pNodeA3);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNodeA2, pNodeA4, pNodeA5);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNodeA5, pNodeA6, pNodeA7);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeB1 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(8);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeB2 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(9);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeB3 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(2);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNodeB1, pNodeB2, pNodeB3);
Test("Test2", pNodeA1, pNodeB1, false);
DestroyTree(pNodeA1);
DestroyTree(pNodeB1);
}
// 树中结点只有左子结点,树B是树A的子结构
// 8 8
// / /
// 8 9
// / /
// 9 2
// /
// 2
// /
// 5
void Test3()
{
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeA1 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(8);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeA2 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(8);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeA3 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(9);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeA4 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(2);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeA5 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(5);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNodeA1, pNodeA2, nullptr);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNodeA2, pNodeA3, nullptr);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNodeA3, pNodeA4, nullptr);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNodeA4, pNodeA5, nullptr);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeB1 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(8);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeB2 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(9);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeB3 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(2);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNodeB1, pNodeB2, nullptr);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNodeB2, pNodeB3, nullptr);
Test("Test3", pNodeA1, pNodeB1, true);
DestroyTree(pNodeA1);
DestroyTree(pNodeB1);
}
// 树中结点只有左子结点,树B不是树A的子结构
// 8 8
// / /
// 8 9
// / /
// 9 3
// /
// 2
// /
// 5
void Test4()
{
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeA1 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(8);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeA2 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(8);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeA3 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(9);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeA4 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(2);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeA5 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(5);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNodeA1, pNodeA2, nullptr);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNodeA2, pNodeA3, nullptr);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNodeA3, pNodeA4, nullptr);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNodeA4, pNodeA5, nullptr);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeB1 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(8);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeB2 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(9);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeB3 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(3);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNodeB1, pNodeB2, nullptr);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNodeB2, pNodeB3, nullptr);
Test("Test4", pNodeA1, pNodeB1, false);
DestroyTree(pNodeA1);
DestroyTree(pNodeB1);
}
// 树中结点只有右子结点,树B是树A的子结构
// 8 8
//
// 8 9
//
// 9 2
//
// 2
//
// 5
void Test5()
{
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeA1 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(8);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeA2 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(8);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeA3 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(9);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeA4 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(2);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeA5 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(5);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNodeA1, nullptr, pNodeA2);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNodeA2, nullptr, pNodeA3);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNodeA3, nullptr, pNodeA4);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNodeA4, nullptr, pNodeA5);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeB1 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(8);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeB2 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(9);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeB3 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(2);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNodeB1, nullptr, pNodeB2);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNodeB2, nullptr, pNodeB3);
Test("Test5", pNodeA1, pNodeB1, true);
DestroyTree(pNodeA1);
DestroyTree(pNodeB1);
}
// 树A中结点只有右子结点,树B不是树A的子结构
// 8 8
//
// 8 9
// /
// 9 3 2
//
// 2
//
// 5
void Test6()
{
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeA1 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(8);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeA2 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(8);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeA3 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(9);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeA4 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(2);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeA5 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(5);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNodeA1, nullptr, pNodeA2);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNodeA2, nullptr, pNodeA3);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNodeA3, nullptr, pNodeA4);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNodeA4, nullptr, pNodeA5);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeB1 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(8);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeB2 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(9);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeB3 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(3);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeB4 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(2);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNodeB1, nullptr, pNodeB2);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNodeB2, pNodeB3, pNodeB4);
Test("Test6", pNodeA1, pNodeB1, false);
DestroyTree(pNodeA1);
DestroyTree(pNodeB1);
}
// 树A为空树
void Test7()
{
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeB1 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(8);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeB2 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(9);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeB3 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(3);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeB4 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(2);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNodeB1, nullptr, pNodeB2);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNodeB2, pNodeB3, pNodeB4);
Test("Test7", nullptr, pNodeB1, false);
DestroyTree(pNodeB1);
}
// 树B为空树
void Test8()
{
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeA1 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(8);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeA2 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(9);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeA3 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(3);
BinaryTreeNode* pNodeA4 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(2);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNodeA1, nullptr, pNodeA2);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNodeA2, pNodeA3, pNodeA4);
Test("Test8", pNodeA1, nullptr, false);
DestroyTree(pNodeA1);
}
// 树A和树B都为空
void Test9()
{
Test("Test9", nullptr, nullptr, false);
}考点
1.二叉树遍历
2.递归
3.鲁棒性:每次访问指针要检查是否为nullptr,防御性编程
4.用几个测试用例进行单元测试。
思路
辅助测试代码
BinaryTreeNode* CreateBinaryTreeNode(double dbValue)
{
BinaryTreeNode* pNode = new BinaryTreeNode();
pNode->m_dbValue = dbValue;
pNode->m_pLeft = nullptr;
pNode->m_pRight = nullptr;
return pNode;
}
void ConnectTreeNodes(BinaryTreeNode* pParent, BinaryTreeNode* pLeft, BinaryTreeNode* pRight)
{
if(pParent != nullptr)
{
pParent->m_pLeft = pLeft;
pParent->m_pRight = pRight;
}
}
void DestroyTree(BinaryTreeNode* pRoot)
{
if(pRoot != nullptr)
{
BinaryTreeNode* pLeft = pRoot->m_pLeft;
BinaryTreeNode* pRight = pRoot->m_pRight;
delete pRoot;
pRoot = nullptr;
DestroyTree(pLeft);
DestroyTree(pRight);
}
}第一遍
//对于float和double型的小数,无法直接比较大小,判断这两个数相等的做法是:两数之差的绝对值在一个很小的范围内,0.0000001
bool Equal(double num1, double num2)
{
return ((num1 - num2) > -0.000000001 && (num1 - num2) < 0.00000001) ? true : false;
}
//递归检查根节点下的子树是否结构一样
bool DoesTree1HaveTree2(BinaryTreeNode* pRoot1, BinaryTreeNode* pRoot2)
{
//技巧2:递归结束条件:大树为空,说明已经遍历完了,说明存在;子树为空,就返回假
//1.如果B子树为空,返回真,说明已经遍历完子树了
if (!pRoot2)
return true;
//2.如果A子树为空,返回假,说明不匹配
if (!pRoot1)
return false;
//3.如果两个节点不相同,返回假,说明不匹配
if (!Equal(pRoot1->m_dbValue, pRoot2->m_dbValue))
return false;
//4.返回递归调用,各自的左节点和各自的右节点递归
return DoesTree1HaveTree2(pRoot1->m_pLeft, pRoot2->m_pLeft) && DoesTree1HaveTree2(pRoot1->m_pRight, pRoot2->m_pRight);
}
//是否为子树
bool HasSubtree(BinaryTreeNode* pRoot1, BinaryTreeNode* pRoot2)
{
//1.如果有空树,返回假
if (!pRoot1 || !pRoot2)
return false;
//2.默认返回结果为假
bool result = false;
//3.如果两个根节点相同就判断第二步
if (Equal( pRoot1->m_dbValue,pRoot2->m_dbValue))//技巧1:小数用定义的函数判断,不用==判断相等。
result = DoesTree1HaveTree2(pRoot1, pRoot2);
if (!result)
//如果不相同,就往左遍历,直到找到第一个相同的根节点
result = HasSubtree(pRoot1->m_pLeft, pRoot2);
if (!result)//如果不相同,就往右遍历,直到找到第一个相同的根节点
result = HasSubtree(pRoot1->m_pRight, pRoot2);
//4.返回结果
return result;
}
第二遍(newcoder)
/*
struct TreeNode {
int val;
struct TreeNode *left;
struct TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) :
val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {
}
};*/
class Solution {
public:
bool HasSubtree(TreeNode* pRoot1, TreeNode* pRoot2)
{
//1.如果有空树,直接返回
if(!pRoot1||!pRoot2)
return false;
//2.bool 记录结果
bool result=false;
//3.如果根节点不相等,result=false
if(!numCompare(pRoot1,pRoot2))
result=false;
else//3.1如果相等,就进行第二步
result= HasSubtree2( pRoot1, pRoot2);
//4.如果result=false,遍历左子树的根节点是否与B树根节点相等
if(!result)
result=HasSubtree(pRoot1->left,pRoot2);
//5.如果result=false,遍历右子树的根节点是否与B树根节点相等
if(!result)
result=HasSubtree(pRoot1->right,pRoot2);
//6.返回result
return result;
}
//递归
bool HasSubtree2(TreeNode* pRoot1, TreeNode* pRoot2)
{
//1.递归结束条件:B树为空,返回真
if(!pRoot2)
return true;
//2.递归结束条件2:A树为空,返回假
if(!pRoot1)
return false;
//3.如果这两个节点相等,分别继续判断左子树和右子树
if(numCompare(pRoot1,pRoot2))
return HasSubtree2(pRoot1->left,pRoot2->left)&&HasSubtree2(pRoot1->right,pRoot2->right);
else
//如果不相等 返回假
return false;
}
bool numCompare(TreeNode* pRoot1, TreeNode* pRoot2)
{
return (pRoot1->val-pRoot2->val)<0.0000001&&(pRoot1->val-pRoot2->val)>-0.0000001?true:false;
}
};第三遍(leetcode572)
错误解答:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isSubtree(TreeNode* s, TreeNode* t) {
//1.如果有一个为空,返回假
if(!s||!t)
return false;
//2.记录结果
bool result=false;
//3.如果根节点相同
if(compare(s,t))
//进入第二步
result=HasSubtree(s,t);
//4.如果根节点不同,result=false,遍历左节点
if(!result)
result=isSubtree(s->left,t);
//5.如果S的左树都没有相同的根节点,遍历右树
if(!result)
result=isSubtree(s->right,t);
//6.返回result
return result;
}
//第二步,递归函数,
bool HasSubtree(TreeNode* s, TreeNode* t)
{
//1.如果子树遍历完,返回真
if(!t)
return true;
//2.如果大树遍历完,返回假
if(!s)
return false;
//3.比较根节点大小
if(compare(s,t))
//根节点相同,分别遍历左右子树,返回fun(left)&&fun(right)的结果
return HasSubtree(s->left,t->left)&&HasSubtree(s->right,t->right);
else
//否则返回假
return false;
}
//比较小数大小
bool compare(TreeNode* s,TreeNode* t)
{
return (s->val-t->val)<0.0000001&&(s->val-t->val)>-0.0000001?true:false;
}
};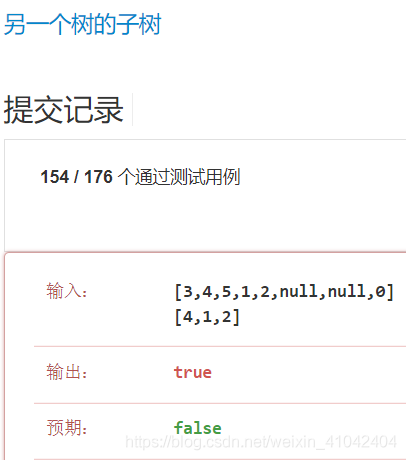
//[3, 4, 5, 1, 2, null, null, 0]
//[4, 1, 2]
// 3
// /
// 4 5
// /
// 1 2
// /
// 0[4,1,2]少了一个左孩子0 ,所以不是子树
Q:
为什么输入是
[1,2,3]
[1,2]
预期结果是:false呢?A:
因为【1,2】不是【1,2,3】的子树啊,【1,2,3】的子树是它自身和【2】,【3】
正解:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isSameTree(TreeNode*s, TreeNode* t){
if (!s) return !t;
if (!t) return false;
if (s->val != t->val) return false;
return isSameTree(s->left, t->left) & isSameTree(s->right, t->right);
}
bool isSubtree(TreeNode* s, TreeNode* t) {
if (!s) return !t;
if (s->val == t->val && isSameTree(s, t))
return true;
return isSubtree(s->left, t) | isSubtree(s->right, t);
}
};最优解
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isSameTree(TreeNode* s, TreeNode* t,bool check)
{
//1.都为空,返回真
if(!s&&!t)
return true;
//2.只有一个为空,返回假
if(!s || !t)
return false;
//3.如果第一步相同,第二步不同,返回假
if(check&&s->val!=t->val)
return false;
bool ret=false;
//4.如果根的值相同,&&分别递归遍历左右子树
if(s->val==t->val)
ret=isSameTree(s->left,t->left,true)&&isSameTree(s->right,t->right,true);
//5.ret=ret或左子树或右子树,||
ret=ret||isSameTree(s->left,t,false)||isSameTree(s->right,t,false);
//6.返回ret
return ret;
}
bool isSubtree(TreeNode* s, TreeNode* t ) {
return isSameTree(s,t,false);
}
};这道题还可以用序列化二叉树,然后用KMP方法做,树M,子树N,M>=N,时间复杂度O(M)。
后面再贴KMP的做法。