字符串比较大小

1 //字符串比较大小 2 #include <stdio.h> 3 #include <string.h> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 int main() 7 { 8 char a[100],b[100],c[100],max[100]; 9 gets(a); 10 gets(b); 11 gets(c); 12 strcpy(max,a);//假设a最大 13 if(strcmp(b,max)>0) strcpy(max,b); 14 if(strcmp(c,max)>0) strcpy(max,c); 15 strcat(a,max); 16 puts(max); 17 return 0; 18 } 19 20 //strncpy(str1,str2,n):字符串数组条件拷贝函数。将一字符串的一部分拷贝到另一个字符串中。 21 //3个参数:str1是目录字符串;str2是源字符串;n是一个整数,代表要从源字符串拷贝到目标字符串中的字符数。 22 //strcpy(str1,str2):字符串数组拷贝函数。将str2复制到str1中 23 //2个参数:str1是目录字符串,str2是源字符串 24 //strcmp(str1,str2):字符串比较函数。对两个字符串字符的ASCII码进行比较,然后返回比较结果 25 //两个参数:str1和str2可以是字符串常量或者字符串变量,返回值为整形。返回结果如下规定:①str1小于str2,返回负值或者-1(VC返回-1);②str1等于str2,返回0;③str1大于str2,返回正值或者1(VC返回1); 26 //strcat(str1,str2):字符串数组拼接函数。将str2拼接到str1后 27 //2个参数:str1是目录字符串;str2是源字符串;注意:str1拼接后空间注意不要溢出
字符串反转的三种常见方法
1. 使用cstring中的strrev函数:strrev(s)
2. 使用algorithm中的reverse函数: reverse(s.begin(),s.end())
3. 自己编写Reverse函数
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 #include <cstring> //strrev头文件 4 #include <algorithm> //reverse函数头文件 5 using namespace std; 6 7 void Reverse(char *s) 8 { 9 for(int i=0,j=strlen(s)-1;i<j;i++,j--){ 10 char c=s[i]; 11 s[i]=s[j]; 12 s[j]=c; 13 } 14 } 15 16 int main() 17 { 18 char s[100]; 19 cin>>s; 20 strrev(s); //字符数组的字符串反转 21 cout<<s<<endl; //此时输出已反转的s 22 string s2=s; 23 reverse(s2.begin(),s2.end()); //string类的字符串反转 24 cout<<s2<<endl; 25 Reverse(s); //自己编写 26 cout<<s<<endl; 27 return 0; 28 }
例:

字符串大小写转换
1. string类
1.1利用函数:转化成小写:transform(str.begin(),str.end(),str.begin(),::tolower);转化成大写:transform(str.begin(),str.end(),str.begin(),::toupper);
1.2自己编写函数
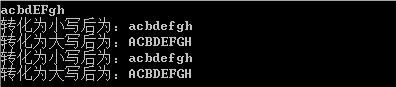
1 //字符串大小写转换 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 void mytolower(string& s){ 7 int len=s.size(); 8 for(int i=0;i<len;i++){ 9 if(s[i]>='A'&&s[i]<='Z'){ 10 s[i]+=32;//+32转换为小写 11 //s[i]=s[i]-'A'+'a'; 12 } 13 } 14 } 15 void mytoupper(string& s){ 16 int len=s.size(); 17 for(int i=0;i<len;i++){ 18 if(s[i]>='a'&&s[i]<='z'){ 19 s[i]-=32;//+32转换为小写 20 //s[i]=s[i]-'a'+'A'; 21 } 22 } 23 } 24 25 26 int main() 27 { 28 string str; 29 cin>>str; 30 transform(str.begin(),str.end(),str.begin(),::tolower); 31 cout<<"转化为小写后为:"<<str<<endl; 32 transform(str.begin(),str.end(),str.begin(),::toupper); 33 cout<<"转化为大写后为:"<<str<<endl; 34 mytolower(str); 35 cout<<"转化为小写后为:"<<str<<endl; 36 mytoupper(str); 37 cout<<"转化为大写后为:"<<str<<endl; 38 return 0; 39 }
例:
2. char类
2.1利用tolower(char c)和toupper(char c)两个方法
2.2自己编写函数
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <algorithm> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <stdio.h> 5 using namespace std; 6 void mytolower(char *s){ 7 int len=strlen(s); 8 for(int i=0;i<len;i++){ 9 if(s[i]>='A'&&s[i]<='Z'){ 10 s[i]=tolower(s[i]); 11 //s[i]+=32;//+32转换为小写 12 //s[i]=s[i]-'A'+'a'; 13 } 14 } 15 } 16 void mytoupper(char *s){ 17 int len=strlen(s); 18 for(int i=0;i<len;i++){ 19 if(s[i]>='a'&&s[i]<='z'){ 20 s[i]=toupper(s[i]); 21 //s[i]-=32;//+32转换为小写 22 //s[i]=s[i]-'a'+'A'; 23 } 24 } 25 } 26 27 int main() 28 { 29 char s[100]; 30 gets(s); 31 mytolower(s); 32 cout<<"转化为小写后为:"<<s<<endl; 33 mytoupper(s); 34 cout<<"转化为大写后为:"<<s<<endl; 35 return 0; 36 }
例:
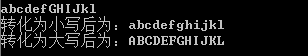
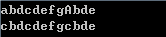
字符串中a与A转化为c输出
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string.h> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 int main() 7 { 8 char s[100]; 9 cin>>s; 10 for(int i=0;i<strlen(s);i++) 11 { 12 if(s[i]=='a'||s[i]=='A') s[i]='c'; 13 } 14 cout<<s<<endl; 15 return 0; 16 }
例:
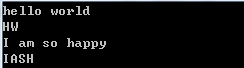
给出一个字符串,不同单词由空格隔开,取出首字母大写并输出。例输入“hello world”,输出为“HW”
1 //给出一个字符串,不同单词由空格隔开,取出首字母大写并输出。 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <string.h> 4 #include <stdio.h> 5 char ss[100]; 6 using namespace std; 7 int main() 8 { 9 int n; 10 scanf("%d",&n); 11 while(n--) 12 { 13 gets(ss); 14 printf("%c",toupper(ss[0])); //默认第一个字母就是首字母 15 for (int i=0;i<(int)strlen(ss);i++) 16 { 17 if (ss[i]==' ') 18 { 19 while(ss[i]==' ') i++; //滤去所有空格 20 printf("%c",toupper(ss[i])); 21 } 22 } 23 printf(" "); 24 } 25 return 0; 26 }
例:
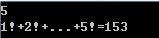
阶乘
1 #include <iostream> 2 3 using namespace std; 4 5 int main() 6 { 7 int n,tem=1,sum=1; 8 cin>>n; 9 for(int i=2;i<=n;i++) 10 { 11 tem*=i; 12 sum+=tem; 13 } 14 cout<<"1!+2!+...+"<<n<<"!="<<sum<<endl; 15 return 0; 16 }
例:
数列求和

1 //数列求和 2 #include <iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 double fun(int n) 6 { 7 if(n==1) return 0.5; 8 return n/1.0/(n+1)+fun(n-1); //此处的/1.0不可省去,因为存在不可整除。 9 } 10 11 int main() 12 { 13 int n; 14 cout<<"n:"<<endl; 15 cin>>n; 16 cout<<"f(n)="<<fun(n)<<endl; 17 return 0; 18 }

1 //数列求和,加了判定n=0时,输出error。 2 #include <stdio.h> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 double sum(int n) 6 { 7 int i=0; 8 double s=0; 9 for(i=0;i<=n;i++) 10 { 11 s+=i/1.0/(i+1); 12 } 13 return s; 14 } 15 16 int main() 17 { 18 int n; 19 printf("n: "); 20 do 21 { 22 scanf("%d",&n); 23 if(n) break; 24 else printf("error"); 25 }while(1); 26 printf("sum=%f ",sum(n)); 27 return 0; 28 }
闰年
1 #include <iostream> 2 3 using namespace std; 4 void year(int m,int n) 5 { 6 for(int i=m;i<=n;i++) 7 { 8 if(i%4==0&&i%100!=0||i%400==0) cout<<i<<"是闰年"<< endl; 9 } 10 } 11 int main() 12 { 13 int m,n; 14 cin>>m>>n; 15 year(m,n); 16 /* 17 if(year%4==0&&year%100!=0||year%400==0) cout<<year<<"是闰年"<< endl; 18 else cout<<year<<"不是闰年"<<endl; 19 */ 20 return 0; 21 }
给出年月日,求出是这年的第几天
1 //给出日期计算该日是该年的第几天 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <stdio.h> 4 using namespace std; 5 struct 6 { 7 int year; 8 int month; 9 int day; 10 }date; 11 int IsRun(int year) 12 { 13 if(year%4==0&&year%100!=0||year%400==0) return 1; 14 else return 0; 15 } 16 int main() 17 { 18 int i,sum=0; 19 int months[13]={0,31,0,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; 20 scanf("%d%d%d",&date.year,&date.month,&date.day); 21 if(date.month<=1&&date.month>0) 22 { 23 sum+=date.day; 24 cout<<"是一年中的第"<<sum<<"天"<<endl; 25 } 26 else if(!IsRun(date.year)) 27 { 28 months[2]=28; 29 for(i=1;i<=date.month-1;i++) 30 { 31 sum=sum+months[i]; 32 } 33 sum+=date.day; 34 cout<<"是一年中的第"<<sum<<"天"<<endl; 35 } 36 else 37 { 38 months[2]=29; 39 for(i=1;i<=date.month-1;i++) 40 { 41 sum+=months[i]; 42 } 43 sum+=date.day; 44 cout<<"是一年中的第"<<sum<<"天"<<endl; 45 } 46 return 0; 47 }
