字典,数组 ,集排序
一、字典类
存储以下数据
name:张三; sex:男;age:18
film:风暴; playcount:10000次;price:60元
字典类用于保存具有映射关系(key-value对)的数据
对于“name:张三”来讲,key就是“name”,key对应的value是“张 三”
一个key-value对认为是一个元素(实体),字典是存储key-value对 的容器。
//字典里一个key只有一个vlaue, 但是一个value可以有好几个key
NSDictionary * dic1 = [[NSDictionary alloc] initWithObjectsAndKeys:@"zhangsan", @"name", @"boy", @"sex", @"toyke", @"address", nil];//初始化创建字典
NSLog(@"%@", dic1);
NSArray * value = [[NSArray alloc] initWithObjects:@"张三", @"李四", @"王五", @"赵六", nil];
NSArray * key = [[NSArray alloc] initWithObjects:@"name3", @"name4", @"name5", @"name6", nil];
NSDictionary * nk = [[NSDictionary alloc] initWithObjects:value forKeys:key];//初始化+数组创建字典
NSLog(@"%@", nk);
特点:
与数组不同,数组靠下标存取数据,数组的下标是唯一的。
字典靠key存取元素。key不能重复,value必须是对象。
键值对在字典中是无序存储的。
NSDictionary 不可变字典
字典一旦创建,键值就不可更改,不可添加,不可删除 仅能读取key或者value
创建字典 //
NSDictionary *dict = [NSDictionary dictionaryWithObjectsAndKeys:@"lisi",@"name",@"man",@"sex",@18,@"age", nil];
NSDictionary *dict = [[NSDictionary alloc] initWithObjectsAndKeys:@"lisi",@"name",@"man",@"sex",@18,@"age", nil];
NSDictionary的子类
NSLog(@"%@ %@",dict,[dict objectForKey:@"sex"]);
可变字典 NSMutableDictionary 是NSDictionary的子类 可以对管理的键值进行增,删,改
/ NSDictionary *dict = [NSDictionary dictionaryWithObjectsAndKeys:@"lisi",@"name",@"man",@"sex",@18,@"age", nil]; NSDictionary *dict = [[NSDictionary alloc] initWithObjectsAndKeys:@"lisi",@"name",@"man",@"sex",@18,@"age", nil];//初始化一个不可变字典 NSLog(@"%@ %@",dict,[dict objectForKey:@"sex"]); NSMutableDictionary *mdict = [NSMutableDictionary dictionaryWithCapacity:5];//初始化一个可变字典 [mdict addEntriesFromDictionary:dict];//把一个字典加到一个可变字典中 [mdict setObject:@"zhangsan" forKey:@"name"];//name变成zhangsan [mdict setObject:@"study" forKey:@"hobby"];//增加一个key-value值 [mdict removeObjectForKey:@"name"];//移除姓名 [mdict removeAllObjects];//移除所有键-值对 NSLog(@"%@ ",mdict);
遍历字典
NSArray *allkeys = [mdict allKeys]; for (int i = 0; i< [allkeys count]; i++) { NSString *key = [allkeys objectAtIndex:i]; id value = [mdict objectForKey:key]; NSLog(@"%@ :%@",key,value); }
二、集合类
数学中有集合的概念如整数集,自然数集,iOS中也有集合类与数学中得集合对应
特点:与数学中的集合一样,存储的元素互不相同 存储的元素是无序的
存储元素必须是对象类型 iOS中用set表示集合,分NSSet和NSMutableSet
使用复数,用容器来保存,90%情况下用数组,一般用NSString
NSSet *ssee = [NSSet setWithObjects:@"zhangsan",@"lisi",@"wangwu",@"zhaoliu",@"xiaoer", nil];//初始化集合 [ssee count];//集合元素个数 NSLog(@"%@",[ssee anyObject]);//随机取一个元素 NSLog(@"%d",[ssee containsObject:@"zhangsan"]);//判断是否包含某个元素 NSLog(@"%@",ssee);
NSMutableSet可变集合 是 NSSet的子类
NSCountedSet是NSMutableSet的子类
能记录元素的重复次数
NSCountedSet *ssee1 = [NSCountedSet setWithObjects:@"zhangsan",@"lisi",@"wangwu",@"zhaoliu",@"xiaoer",@"zhaoliu",@"zhaoliu",@"zhaoliu", nil]; NSLog(@"%ld",[ssee1 countForObject:@"zhaoliu"]);//4
在set的基础上添加了计数功能
三、集合类型的快速枚举
for (<#type *object#> in <#collection#>) {
}
1、object是遍历得到的元素对象。 2、collection是集合类型的对象:数组、字典、集合
NSArray *arr1 = [NSArray arrayWithObjects:@"one",@"two",@"three",@"four",@"five", nil]; for (NSString *num in arr1) { NSLog(@"%@",num); }
NSDictionary *dict1 = [NSDictionary dictionaryWithObjectsAndKeys:@"zhangsan",@"name",@"man",@"sex",@18,@"age",@"study",@"hobby", nil]; for (NSString *key in dict1) { NSLog(@"%@ : %@",key,[dict1 objectForKey:key]); }//枚举字典
NSSet *set1 = [NSSet setWithObjects:@"we",@"me",@"you",@"her",@"he",@"it", nil]; for (NSString *name in set1) { NSLog(@"%@",name); }//枚举集合
四、数组排序
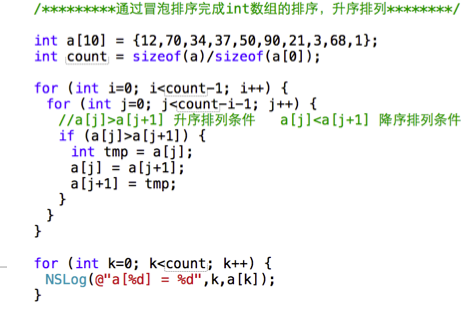
oc中得数组排序
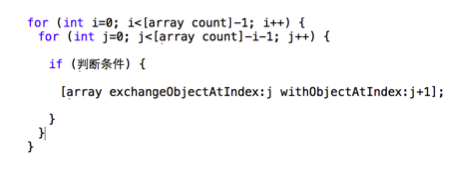
NSMutableArray *arr = [NSMutableArray arrayWithObjects:@"d18",@"a55",@"c23",@"b64",@"e100",@"f80", nil]; [arr sortUsingSelector:@selector(compare:)];//按升序排序 // for (int i = 0; i<[arr count]-1; i++) { // for (int j = 0; j<[arr count]-i-1; j++) { // NSString *str1 = [arr objectAtIndex:j]; // NSString *str2 = [arr objectAtIndex:j+1]; // //if ([str1 intValue]>[str2 intValue]) {//数字从小到大排序 // //if ([str1 compare:str2 options:NSNumericSearch]==NSOrderedAscending) {//数字从大到小 // if ([str1 compare:str2]==NSOrderedAscending) {//按字符类型从大到小排序 // [arr exchangeObjectAtIndex:j withObjectAtIndex:j+1]; // } // } // } NSLog(@"%@",arr);
