1、配置文件
Spring Boot使用一个全局的配置文件,配置文件名是固定的
-
application.properties
-
applicatioin.yml
YAML(YAML Ain't Markup Language)
YAML A Markup Language:是一个标记语言
YAML isn't Markup Language:不是一个标记语言;
标记语言:
以前的配置文件;大多都使用的是xxx.xml文件;
YAML:以数据为中心,比json、xml等更适合做配置文件;
YAML:配置例子
server:
port: 8081
xml:
<server> <port>8081</port> </server>
2、YAML语法
2.1 基本语法
K:(空格)v :表示一对键值对(空格必须有);
以空格的缩进来控制层级关系;只要是左对齐的一列数据,都是同一个层级的
server:
port: 8081
path:/hello
2.2 值 的写法
字面量:普通的值(数字,字符串,布尔)
k:v :字面量直接写;
字符串默认不用加上单引号或者双引号;
“ ”:双引号;不会转义字符串里面的特殊字符;特殊字符会作为本身表示的意思
name:"zhangsan lisi" : 输出: zhang san 换行 list
' ' : 单引号:会转义特殊字符,特殊字符最终只是一个普通的字符串数据
name:'zhangsan list' : 输出 : zhangsan list
对象、Map(属性和值)(键值对):
k: v :在下一行来写对象的属性和值的关系;注意缩进
对象还是k: v的方式
friends:
lastName: zhangsan
age: 20
行内写法
friends: {lastName: zhangsan,age: 20}
用- 值表示数组中的一个元素
pets:
- cat
- dog
- pig
行内写法
pets: [cat,dog,pig]
3、配置文件注入
配置文件
person:
lastName: zhangsan
age: 20
boss: false
birth: 2018/08/25
maps: {k1: v1,k2: v2}
lists:
- lisi
- zhaoliu
dog:
name: 小狗
age: 2
javaBean:
/** * 将配置文件中的每一个属性值 ,映射到这个组件中 * @ConfigurationProperties 告诉Spring Boot将本类中的所有属性和配置文件中相关的配置进行绑定 * * 只有这个组件是容器中组件,才能使用容器提供的@ConfigurationProperties 功能 */ @Component @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person") public class Person { private String lastName; private Integer age; private Boolean boss; private Date birth; private Map<String,Object> maps; private List<Object> lists; private Dog dog;
我们可以导入配置文件处理器,以后编写配置就的提示了
<!--导入配置文件处理器,配置文件进行绑定就会有提示--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId> <optional>true</optional> </dependency>
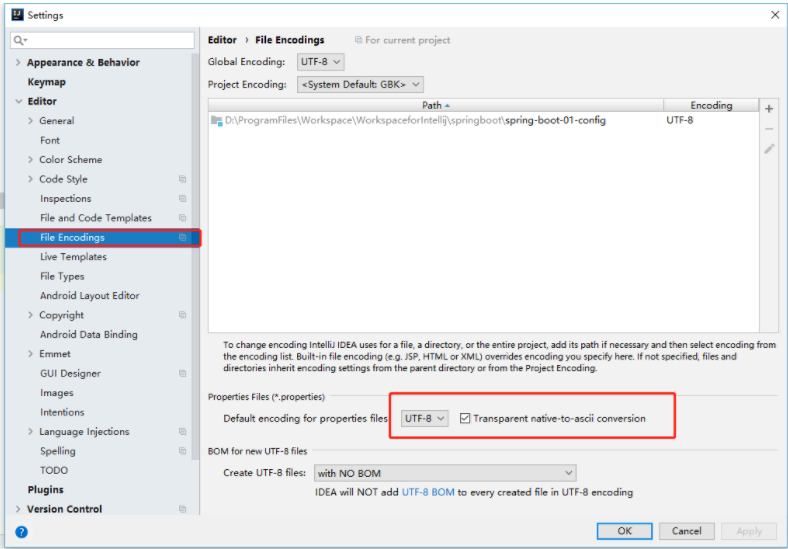
3.1 properties配置文件在idea中默认utf-8可能会乱码
配置文件yml还是properties他们都能获取到值;
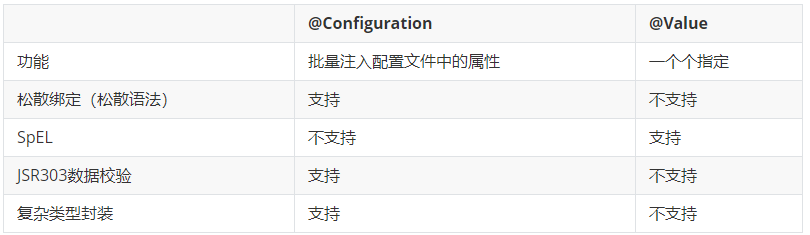
如果说,我们只是在某个业务逻辑中需要获取一下配置文件中的某项值,可以使用@Value;
如果说,我们专门写了一个JavaBean来配置文件进行映射,我们就直接使用@ConfigurationProperties;
加入@Validated
加入@Email校验是否是邮箱
@Component @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person") @Validated public class Person { //lastName必须是邮箱格式 @Email // @Value("${person.last-name}") private String lastName; // @Value("#{11*2}") private Integer age; //@Value("true") private Boolean boss; private Date birth;
3.4 @PropertySource & @ImportResource & @Bean
@PropertySource:加载指定的配置文件
/** * 将配置文件中的每一个属性值 ,映射到这个组件中 * * @ConfigurationProperties 告诉Spring Boot将本类中的所有属性和配置文件中相关的配置进行绑定 * <p> * 只有这个组件是容器中组件,才能使用容器提供的@ConfigurationProperties 功能 * @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")默认从全局配置文件中获取值; */ @Component @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person") @PropertySource(value = "classpath:person.properties") //@Validated public class Person { //lastName必须是邮箱格式 //@Email // @Value("${person.last-name}") private String lastName; // @Value("#{11*2}") private Integer age; //@Value("true") private Boolean boss; private Date birth; private Map<String, Object> maps; private List<Object> lists; private Dog dog;
@ImportResource:导入Spring的配置文件,让配置文件里面的内容生效;
Spring Boot里面没有Spring的配置文件,我们自己编写的配置文件,也不能自动识别;
想让Spring的配置文件生效,加载进行;@ImportResource标注在一个配置类上;
@ImportResource(locations = {"classpath:bean.xml"})
导入spring的配置文件让其生效
public class SpringBoot01ConfigApplication {
编写Spring的配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="helloService" class="cn.lzc.springboot.service.HelloService"></bean> </beans>
Spring Boot推荐给容器中添加组件的方式;推荐使用全注解的方式
1、配置类@Configuration ---->Spring配置文件
/** * @Configuration 批明当前类是一个配置类,就是来替代之前的spring配置文件 */ @Configuration public class MyAppConfig { //将方法的返回值添加到窗口中;容器中这个组件默认的id就是方法名 @Bean public HelloService helloService(){ return new HelloService(); } }
4、配置文件占位符
4.1 随机数
${random.value}、${random.int}、${random.long}
${random.int(10)}、${random.int[1024,65536]}
person.last-name=张三${random.uuid}
person.age=${random.int}
person.birth=2018/08/25
person.boss=false
person.maps.k1=v1
person.maps.k2=14
person.lists=a,b,c
person.dog.name=${person.hello:hello}_dog
person.dog.age=15
5.1 多profile文件
我们可以在主配置文件编写的时候,文件名可以是application-{profile}.properties/yml
5.2 yml支持多文档块方式
server:
port: 8080
spring:
profiles:
active: test
---
server:
port: 8081
spring:
profiles: test
---
server:
port: 80
spring:
profiles: dev
-
1、在配置文件中指定spring.profiles.active=dev
-
2、命令行:
-
java -jar spring-boot-01-config-SNAPSHOT.jar --spring.profiles.active=dev
-
-
3、虚拟机参数
-Dspring.profiles.active=dev
6、配置文件加载位置
spring boot启动会扫描以下位置的application.properties或者application.yml文件作为spring boot的默认配置文件
–file:./config/
–file:./
–classpath:/config/
–classpath:/
优先级由高到低,高优先级的配置会覆盖低优先级的配置;
Spring Boot会从这四个位置全部加载主配置文件:互补配置;
我们还可以通过spring.config.location来改变默认的配置文件的位置
项目打包好以后,我们可以使用命令行参数的形式,启动项目的时候业指定配置文件的新位置;指定的配置文件和默认加载的这些配置文件共同起作用形成互补配置。
java -jar spring-boot-02-config-02-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar --spring.config.location=G:/application.properties
7、外部配置加载顺序
SpringBoot也可以从以下位置加载配置; 优先级从高到低;高优先级的配置覆盖低优先级的配置,所有的配置会 形成互补配置
1.命令行参数
所有的配置都可以在命令行上进行指定
java -jar spring-boot-02-config-02-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar --server.port=8087 --server.context-path=/abc 多个配
置用空格分开; --配置项=值
2.来自java:comp/env的JNDI属性
3.Java系统属性(System.getProperties())
4.操作系统环境变量
5.RandomValuePropertySource配置的random.*属性值
由jar包外向jar包内进行寻找;
优先加载带profile
6.jar包外部的application-{profile}.properties或application.yml(带spring.profile)配置文件
7.jar包内部的application-{profile}.properties或application.yml(带spring.profile)配置文件
再来加载不带profile
8.jar包外部的application.properties或application.yml(不带spring.profile)配置文件
9.jar包内部的application.properties或application.yml(不带spring.profile)配置文件
10.@Configuration注解类上的@PropertySource
11.通过SpringApplication.setDefaultProperties指定的默认属性
所有支持的配置加载来源;
8、自动配置原理
8.1 自动配置原理
配置文件到底能写什么?怎么写?自动配置原理;
-
(1)Spring Boot 启动的时候加载主配置类,开启了自动配置功能@EnableAutoConfiguration
-
(2)@EnableAutoConfiguration作用:
-
利用AutoConfigurationImportSelector给容器中导入一些组件
-
可以查看selectImports()方法内容
-
List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes);获取候选的配置
-
SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames()
扫描所有jar包类路径下的 META-INF/spring.factories
把扫描到的这些文件的内容包装成properties对象
从properties中获取到EnableAutoConfiguration.class类(类名)对应的值,然后把他们添加到窗口中
# Auto Configure
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.admin.SpringApplicationAdminJmxAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.aop.AopAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.amqp.RabbitAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.batch.BatchAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CacheAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cassandra.CassandraAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cloud.CloudAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.ConfigurationPropertiesAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.MessageSourceAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.couchbase.CouchbaseAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.dao.PersistenceExceptionTranslationAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraDataAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraReactiveDataAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraReactiveRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseDataAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseReactiveDataAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseReactiveRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchDataAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.jpa.JpaRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.ldap.LdapDataAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.ldap.LdapRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoDataAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoReactiveDataAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoReactiveRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jDataAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.solr.SolrRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisReactiveAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.rest.RepositoryRestMvcAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.web.SpringDataWebAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.elasticsearch.jest.JestAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.flyway.FlywayAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.freemarker.FreeMarkerAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.gson.GsonAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.h2.H2ConsoleAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hateoas.HypermediaAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hazelcast.HazelcastAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hazelcast.HazelcastJpaDependencyAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.HttpMessageConvertersAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.codec.CodecsAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.influx.InfluxDbAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.info.ProjectInfoAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.integration.IntegrationAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jackson.JacksonAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.JdbcTemplateAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.JndiDataSourceAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.XADataSourceAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.JmsAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jmx.JmxAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.JndiConnectionFactoryAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.activemq.ActiveMQAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.artemis.ArtemisAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.groovy.template.GroovyTemplateAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jersey.JerseyAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jooq.JooqAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jsonb.JsonbAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.kafka.KafkaAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.ldap.embedded.EmbeddedLdapAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.ldap.LdapAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.liquibase.LiquibaseAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mail.MailSenderAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mail.MailSenderValidatorAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.embedded.EmbeddedMongoAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.MongoAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.MongoReactiveAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mustache.MustacheAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.HibernateJpaAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.quartz.QuartzAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.reactor.core.ReactorCoreAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.SecurityAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.UserDetailsServiceAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.SecurityFilterAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.reactive.ReactiveSecurityAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.reactive.ReactiveUserDetailsServiceAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.sendgrid.SendGridAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.session.SessionAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.client.OAuth2ClientAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.solr.SolrAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.thymeleaf.ThymeleafAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.TransactionAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.jta.JtaAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.validation.ValidationAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.client.RestTemplateAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.embedded.EmbeddedWebServerFactoryCustomizerAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.HttpHandlerAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.ReactiveWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.WebFluxAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.error.ErrorWebFluxAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.function.client.WebClientAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.MultipartAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.reactive.WebSocketReactiveAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.servlet.WebSocketServletAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.servlet.WebSocketMessagingAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.webservices.WebServicesAutoConfiguration
-
(3)每一个自动配置类进行自动配置功能;
-
(4)以HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration(Http编码自动配置)为例解释自动配置原理;
@Configuration //表示这是一个配置类,以前编写的配置文件一样,也可以给容器中添加组件 @EnableConfigurationProperties(HttpEncodingProperties.class) //启动指定类的ConfigurationProperties功能;将配置文件中对应的值和HttpEncodingProperties绑定起来;并把HttpEncodingProperties加入到容器中 @ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = ConditionalOnWebApplication.Type.SERVLET) //Spring底层@Conditional注解,根据不同的条件,如果满足指定的条件,整个配置类里面的配置才会生效; 判断当前应用是否是web应用,如果是,当前配置类生效 @ConditionalOnClass(CharacterEncodingFilter.class) //判断当前项目有没有这个类CharacterEncodingFilter; SpringMvc中进行乱码解决的过滤器 @ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.http.encoding", value = "enabled", matchIfMissing = true) //判断配置文件中是否存在某个配置 spring.http.encoding.enable;如果不存在,判断也是成立的 //即使我闪配置文件中不配置spring.http.encoding.enable=true,也是默认生效的 public class HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration { //他已经和spring boot的配置文件映射了 private final HttpEncodingProperties properties; //只有一个有参构造器中情况下,参数的值就会从容器中拿到 public HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration(HttpEncodingProperties properties) { this.properties = properties; } @Bean //给容器中添加一个组件,这个组件的某些值需要从properties中获取 @ConditionalOnMissingBean public CharacterEncodingFilter characterEncodingFilter() { CharacterEncodingFilter filter = new OrderedCharacterEncodingFilter(); filter.setEncoding(this.properties.getCharset().name()); filter.setForceRequestEncoding(this.properties.shouldForce(Type.REQUEST)); filter.setForceResponseEncoding(this.properties.shouldForce(Type.RESPONSE)); return filter; }
一但这个配置类生效;这个配置类就会给容器中添加各种组件;这些组件的属性是从对应的properties类中获取的,这些类里面的每一个属性又是和配置文件绑定的。
-
(5)所有在配置文件中能配置 的属性都是在xxxProperties类中封装着;配置文件能配置什么就可以参照某个功能对应的这个属性类
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.http.encoding") //从配置文件中获取指定的值和bean的属性进行绑定 public class HttpEncodingProperties {
精髓:
-
(1)Spring Boot启动会加载大量的自动配置类
-
(2)我们看我们需要的功能有没有Spring Boot默认写好的自动配置类
-
(3)我们再来看这个自动配置类中到底配置了哪些组件;(只要我们要用的组件有,我们就不用再来配置了)
-
(4)给容器中自动配置类添加组件的时候,会从properties类中获取某些属性,我们就可以在配置类文件中指定这些属性的值
xxxAutoConfiguration:自动配置类;
给容器中添加组件
xxxProperties:封装配置文件中相关属性;
8.2 细节
8.2.1 @Conditional派生注解(Spring注解版原生的@Conditional作用)
作用:必须是@Conditional指定的条件成立,才给容器中添加组件,配置配里面的所有内容才生效;

自动配置类必须在一定的条件下才能生效; 我们怎么知道哪些自动配置类生效; 我们可以通过启用 debug=true属性;来让控制台打印自动配置报告,这样我们就可以很方便的知道哪些自动配置 类生效;