transient [ˈtrænziənt]
adj. 短暂的; 转瞬即逝的; 临时的
n 临时旅客; 瞬变现象; 候鸟;
1. transient的作用及使用方法
我们都知道一个对象只要实现了Serilizable接口,这个对象就可以被序列化,java的这种序列化模式为开发者提供了很多便利,我们可以不必关系具体序列化的过程,只要这个类实现了Serilizable接口,这个类的所有属性和方法都会自动序列化。
然而在实际开发过程中,我们常常会遇到这样的问题,这个类的有些属性需要序列化,而其他属性不需要被序列化,打个比方,如果一个用户有一些敏感信息(如密码,银行卡号等),为了安全起见,不希望在网络操作(主要涉及到序列化操作,本地序列化缓存也适用)中被传输,这些信息对应的变量就可以加上transient关键字。换句话说,这个字段的生命周期仅存于调用者的内存中而不会写到磁盘里持久化。
总之,java 的transient关键字为我们提供了便利,你只需要实现Serilizable接口,将不需要序列化的属性前添加关键字transient,序列化对象的时候,这个属性就不会序列化到指定的目的地中。
示例code如下:
package test;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class SerializableTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("game-person.info");
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(fos);
GamePerson personIn = new GamePerson();
personIn.setName("abcde");
personIn.setLevel(1);
personIn.setForceValue(2);
personIn.setDefenseValue(3);
personIn.setMoney(200);
// 通过在序列化之前,使用类变量直接赋值,可知
// 一个静态变量不管是否被transient修饰,均不能被序列化),反序列化后类中static型变量username的值为当前JVM中
// 对应static变量的值,这个值是JVM中的不是反序列化得出的
GamePerson.level = 300;
oos.writeObject(personIn);
oos.flush();
oos.close();
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("game-person.info");
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(fis);
GamePerson personOut = (GamePerson) ois.readObject();
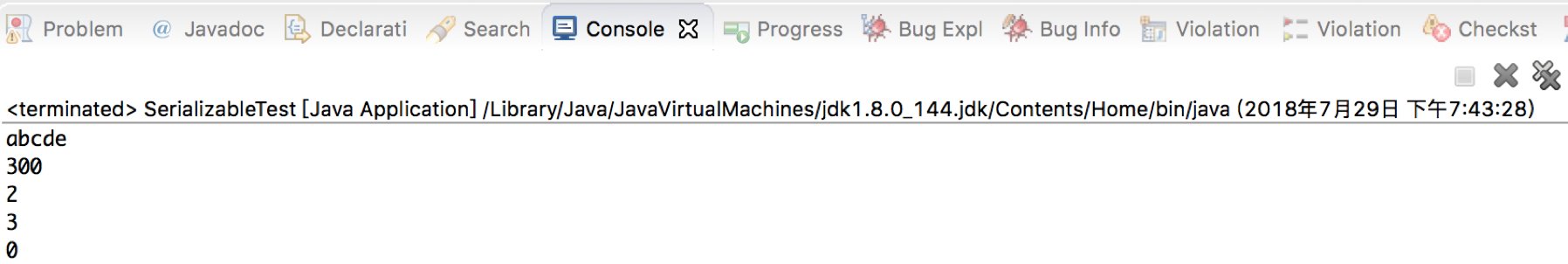
System.out.println(personOut.getName());
System.out.println(personOut.getLevel());
System.out.println(personOut.getForceValue());
System.out.println(personOut.getDefenseValue());
System.out.println(personOut.getMoney());
}
}
class GamePerson implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private String name;
public static int level;
private int forceValue;
private int defenseValue;
// 金额是敏感数据:不对此属性进行序列化
private transient long money;
public long getMoney() {
return money;
}
public void setMoney(long money) {
this.money = money;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getLevel() {
return level;
}
public void setLevel(int level) {
this.level = level;
}
public int getForceValue() {
return forceValue;
}
public void setForceValue(int forceValue) {
this.forceValue = forceValue;
}
public int getDefenseValue() {
return defenseValue;
}
public void setDefenseValue(int defenseValue) {
this.defenseValue = defenseValue;
}
}
2. transient使用小结
1)一旦变量被transient修饰,变量将不再是对象持久化的一部分,该变量内容在序列化后无法获得访问。
2)transient关键字只能修饰变量,而不能修饰方法和类。注意,本地变量是不能被transient关键字修饰的。变量如果是用户自定义类变量,则该类需要实现Serializable接口。
3)被transient关键字修饰的变量不再能被序列化,一个静态变量不管是否被transient修饰,均不能被序列化。
第三点可能有些人很迷惑,因为发现在User类中的username字段前加上static关键字后,程序运行结果依然不变,即static类型的username也读出来为“Alexia”了,这不与第三点说的矛盾吗?实际上是这样的:第三点确实没错(一个静态变量不管是否被transient修饰,均不能被序列化),反序列化后类中static型变量username的值为当前JVM中对应static变量的值,这个值是JVM中的不是反序列化得出的,不相信?好吧,下面我来证明:
同样是上面那个代码

这说明反序列化后类中static型变量username的值为当前JVM中对应static变量的值,为修改后jmwang,而不是序列化时的值Alexia。
3. transient使用细节——被transient关键字修饰的变量真的不能被序列化吗?
思考下面的例子:
import java.io.Externalizable;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInput;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutput;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
/**
* @descripiton Externalizable接口的使用
*
* @author Alexia
* @date 2013-10-15
*
*/
public class ExternalizableTest implements Externalizable {
private transient String content = "是的,我将会被序列化,不管我是否被transient关键字修饰";
@Override
public void writeExternal(ObjectOutput out) throws IOException {
out.writeObject(content);
}
@Override
public void readExternal(ObjectInput in) throws IOException,
ClassNotFoundException {
content = (String) in.readObject();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ExternalizableTest et = new ExternalizableTest();
ObjectOutput out = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(
new File("test")));
out.writeObject(et);
ObjectInput in = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(new File(
"test")));
et = (ExternalizableTest) in.readObject();
System.out.println(et.content);
out.close();
in.close();
}
}
content变量会被序列化吗?好吧,我把答案都输出来了,是的,运行结果就是:
是的,我将会被序列化,不管我是否被transient关键字修饰
这是为什么呢,不是说类的变量被transient关键字修饰以后将不能序列化了吗?
我们知道在Java中,对象的序列化可以通过实现两种接口来实现,若实现的是Serializable接口,则所有的序列化将会自动进行,若实现的是Externalizable接口,则没有任何东西可以自动序列化,需要在writeExternal方法中进行手工指定所要序列化的变量,这与是否被transient修饰无关。因此第二个例子输出的是变量content初始化的内容,而不是null。