高通的HAL层其实分为两种,一种是直接从kernel这边报数据上来的,由sensor HAL层来监听,另一种是走ADSP的模式,HAL层是通过qmi的形式进行监听的;
走ADSP架构的可以看下面的博客:http://blog.csdn.net/u011006622/article/details/54598426
而msm8909架构下的便是以HAL层来监听数据的;
简介:
Google为Sensor提供了统一的HAL接口,不同的硬件厂商需要根据该接口来实现并完成具体的硬件抽象层,Android中Sensor的HAL接口定义在:hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/sensors.h:
为了了解HAL层的sensor,我们必须理解几个结构体:分别是sensor_type,sensor_t,sensors_module_t;
从下面可以看到此文件定义了sensor的type以及string type;
1 /* 2 * SENSOR_TYPE_ACCELEROMETER 3 * reporting-mode: continuous 4 * 5 * All values are in SI units (m/s^2) and measure the acceleration of the 6 * device minus the force of gravity. 7 * 8 * Implement the non-wake-up version of this sensor and implement the wake-up 9 * version if the system possesses a wake up fifo. 10 */ 11 #define SENSOR_TYPE_ACCELEROMETER (1) 12 #define SENSOR_STRING_TYPE_ACCELEROMETER "android.sensor.accelerometer"
sensors_module_t结构体:
该结构体实际上是对标准硬件模块hw_module_t的一个扩展,增加一个get_sensor_list函数,用于获取传感器的列表,以及set_operation_mode设置为相关的mode;

1 /** 2 * Every hardware module must have a data structure named HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM 3 * and the fields of this data structure must begin with hw_module_t 4 * followed by module specific information. 5 */ 6 struct sensors_module_t { 7 struct hw_module_t common; 8 9 /** 10 * Enumerate all available sensors. The list is returned in "list". 11 * @return number of sensors in the list 12 */ 13 int (*get_sensors_list)(struct sensors_module_t* module, 14 struct sensor_t const** list); 15 16 /** 17 * Place the module in a specific mode. The following modes are defined 18 * 19 * 0 - Normal operation. Default state of the module. 20 * 1 - Loopback mode. Data is injected for the supported 21 * sensors by the sensor service in this mode. 22 * @return 0 on success 23 * -EINVAL if requested mode is not supported 24 * -EPERM if operation is not allowed 25 */ 26 int (*set_operation_mode)(unsigned int mode); 27 };
sensor_t结构体:

1 struct sensor_t { 2 3 /* Name of this sensor. 4 * All sensors of the same "type" must have a different "name". 5 */ 6 const char* name; //传感器名字 7 8 /* vendor of the hardware part */ 9 const char* vendor; //生产厂家名字 10 11 /* version of the hardware part + driver. The value of this field 12 * must increase when the driver is updated in a way that changes the 13 * output of this sensor. This is important for fused sensors when the 14 * fusion algorithm is updated. 15 */ 16 int version; 17 18 /* handle that identifies this sensors. This handle is used to reference 19 * this sensor throughout the HAL API. 20 */ 21 int handle; //传感器handle句柄 22 23 /* this sensor's type. */ 24 int type; //传感器类型 25 26 /* maximum range of this sensor's value in SI units */ 27 float maxRange; //最大范围 28 29 /* smallest difference between two values reported by this sensor */ 30 float resolution; //解析度 31 32 /* rough estimate of this sensor's power consumption in mA */ 33 float power; 34 35 /* this value depends on the reporting mode: 36 * 37 * continuous: minimum sample period allowed in microseconds 38 * on-change : 0 39 * one-shot :-1 40 * special : 0, unless otherwise noted 41 */ 42 int32_t minDelay; 43 44 /* number of events reserved for this sensor in the batch mode FIFO. 45 * If there is a dedicated FIFO for this sensor, then this is the 46 * size of this FIFO. If the FIFO is shared with other sensors, 47 * this is the size reserved for that sensor and it can be zero. 48 */ 49 uint32_t fifoReservedEventCount; 50 51 /* maximum number of events of this sensor that could be batched. 52 * This is especially relevant when the FIFO is shared between 53 * several sensors; this value is then set to the size of that FIFO. 54 */ 55 uint32_t fifoMaxEventCount; 56 57 /* type of this sensor as a string. Set to corresponding 58 * SENSOR_STRING_TYPE_*. 59 * When defining an OEM specific sensor or sensor manufacturer specific 60 * sensor, use your reserve domain name as a prefix. 61 * ex: com.google.glass.onheaddetector 62 * For sensors of known type, the android framework might overwrite this 63 * string automatically. 64 */ 65 const char* stringType; 66 67 /* permission required to see this sensor, register to it and receive data. 68 * Set to "" if no permission is required. Some sensor types like the 69 * heart rate monitor have a mandatory require_permission. 70 * For sensors that always require a specific permission, like the heart 71 * rate monitor, the android framework might overwrite this string 72 * automatically. 73 */ 74 const char* requiredPermission; 75 76 /* This value is defined only for continuous mode and on-change sensors. It is the delay between 77 * two sensor events corresponding to the lowest frequency that this sensor supports. When lower 78 * frequencies are requested through batch()/setDelay() the events will be generated at this 79 * frequency instead. It can be used by the framework or applications to estimate when the batch 80 * FIFO may be full. 81 * 82 * NOTE: 1) period_ns is in nanoseconds where as maxDelay/minDelay are in microseconds. 83 * continuous, on-change: maximum sampling period allowed in microseconds. 84 * one-shot, special : 0 85 * 2) maxDelay should always fit within a 32 bit signed integer. It is declared as 64 bit 86 * on 64 bit architectures only for binary compatibility reasons. 87 * Availability: SENSORS_DEVICE_API_VERSION_1_3 88 */ 89 #ifdef __LP64__ 90 int64_t maxDelay; 91 #else 92 int32_t maxDelay; 93 #endif 94 95 /* Flags for sensor. See SENSOR_FLAG_* above. Only the least significant 32 bits are used here. 96 * It is declared as 64 bit on 64 bit architectures only for binary compatibility reasons. 97 * Availability: SENSORS_DEVICE_API_VERSION_1_3 98 */ 99 #ifdef __LP64__ 100 uint64_t flags; 101 #else 102 uint32_t flags; 103 #endif 104 105 /* reserved fields, must be zero */ 106 void* reserved[2]; 107 };
高通HAL:
现在回到高通定制的sensor HAL层来:(代码位于hardwareqcomsensors:)
Sensor HAL:
首先sensor这个模块这个id的定义,主要实现了sensors_module_t结构:
1 struct sensors_module_t HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM = { 2 common: { 3 tag: HARDWARE_MODULE_TAG, 4 version_major: 1, 5 version_minor: 0, 6 id: SENSORS_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, 7 name: "Quic Sensor module", 8 author: "Quic", 9 methods: &sensors_module_methods, 10 dso: NULL, 11 reserved: {0}, 12 }, 13 get_sensors_list: sensors__get_sensors_list, 14 };
sensors__get_sensors_list函数返回这个平台的所有sensor:

1 static int sensors__get_sensors_list(struct sensors_module_t*, 2 struct sensor_t const** list) 3 { 4 NativeSensorManager& sm(NativeSensorManager::getInstance()); 5 6 return sm.getSensorList(list); 7 }
里面使用了NativeSensorManager,sensors__get_sensors_list函数中调用单例模式创建了一个实例,然后再调用相应的成员函数获取传感器列表,并返回,返回值对应的sensor_t结构体;
NativeSensorManager统一管理着所有的传感器、物理和虚拟传感器。它的软件框架如下:
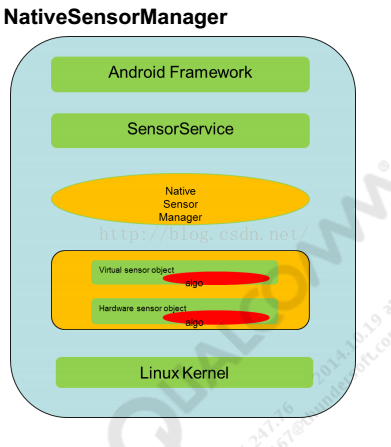
我们继续看sensors_module_methods:
1 static struct hw_module_methods_t sensors_module_methods = { 2 open: open_sensors 3 };
1 /*****************************************************************************/ 2 3 /** Open a new instance of a sensor device using name */ 4 static int open_sensors(const struct hw_module_t* module, const char*, 5 struct hw_device_t** device) 6 { 7 int status = -EINVAL; 8 sensors_poll_context_t *dev = new sensors_poll_context_t(); 9 NativeSensorManager& sm(NativeSensorManager::getInstance()); 10 11 memset(&dev->device, 0, sizeof(sensors_poll_device_1_ext_t)); 12 13 dev->device.common.tag = HARDWARE_DEVICE_TAG; 14 #if defined(SENSORS_DEVICE_API_VERSION_1_3) 15 ALOGI("Sensors device API version 1.3 supported "); 16 dev->device.common.version = SENSORS_DEVICE_API_VERSION_1_3; 17 #else 18 dev->device.common.version = SENSORS_DEVICE_API_VERSION_0_1; 19 #endif 20 dev->device.common.module = const_cast<hw_module_t*>(module); 21 dev->device.common.close = poll__close; 22 dev->device.activate = poll__activate; 23 dev->device.setDelay = poll__setDelay; 24 dev->device.poll = poll__poll; 25 dev->device.calibrate = poll_calibrate; 26 #if defined(SENSORS_DEVICE_API_VERSION_1_3) 27 dev->device.batch = poll__batch; 28 dev->device.flush = poll__flush; 29 #endif 30 31 *device = &dev->device.common; 32 status = 0; 33 34 return status; 35 }
open_sensors用来打开所有的sensor,并返回相应的状态;首先new了一个sensors_poll_context_t ,然后设置device,并返回;
对应的new sensors_poll_context_t,我们来看一下其实现:

1 struct sensors_poll_context_t { 2 // extension for sensors_poll_device_1, must be first 3 struct sensors_poll_device_1_ext_t device;// must be first 4 sensors_poll_context_t(); 5 ~sensors_poll_context_t(); 6 int activate(int handle, int enabled); 7 int setDelay(int handle, int64_t ns); 8 int pollEvents(sensors_event_t* data, int count); 9 int calibrate(int handle, cal_cmd_t *para); 10 int batch(int handle, int sample_ns, int latency_ns); 11 int flush(int handle); 12 13 private: 14 static const size_t wake = MAX_SENSORS; 15 static const char WAKE_MESSAGE = 'W'; 16 struct pollfd mPollFds[MAX_SENSORS+1]; 17 int mWritePipeFd; 18 SensorBase* mSensors[MAX_SENSORS]; 19 mutable Mutex mLock; 20 };
1 /*****************************************************************************/ 2 3 sensors_poll_context_t::sensors_poll_context_t() 4 { 5 int number; 6 int i; 7 const struct sensor_t *slist; 8 const struct SensorContext *context; 9 NativeSensorManager& sm(NativeSensorManager::getInstance()); 10 //获取sensor列表 11 number = sm.getSensorList(&slist); 12 13 /* use the dynamic sensor list */ 14 for (i = 0; i < number; i++) { 15 context = sm.getInfoByHandle(slist[i].handle); 16 17 mPollFds[i].fd = (context == NULL) ? -1 : context->data_fd; 18 mPollFds[i].events = POLLIN; 19 mPollFds[i].revents = 0; 20 } 21 22 ALOGI("The avaliable sensor handle number is %d",i); 23 int wakeFds[2]; 24 int result = pipe(wakeFds); 25 ALOGE_IF(result<0, "error creating wake pipe (%s)", strerror(errno)); 26 fcntl(wakeFds[0], F_SETFL, O_NONBLOCK); 27 fcntl(wakeFds[1], F_SETFL, O_NONBLOCK); 28 mWritePipeFd = wakeFds[1]; 29 30 mPollFds[number].fd = wakeFds[0]; 31 mPollFds[number].events = POLLIN; 32 mPollFds[number].revents = 0; 33 }
通过context = sm.getInfoByHandle(slist[i].handle); 维系了一个handle对应的SensorContext对象指针的句柄;
(context是一个SensorContext结构体,SensorContext包含了一个SensorBase *driver指针;注意这个很重要!就是这个与具体的sensor产生相应的关联;而mPollFds是一个pollfd的结构。context保存着各个打开的sensor,mPollFds用来监听sensor的时候用的文件描述符;)
然后继续往下看,由上面代码可见:sensors_poll_device_t的activate、setDelay和poll的实现函数分别为:
(1) poll__activate
(2) poll__setDelay
(3) poll__poll

1 int sensors_poll_context_t::activate(int handle, int enabled) { 2 int err = -1; 3 NativeSensorManager& sm(NativeSensorManager::getInstance()); 4 Mutex::Autolock _l(mLock); 5 6 err = sm.activate(handle, enabled); 7 if (enabled && !err) { 8 const char wakeMessage(WAKE_MESSAGE); 9 int result = write(mWritePipeFd, &wakeMessage, 1); 10 ALOGE_IF(result<0, "error sending wake message (%s)", strerror(errno)); 11 } 12 13 return err; 14 }

1 int sensors_poll_context_t::setDelay(int handle, int64_t ns) { 2 int err = -1; 3 NativeSensorManager& sm(NativeSensorManager::getInstance()); 4 Mutex::Autolock _l(mLock); 5 6 err = sm.setDelay(handle, ns); 7 8 return err; 9 }

1 int sensors_poll_context_t::pollEvents(sensors_event_t* data, int count) 2 { 3 int nbEvents = 0; 4 int n = 0; 5 NativeSensorManager& sm(NativeSensorManager::getInstance()); 6 const sensor_t *slist; 7 int number = sm.getSensorList(&slist); 8 9 do { 10 // see if we have some leftover from the last poll() 11 for (int i = 0 ; count && i < number ; i++) { 12 if ((mPollFds[i].revents & POLLIN) || (sm.hasPendingEvents(slist[i].handle))) { 13 Mutex::Autolock _l(mLock); 14 int nb = sm.readEvents(slist[i].handle, data, count); 15 if (nb < 0) { 16 ALOGE("readEvents failed.(%d)", errno); 17 return nb; 18 } 19 if (nb <= count) { 20 // no more data for this sensor 21 mPollFds[i].revents = 0; 22 } 23 count -= nb; 24 nbEvents += nb; 25 data += nb; 26 } 27 } 28 29 if (count) { 30 // we still have some room, so try to see if we can get 31 // some events immediately or just wait if we don't have 32 // anything to return 33 do { 34 n = poll(mPollFds, number + 1, nbEvents ? 0 : -1); 35 } while (n < 0 && errno == EINTR); 36 if (n<0) { 37 ALOGE("poll() failed (%s)", strerror(errno)); 38 return -errno; 39 } 40 if (mPollFds[number].revents & POLLIN) { 41 char msg; 42 int result = read(mPollFds[number].fd, &msg, 1); 43 ALOGE_IF(result<0, "error reading from wake pipe (%s)", strerror(errno)); 44 ALOGE_IF(msg != WAKE_MESSAGE, "unknown message on wake queue (0x%02x)", int(msg)); 45 mPollFds[number].revents = 0; 46 } 47 } 48 // if we have events and space, go read them 49 } while (n && count); 50 51 return nbEvents; 52 }

1 static int poll__close(struct hw_device_t *dev) 2 { 3 sensors_poll_context_t *ctx = (sensors_poll_context_t *)dev; 4 if (ctx) { 5 delete ctx; 6 } 7 return 0; 8 }

1 static int poll__activate(struct sensors_poll_device_t *dev, 2 int handle, int enabled) { 3 sensors_poll_context_t *ctx = (sensors_poll_context_t *)dev; 4 return ctx->activate(handle, enabled); 5 }

1 static int poll__setDelay(struct sensors_poll_device_t *dev, 2 int handle, int64_t ns) { 3 sensors_poll_context_t *ctx = (sensors_poll_context_t *)dev; 4 return ctx->setDelay(handle, ns); 5 }

1 static int poll__poll(struct sensors_poll_device_t *dev, 2 sensors_event_t* data, int count) { 3 sensors_poll_context_t *ctx = (sensors_poll_context_t *)dev; 4 return ctx->pollEvents(data, count); 5 }
以poll_poll为例,看看如何与具体的sensor建立连接的:
1 return ctx->pollEvents(data, count);
ctx->pollEvents函数又调用了NativeSensorManager::readEvents;

1 int sensors_poll_context_t::pollEvents(sensors_event_t* data, int count) 2 { 3 int nbEvents = 0; 4 int n = 0; 5 NativeSensorManager& sm(NativeSensorManager::getInstance()); 6 const sensor_t *slist; 7 int number = sm.getSensorList(&slist); 8 9 do { 10 // see if we have some leftover from the last poll() 11 for (int i = 0 ; count && i < number ; i++) { 12 if ((mPollFds[i].revents & POLLIN) || (sm.hasPendingEvents(slist[i].handle))) { 13 Mutex::Autolock _l(mLock); 14 int nb = sm.readEvents(slist[i].handle, data, count); 15 if (nb < 0) { 16 ALOGE("readEvents failed.(%d)", errno); 17 return nb; 18 } 19 if (nb <= count) { 20 // no more data for this sensor 21 mPollFds[i].revents = 0; 22 } 23 count -= nb; 24 nbEvents += nb; 25 data += nb; 26 } 27 } 28 29 if (count) { 30 // we still have some room, so try to see if we can get 31 // some events immediately or just wait if we don't have 32 // anything to return 33 do { 34 n = poll(mPollFds, number + 1, nbEvents ? 0 : -1); 35 } while (n < 0 && errno == EINTR); 36 if (n<0) { 37 ALOGE("poll() failed (%s)", strerror(errno)); 38 return -errno; 39 } 40 if (mPollFds[number].revents & POLLIN) { 41 char msg; 42 int result = read(mPollFds[number].fd, &msg, 1); 43 ALOGE_IF(result<0, "error reading from wake pipe (%s)", strerror(errno)); 44 ALOGE_IF(msg != WAKE_MESSAGE, "unknown message on wake queue (0x%02x)", int(msg)); 45 mPollFds[number].revents = 0; 46 } 47 } 48 // if we have events and space, go read them 49 } while (n && count); 50 51 return nbEvents; 52 }
NativeSensorManager::readEvents中又调用了:
1 nb = list->driver->readEvents(data, count);
记得上面说过什么?list->driver是一个SensorBase结构体,于是终于终于我们来到了SensorBase结构体的函数readEvents,接下来就是具体的sensor模块读取的任务了!!
其主要框架如下图所示:
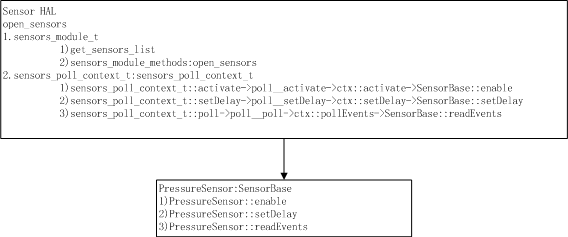
下来继续看具体sensor的处理过程:http://www.cnblogs.com/linhaostudy/p/8432741.html
