https://docs.openstack.org/image-guide/centos-image.html
This example shows you how to install a CentOS image and focuses mainly on CentOS 7. Because the CentOS installation process might differ across versions, the installation steps might differ if you use a different version of CentOS.
Download a CentOS install ISO¶
- Navigate to the CentOS mirrors page.
- Click one of the
HTTPlinks in the right-hand column next to one of the mirrors. - Click the folder link of the CentOS version that you want to use. For example,
7/. - Click the
isos/folder link. - Click the
x86_64/folder link for 64-bit images. - Click the netinstall ISO image that you want to download. For example,
CentOS-7-x86_64-NetInstall-1611.isois a good choice because it is a smaller image that downloads missing packages from the Internet during installation.
Start the installation process¶
Start the installation process using either the virt-manager or the virt-install command as described previously. If you use the virt-install command, do not forget to connect your VNC client to the virtual machine.
Assume that:
- The name of your virtual machine image is
centos; you need this name when you use virsh commands to manipulate the state of the image. - You saved the netinstall ISO image to the
/data/isosdirectory.
If you use the virt-install command, the commands should look something like this:
需要先开启CPU的虚拟化
安装kvm
yum -y install qemu-kvm qemu-system libvirt-bin bridge-utils virt-install libvirt
systemctl start libvirtd && systemctl enable libvirtd
virt-manager 这是图形化管理工具
# qemu-img create -f qcow2 /tmp/centos.qcow2 10G
# virt-install --virt-type kvm --name centos --ram 1024
--disk /tmp/centos.qcow2,format=qcow2
--network network=default
--graphics vnc,listen=0.0.0.0 --noautoconsole
--os-type=linux --os-variant=centos7.0
--location=/data/isos/CentOS-7-x86_64-NetInstall-1611.iso
Step through the installation¶
如果系统盘使用LVM,新建的虚拟机实例 /分区不会自动扩容,但硬盘是按选择的大小尺寸分配的。
At the initial Installer boot menu, choose the Install CentOS 7 option. After the installation program starts, choose your preferred language and click Continue to get to the installation summary. Accept the defaults.
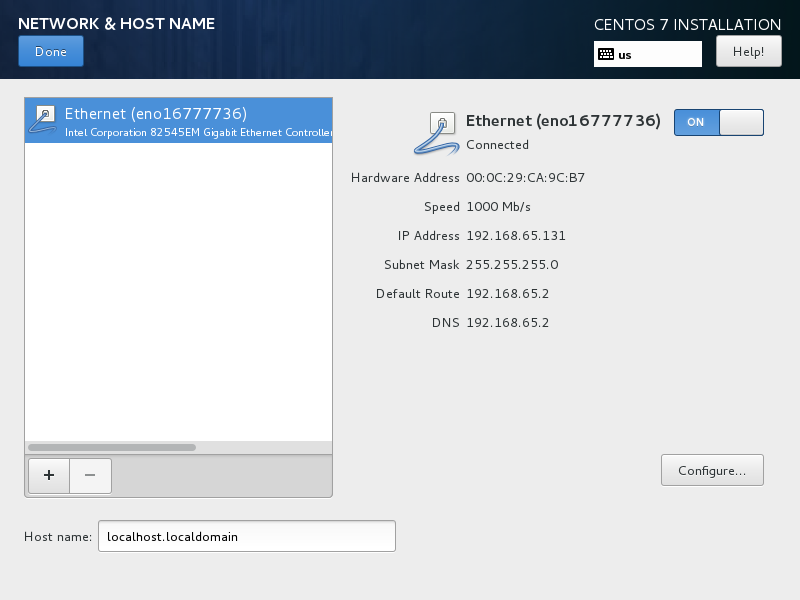
Change the Ethernet status¶
The default Ethernet setting is OFF. Change the setting of the Ethernet form OFF to ON. In particular, ensure that IPv4 Settings'Method is Automatic (DHCP), which is the default.
Hostname¶
The installer allows you to choose a host name. The default (localhost.localdomain) is fine. You install the cloud-init package later, which sets the host name on boot when a new instance is provisioned using this image.
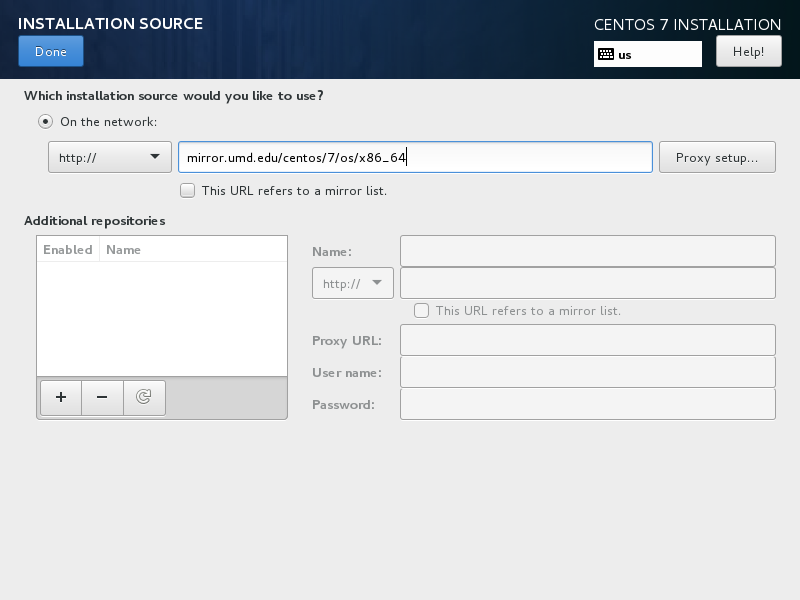
Point the installer to a CentOS web server¶
Depending on the version of CentOS, the net installer requires the user to specify either a URL or the web site and a CentOS directory that corresponds to one of the CentOS mirrors. If the installer asks for a single URL, a valid URL might behttp://mirror.umd.edu/centos/7/os/x86_64.
Consider using other mirrors as an alternative to mirror.umd.edu.
If the installer asks for web site name and CentOS directory separately, you might enter:
- Web site name:
mirror.umd.edu - CentOS directory:
centos/7/os/x86_64
See CentOS mirror page to get a full list of mirrors, click on the HTTP link of a mirror to retrieve the web site name of a mirror.
Storage devices¶
If prompted about which type of devices your installation uses, choose Virtio Block Device.
Partition the disks¶
There are different options for partitioning the disks. The default installation uses LVM partitions, and creates three partitions (/boot, /, swap), which works fine. Alternatively, you might want to create a single ext4 partition that is mounted to /, which also works fine.
If unsure, use the default partition scheme for the installer. While no scheme is inherently better than another, having the partition that you want to dynamically grow at the end of the list will allow it to grow without crossing another partition’s boundary.
Select installation option¶
Step through the installation, using the default options. The simplest thing to do is to choose the Minimal Install install, which installs an SSH server.
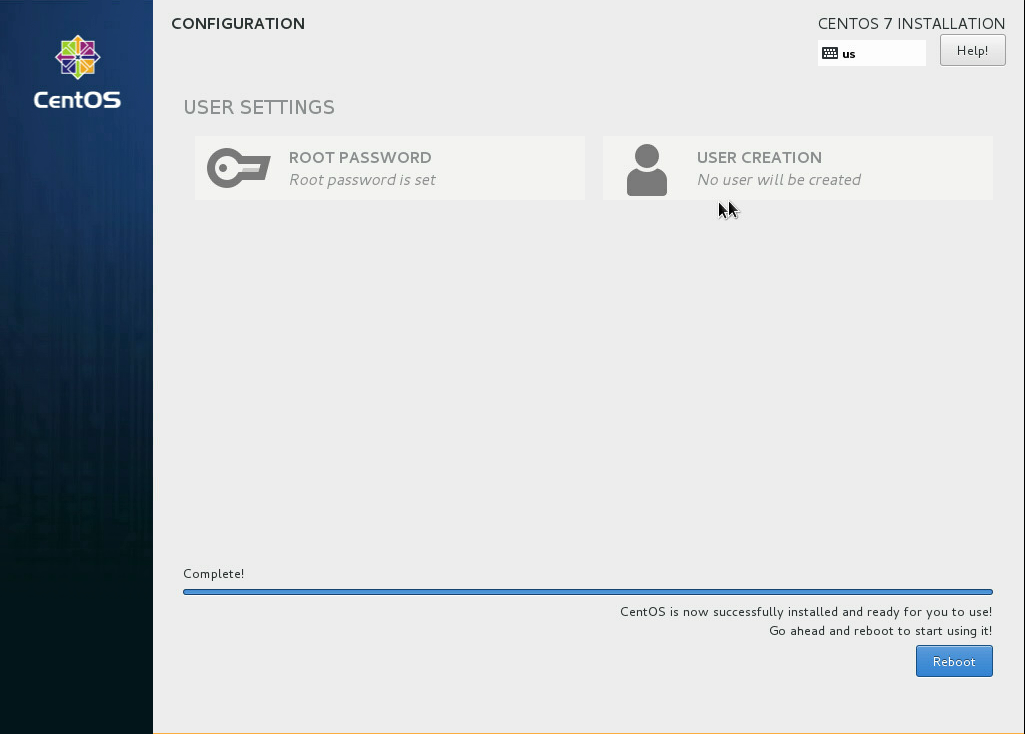
Set the root password¶
During the installation, remember to set the root password when prompted.
Detach the CD-ROM and reboot¶
Wait until the installation is complete.
To eject a disk by using the virsh command, libvirt requires that you attach an empty disk at the same target that the CD-ROM was previously attached, which may be hda. You can confirm the appropriate target using the virsh dumpxml vm-image command.
# virsh dumpxml centos
<domain type='kvm' id='19'>
<name>centos</name>
...
<disk type='block' device='cdrom'>
<driver name='qemu' type='raw'/>
<target dev='hda' bus='ide'/>
<readonly/>
<address type='drive' controller='0' bus='1' target='0' unit='0'/>
</disk>
...
</domain>
Run the following commands from the host to eject the disk and reboot using virsh, as root. If you are using virt-manager, the commands below will work, but you can also use the GUI to detach and reboot it by manually stopping and starting.
# virsh attach-disk --type cdrom --mode readonly centos "" hda
# virsh reboot centos
Install the ACPI service¶
To enable the hypervisor to reboot or shutdown an instance, you must install and run the acpid service on the guest system.
Log in as root to the CentOS guest and run the following commands to install the ACPI service and configure it to start when the system boots:
# yum install acpid
# systemctl enable acpid
Configure to fetch metadata¶
An instance must interact with the metadata service to perform several tasks on start up. For example, the instance must get the ssh public key and run the user data script. To ensure that the instance performs these tasks, use one of these methods:
- Install a
cloud-initRPM, which is a port of the Ubuntu cloud-init package. This is the recommended approach. - Modify the
/etc/rc.localfile to fetch desired information from the metadata service, as described in the next section.
Use cloud-init to fetch the public key¶
The cloud-init package automatically fetches the public key from the metadata server and places the key in an account. Install cloud-init inside the CentOS guest by running:
# yum install cloud-init
The account varies by distribution. On CentOS-based virtual machines, the account is called centos.
You can change the name of the account used by cloud-init by editing the /etc/cloud/cloud.cfg file and adding a line with a different user. For example, to configure cloud-init to put the key in an account named admin, use the following syntax in the configuration file:
users:
- name: admin
(...)
设置启动时自动把没ssh key添加到root用户,并对root用户开启密码认证,密码是你当前系统root密码,可以修改好,再上传镜像
cat /etc/cloud/cloud.cfg users: - default disable_root: 0 ssh_pwauth: 1 mount_default_fields: [~, ~, 'auto', 'defaults,nofail', '0', '2'] resize_rootfs_tmp: /dev ssh_deletekeys: 0 ssh_genkeytypes: ~ syslog_fix_perms: ~ cloud_init_modules: - migrator - bootcmd - write-files - growpart - resizefs - set_hostname - update_hostname - update_etc_hosts - rsyslog - users-groups - ssh cloud_config_modules: - mounts - locale - set-passwords - rh_subscription - yum-add-repo - package-update-upgrade-install - timezone - puppet - chef - salt-minion - mcollective - disable-ec2-metadata - runcmd cloud_final_modules: - rightscale_userdata - scripts-per-once - scripts-per-boot - scripts-per-instance - scripts-user - ssh-authkey-fingerprints - keys-to-console - phone-home - final-message - power-state-change system_info: default_user: name: root lock_passwd: false gecos: Cloud User groups: [wheel, adm, systemd-journal] sudo: ["ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:ALL"] shell: /bin/bash distro: rhel paths: cloud_dir: /var/lib/cloud templates_dir: /etc/cloud/templates ssh_svcname: sshd # vim:syntax=yaml
Install cloud-utils-growpart to allow partitions to resize¶
In order for the root partition to properly resize, install the cloud-utils-growpart package, which contains the proper tools to allow the disk to resize using cloud-init.
# yum install cloud-utils-growpart
Write a script to fetch the public key (if no cloud-init)¶
If you are not able to install the cloud-init package in your image, to fetch the ssh public key and add it to the root account, edit the /etc/rc.d/rc.local file and add the following lines before the line touch /var/lock/subsys/local:
if [ ! -d /root/.ssh ]; then
mkdir -p /root/.ssh
chmod 700 /root/.ssh
fi
# Fetch public key using HTTP
ATTEMPTS=30
FAILED=0
while [ ! -f /root/.ssh/authorized_keys ]; do
curl -f http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/public-keys/0/openssh-key
> /tmp/metadata-key 2>/dev/null
if [ $? -eq 0 ]; then
cat /tmp/metadata-key >> /root/.ssh/authorized_keys
chmod 0600 /root/.ssh/authorized_keys
restorecon /root/.ssh/authorized_keys
rm -f /tmp/metadata-key
echo "Successfully retrieved public key from instance metadata"
echo "*****************"
echo "AUTHORIZED KEYS"
echo "*****************"
cat /root/.ssh/authorized_keys
echo "*****************"
fi
done
Some VNC clients replace the colon (:) with a semicolon (;) and the underscore (_) with a hyphen (-). Make sure to specify http:and not http;. Make sure to specify authorized_keys and not authorized-keys.
The previous script only gets the ssh public key from the metadata server. It does not get user data, which is optional data that can be passed by the user when requesting a new instance. User data is often used to run a custom script when an instance boots.
As the OpenStack metadata service is compatible with version 2009-04-04 of the Amazon EC2 metadata service, consult the Amazon EC2 documentation on Using Instance Metadata for details on how to get user data.
Disable the zeroconf route¶
For the instance to access the metadata service, you must disable the default zeroconf route:
# echo "NOZEROCONF=yes" >> /etc/sysconfig/network
Configure console¶
For the nova console-log command to work properly on CentOS 7, you might need to do the following steps:
-
Edit the
/etc/default/grubfile and configure theGRUB_CMDLINE_LINUXoption. Delete therhgb quietand addconsole=tty0 console=ttyS0,115200n8to the option.For example:
... GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="crashkernel=auto rd.lvm.lv=cl/root rd.lvm.lv=cl/swap console=tty0 console=ttyS0,115200n8"
-
Run the following command to save the changes:
# grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfg Generating grub configuration file ... Found linux image: /boot/vmlinuz-3.10.0-229.14.1.el7.x86_64 Found initrd image: /boot/initramfs-3.10.0-229.14.1.el7.x86_64.img Found linux image: /boot/vmlinuz-3.10.0-229.4.2.el7.x86_64 Found initrd image: /boot/initramfs-3.10.0-229.4.2.el7.x86_64.img Found linux image: /boot/vmlinuz-3.10.0-229.el7.x86_64 Found initrd image: /boot/initramfs-3.10.0-229.el7.x86_64.img Found linux image: /boot/vmlinuz-0-rescue-605f01abef434fb98dd1309e774b72ba Found initrd image: /boot/initramfs-0-rescue-605f01abef434fb98dd1309e774b72ba.img done
Clean up (remove MAC address details)¶
The operating system records the MAC address of the virtual Ethernet card in locations such as /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0 during the instance process. However, each time the image boots up, the virtual Ethernet card will have a different MAC address, so this information must be deleted from the configuration file.
There is a utility called virt-sysprep, that performs various cleanup tasks such as removing the MAC address references. It will clean up a virtual machine image in place:
安装 libguestfs-tools
yum -y install libguestfs-tools
# virt-sysprep -d centos
Undefine the libvirt domain¶
Now that you can upload the image to the Image service, you no longer need to have this virtual machine image managed by libvirt. Use the virsh undefine vm-image command to inform libvirt:
# virsh undefine centos
上传镜像:
. /etc/kolla/admin-openrc.sh
openstack image create "CentOS-7.5" --file /tmp/centos.qcow2 --disk-format qcow2 --container-format bare --public
ImportError: No module named 'requests.packages.urllib3'
解决方法:
pip install --upgrade --force-reinstall 'requests==2.6.0' urllib3