前言
之前使用的读写分离的方案是在mybatis中配置两个数据源,然后生成两个不同的SqlSessionTemplate然后手动去识别执行sql语句是操作主库还是从库。如下图所示:
好处是,你可以人为的去控制操作的数据库。缺点也显而易见,就是代码非常麻烦,总是需要去判断使用什么库,而且遇到事务的时候还必须特别小心。
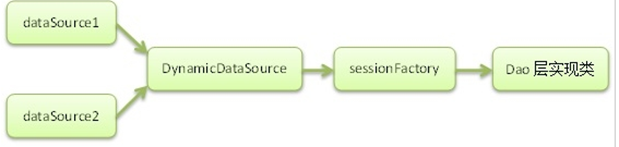
这次我们利用spring抽象路由数据源+MyBatis拦截器来实现自动的读写分离,并且保证在使用事务的情况下也能正确。结构如下图所示
我们还是按照老套路,首先我会直接进行代码的实现,然后根据源码进行分析,最后做一个总结。
代码实现
我们一共需要5个类和两个配置文件
首先来说类
/** * 全局动态数据源实体 * @author LinkinStar * */ public enum DynamicDataSourceGlobal { READ, WRITE; }
这是一个枚举的实体,后面会用到
/** * 动态数据源线程持有者 * @author LinkinStar * */ public final class DynamicDataSourceHolder { private static final ThreadLocal<DynamicDataSourceGlobal> holder = new ThreadLocal<DynamicDataSourceGlobal>(); /** * 设置当前线程使用的数据源 */ public static void putDataSource(DynamicDataSourceGlobal dataSource){ holder.set(dataSource); } /** * 获取当前线程需要使用的数据源 */ public static DynamicDataSourceGlobal getDataSource(){ return holder.get(); } /** * 清空使用的数据源 */ public static void clearDataSource() { holder.remove(); } }
以上是两个工具,下面就是重点了
一个是我们的主角,动态数据源,它继承自spring的抽象动态路由数据源
/** * 动态数据源(继承自spring抽象动态路由数据源) * @author LinkinStar * */ public class DynamicDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource { private Object writeDataSource; //写数据源 private Object readDataSource; //读数据源 /** * 在初始化之前被调用,设置默认数据源,以及数据源资源(这里的写法是参考源码中的) */ @Override public void afterPropertiesSet() { //如果写数据源不存在,则抛出非法异常 if (this.writeDataSource == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Property 'writeDataSource' is required"); } //设置默认目标数据源为主库 setDefaultTargetDataSource(writeDataSource); //设置所有数据源资源,有从库添加,没有就添加 Map<Object, Object> targetDataSources = new HashMap<>(); targetDataSources.put(DynamicDataSourceGlobal.WRITE.name(), writeDataSource); if(readDataSource != null) { targetDataSources.put(DynamicDataSourceGlobal.READ.name(), readDataSource); } setTargetDataSources(targetDataSources); super.afterPropertiesSet(); } /** * 这是AbstractRoutingDataSource类中的一个抽象方法,而它的返回值是你所要用的数据源dataSource的key值 */ @Override protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() { //根据当前线程所使用的数据源进行切换 DynamicDataSourceGlobal dynamicDataSourceGlobal = DynamicDataSourceHolder.getDataSource(); //如果没有被赋值,那么默认使用主库 if(dynamicDataSourceGlobal == null || dynamicDataSourceGlobal == DynamicDataSourceGlobal.WRITE) { return DynamicDataSourceGlobal.WRITE.name(); } //其他情况使用从库 return DynamicDataSourceGlobal.READ.name(); } public void setWriteDataSource(Object writeDataSource) { this.writeDataSource = writeDataSource; } public Object getWriteDataSource() { return writeDataSource; } public Object getReadDataSource() { return readDataSource; } public void setReadDataSource(Object readDataSource) { this.readDataSource = readDataSource; } }
然后是我们的另一个主角,动态数据源插件,实现MyBatis拦截器接口
import java.util.Locale; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Properties; import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap; import org.apache.ibatis.executor.Executor; import org.apache.ibatis.executor.keygen.SelectKeyGenerator; import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.BoundSql; import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.MappedStatement; import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.SqlCommandType; import org.apache.ibatis.plugin.Interceptor; import org.apache.ibatis.plugin.Intercepts; import org.apache.ibatis.plugin.Invocation; import org.apache.ibatis.plugin.Plugin; import org.apache.ibatis.plugin.Signature; import org.apache.ibatis.session.ResultHandler; import org.apache.ibatis.session.RowBounds; import org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionSynchronizationManager; /** * 动态数据源插件,实现MyBatis拦截器接口 * @author LinkinStar * */ @Intercepts({ @Signature(type = Executor.class, method = "update", args = { MappedStatement.class, Object.class }), @Signature(type = Executor.class, method = "query", args = { MappedStatement.class, Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class }) }) public class DynamicPlugin implements Interceptor { /** * 匹配SQL语句的正则表达式 */ private static final String REGEX = ".*insert\u0020.*|.*delete\u0020.*|.*update\u0020.*"; /** * 这个map用于存放已经执行过的sql语句所对应的数据源 */ private static final Map<String, DynamicDataSourceGlobal> cacheMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); @Override public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable { //获取当前事务同步性进行判断 boolean synchronizationActive = TransactionSynchronizationManager.isSynchronizationActive(); //如果当前正在使用事务,则使用默认的库 if (synchronizationActive) { return invocation.proceed(); } //从代理类参数中获取参数 Object[] objects = invocation.getArgs(); //其中参数的第一个值为执行的sql语句 MappedStatement ms = (MappedStatement) objects[0]; //当前sql语句所应该使用的数据源,通过sql语句的id从map中获取,如果获取到,则之前已经执行过直接取, DynamicDataSourceGlobal dynamicDataSourceGlobal = cacheMap.get(ms.getId()); if (dynamicDataSourceGlobal != null) { DynamicDataSourceHolder.putDataSource(dynamicDataSourceGlobal); return invocation.proceed(); } //如果没有,则重新进行存放 //ms中获取方法,如果是查询方法 if (ms.getSqlCommandType().equals(SqlCommandType.SELECT)) { //!selectKey 为自增id查询主键(SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID() )方法,使用主库 if(ms.getId().contains(SelectKeyGenerator.SELECT_KEY_SUFFIX)) { dynamicDataSourceGlobal = DynamicDataSourceGlobal.WRITE; } else { BoundSql boundSql = ms.getSqlSource().getBoundSql(objects[1]); //通过正则表达式匹配,确定使用那一个数据源 String sql = boundSql.getSql().toLowerCase(Locale.CHINA).replaceAll("[\t\n\r]", " "); if(sql.matches(REGEX)) { dynamicDataSourceGlobal = DynamicDataSourceGlobal.WRITE; } else { dynamicDataSourceGlobal = DynamicDataSourceGlobal.READ; } } } else { dynamicDataSourceGlobal = DynamicDataSourceGlobal.WRITE; } //将sql对应使用的数据源放进map中存放 cacheMap.put(ms.getId(), dynamicDataSourceGlobal); //最后设置使用的数据源 DynamicDataSourceHolder.putDataSource(dynamicDataSourceGlobal); //执行代理之后的方法 return invocation.proceed(); } @Override public Object plugin(Object target) { if (target instanceof Executor) { return Plugin.wrap(target, this); } else { return target; } } @Override public void setProperties(Properties properties) { } }
最后是我们的配角,动态数据源的事务管理器
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager; import org.springframework.transaction.TransactionDefinition; /** * 动态数据源事务管理器 * @author LinkinStar * */ public class DynamicDataSourceTransactionManager extends DataSourceTransactionManager { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; /** * 只读事务到读库,读写事务到写库 */ @Override protected void doBegin(Object transaction, TransactionDefinition definition) { //根据事务可读性进行判断 boolean readOnly = definition.isReadOnly(); //只读类型事务可以只用从库 if(readOnly) { DynamicDataSourceHolder.putDataSource(DynamicDataSourceGlobal.READ); } else { DynamicDataSourceHolder.putDataSource(DynamicDataSourceGlobal.WRITE); } super.doBegin(transaction, definition); } /** * 清理本地线程的数据源(会被默认调用,调用时清除相应数据源) */ @Override protected void doCleanupAfterCompletion(Object transaction) { super.doCleanupAfterCompletion(transaction); DynamicDataSourceHolder.clearDataSource(); } }
然后是两个配置文件,根据你自己的需要进行修改
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd"> <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:resources/jdbc.properties"/> <bean id="abstractDataSource" abstract="true" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource" destroy-method="close"> <property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}" /> <property name="minIdle" value="${jdbc.minIdle}"></property> <property name="maxIdle" value="${jdbc.maxIdle}"></property> <property name="maxWait" value="${jdbc.maxWait}"></property> <property name="maxActive" value="${jdbc.maxActive}"></property> <property name="initialSize" value="${jdbc.initialSize}"></property> <property name="testWhileIdle"><value>true</value></property> <property name="testOnBorrow"><value>true</value></property> <property name="testOnReturn"><value>false</value></property> <property name="validationQuery"><value>SELECT 1 FROM DUAL</value></property> <property name="validationQueryTimeout"><value>1</value></property> <property name="timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis"><value>3000</value></property> <property name="numTestsPerEvictionRun"><value>2</value></property> </bean> <bean id="dataSourceRead" parent="abstractDataSource"> <property name="url" value="${jdbc.url.read}" /> <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username.read}"/> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password.read}"/> </bean> <bean id="dataSourceWrite" parent="abstractDataSource"> <property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}" /> <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/> </bean> <bean id="dataSource" class="com.ssm.dao.data.DynamicDataSource"> <property name="writeDataSource" ref="dataSourceWrite"></property> <property name="readDataSource" ref="dataSourceRead"></property> </bean> <!--配置基于注解的声明式事务,默认使用注解来管理事务行为--> <tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/> <!--配置事务管理器(mybatis采用的是JDBC的事务管理器)--> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property> </bean> <bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean"> <!--注入数据库连接池--> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" /> <!--扫描entity包,使用别名,多个用;隔开--> <property name="typeAliasesPackage" value="com/ssm/entity" /> <!--扫描sql配置文件:mapper需要的xml文件--> <property name="mapperLocations" value="classpath*:com/ssm/dao/sqlxml/*.xml"></property> <property name="plugins"> <array> <bean class="com.ssm.dao.data.DynamicPlugin" /> </array> </property> </bean> <bean id="sqlSessionTemplate" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate"> <constructor-arg name="sqlSessionFactory" ref="sqlSessionFactory" /> </bean> <!--配置扫描Dao接口包,动态实现DAO接口,注入到spring容器--> <bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer"> <!--注入SqlSessionFactory--> <property name="sqlSessionFactoryBeanName" value="sqlSessionFactory"/> <!-- 给出需要扫描的Dao接口--> <property name="basePackage" value="com.ssm.dao"/> </bean> </beans>
另外就是jdbc的配置文件,也需要根据自己进行修改,这边使用两个
jdbc.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8 jdbc.username=root jdbc.password=123456 jdbc.url.read=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/xxx?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8 jdbc.username.read=root jdbc.password.read=123456 jdbc.maxActive = 2 jdbc.maxIdle =5 jdbc.minIdle=1 jdbc.initialSize =3 jdbc.maxWait =3000
至此所有的配置都已经完成,现在你已经可以进行测试,看看在查询和新增的时候是否使用的是不同的数据库。
看看在使用事务的情况下,是否使用相同的数据库。
实现分析
首先我们来分析两个主角
动态数据源(继承自spring抽象动态路由数据源)
先看一下源码中父类的说明
/** * Abstract {@link javax.sql.DataSource} implementation that routes {@link #getConnection()} * calls to one of various target DataSources based on a lookup key. The latter is usually * (but not necessarily) determined through some thread-bound transaction context. * * @author Juergen Hoeller * @since 2.0.1 * @see #setTargetDataSources * @see #setDefaultTargetDataSource * @see #determineCurrentLookupKey() */ public abstract class AbstractRoutingDataSource extends AbstractDataSource implements InitializingBean {
我们写的这个类中重写了父类两个重要的方法
1、afterPropertiesSet
首先源码中是这样的:
@Override public void afterPropertiesSet() { if (this.targetDataSources == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Property 'targetDataSources' is required"); } this.resolvedDataSources = new HashMap<Object, DataSource>(this.targetDataSources.size()); for (Map.Entry<Object, Object> entry : this.targetDataSources.entrySet()) { Object lookupKey = resolveSpecifiedLookupKey(entry.getKey()); DataSource dataSource = resolveSpecifiedDataSource(entry.getValue()); this.resolvedDataSources.put(lookupKey, dataSource); } if (this.defaultTargetDataSource != null) { this.resolvedDefaultDataSource = resolveSpecifiedDataSource(this.defaultTargetDataSource); } }
而我们重写的目的就是为了设置默认我们的主库和从库
2、determineCurrentLookupKey
这是AbstractRoutingDataSource类中的一个抽象方法,而它的返回值是你所要用的数据源dataSource的key值
在这个方法中我们通过DynamicDataSourceHolder获取当前线程所应该使用的数据源,然后将数据源的名字返回。也就是dataSource的key值。
然后是下一个主角,动态数据源插件,实现MyBatis拦截器接口,这个类一共干了下面几个事情
(当我们实现了MyBatis拦截器接口之后就能在数据库执行sql之前做操作,具体请参考别的博客,这里不细说)
1、通过当前是否使用事务确定数据源,如果使用事务,那么默认使用主库
2、从sql语句中获取sql执行的类型,根据具体的类型确定使用的数据源
3、利用cacheMap缓存已经进行判断过的sql和对应执行时使用的数据源
4、通过DynamicDataSourceHolder保存当前线程所需要使用的数据源
最后一个是动态数据源事务管理器
这个类主要是保证,当一些事务是只读类型的事务时,使用的数据源是从库。
然后保存到DynamicDataSourceHolder中
总结
1、使用此种方式实现数据库读写分离,对于代码来说不会对现有代码造成影响,没有入侵性,容易剥离和加入。
2、对于事务使用同一个数据库能保证读写的一致性。
3、不需要人为去判断使用哪一个数据库,不用担心会出现人物问题。
4、扩展性上面,当有多个从库的时候,不要想着配置多个从库数据源解决问题,而是应该配置数据库负载均衡然后实现多个从数据库的访问。