1. JUC 简介
- 在 Java 5.0 提供了
java.util.concurrent(简称JUC)包,在此包中增加了在并发编程中很常用的工具类,
用于定义类似于线程的自定义子系统,包括线程池,异步 IO 和轻量级任务框架;还提供了设计用于多线程上下文中
的 Collection 实现等;
2. volatile 关键字
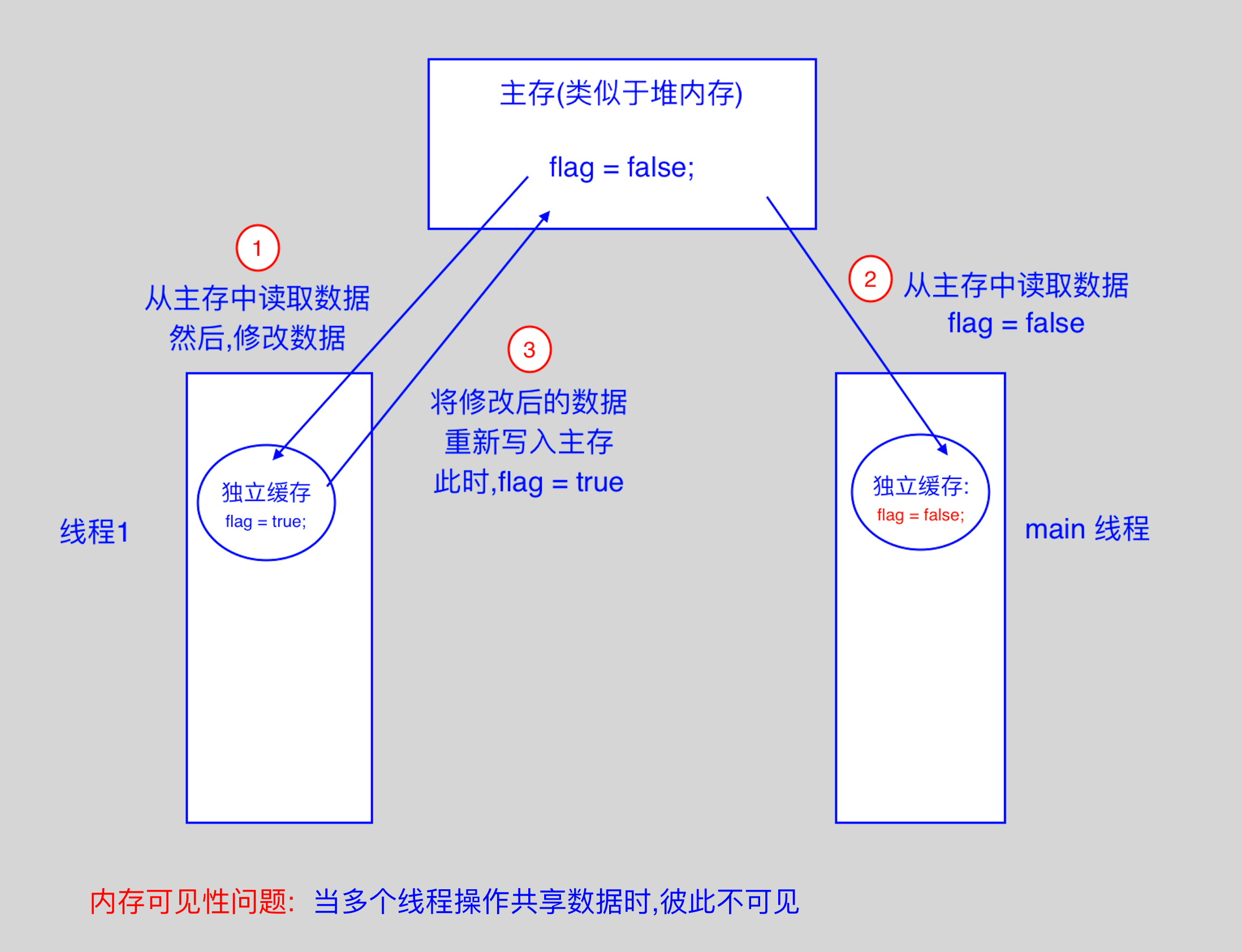
- volatile 关键字: 当多个线程进行操作共享数据时,可以保证内存中的数据是可见的;相较于 synchronized 是一种
较为轻量级的同步策略; - volatile 不具备"互斥性";
- volatile 不能保证变量的"原子性";
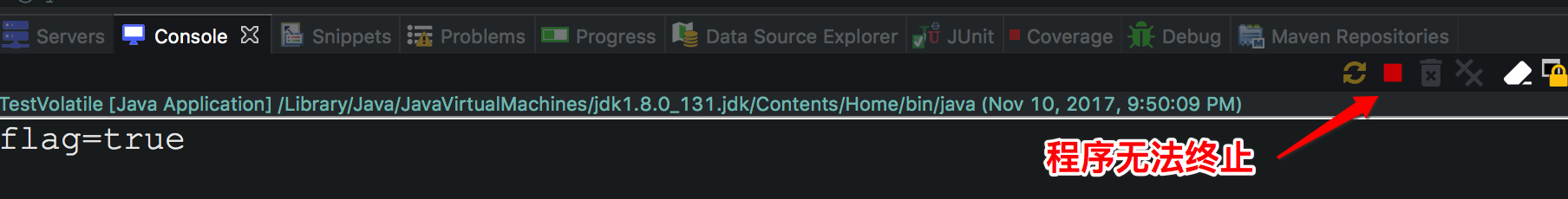
// 使用 volatile 之前
public class TestVolatile{
public static void main(String[] args){
ThreadDemo td = new ThreadDemo();
new Thread(td).start();
while(true){
if(td.isFlag()){
System.out.println("########");
break;
}
}
}
}
class ThreadDemo implements Runnable{
private boolean flag = false;
public void run(){
try{
// 该线程 sleep(200), 导致了程序无法执行成功
Thread.sleep(200);
}catch(InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
flag = true;
Sytem.out.println("flag="+isFlag());
}
public boolean isFlag(){
return flag;
}
public void setFlag(boolean flag){
this.flag = flag;
}
}
// 解决问题方式一: 同步锁
// 但是,效率太低
public class TestVolatile{
public static void main(String[] args){
ThreadDemo td = new ThreadDemo();
new Thread(td).start();
while(true){
// 使用同步锁
synchronized(td){
if(td.isFlag()){
System.out.println("########");
break;
}
}
}
}
}
// 解决方式二: 使用 volatile 关键字
public class TestVolatile{
public static void main(String[] args){
ThreadDemo td = new ThreadDemo();
new Thread(td).start();
while(true){
if(td.isFlag()){
System.out.println("########");
break;
}
}
}
}
class ThreadDemo implements Runnable{
private volatile boolean flag = false;
同上(略)
}
3. i++ 的原子性问题
i++的操作实际上分为三个步骤: "读-改-写";- 原子性: 就是"i++"的"读-改-写"是不可分割的三个步骤;
- 原子变量: JDK1.5 以后,
java.util.concurrent.atomic包下,提供了常用的原子变量;- 原子变量中的值,使用
volatile修饰,保证了内存可见性; - CAS(Compare-And-Swap) 算法保证数据的原子性;
- 原子变量中的值,使用
int i = 10;
i = i++; // 此时, i=10
执行步骤:
int temp = i;
i = i + 1;
i = temp;
// 测试类
public class TestAtomicDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
AtomicDemo ad = new AtomicDemo();
for(int i=0; i < 10; i++){
new Thread(ad).start();
}
}
}
class AtomicDemo implements Runnable{
private int serialNumber = 0;
public void run(){
try{
Thread.sleep(200);
}catch(InterruptedException e){
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + getSerialNumber());
}
public int getSerialNumber(){
return serialNumber++;
}
}

// 改进: 使用原子变量
class AtomicDemo implements Runnable{
private AtomicInteger serialNumber = new AtomicInteger();
public void run(){
try{
Thread.sleep(200);
}catch(InterruptedException e){
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+getSerialNumber());
}
public int getSerialNumber(){
// 自增运算
return serialNumber.getAndIncrement();
}
}
3.1 CAS 算法
- CAS(Compare-And-Swap) 算法是硬件对于并发的支持,针对多处理器操作而设计的处理器中的一种特殊指令,用于
管理对共享数据的并发访问; - CAS 是一种无锁的非阻塞算法的实现;
- CAS 包含了三个操作数:
- 需要读写的内存值: V
- 进行比较的预估值: A
- 拟写入的更新值: B
- 当且仅当 V == A 时, V = B, 否则,将不做任何操作;
// 模拟CAS 算法
class CompareAndSwap{
private int value;
// 获取内存值
public synchronized int get(){
return value;
}
// 无论更新成功与否,都返回修改之前的内存值
public synchronized int compareAndSwap(int expectedValue, int newValue){
// 获取旧值
int oldValue = value;
if(oldValue == expectedValue){
this.value = newValue;
}
// 返回修改之前的值
return oldValue;
}
// 判断是否设置成功
public synchronized boolean compareAndSet(int expectedValue, int newValue){
return expectedValue == compareAndSwap(expectedValue, newValue);
}
}
public class TestCompareAndSwap{
public static void main(String[] args){
final CopareAndSwap cas = new CompareAndSwap();
for(int i=0; i<10; i++){
// 创建10个线程,模拟多线程环境
new Thead(new Runnable(){
public void run(){
int expectedValue = cas.get();
boolean b = cas.compareAndSet(expectedValue, (int)(Math.random()*100));
System.out.println(b);
}
}).start();
}
}
}
4. 并发容器类
- Java 5.0 在
java.util.concurrent包中提供了多种并发容器类来改进同步容器的性能;
4.1 ConcurrentHashMap
- ConcurrentHashMap 同步容器类是 Java5 增加的一个线程安全的哈希表;介于 HashMap 与 Hashtable 之间;
内部采用"锁分段"机制替代Hashtable的独占锁,进而提高性能; - 此包还提供了设计用于多线程上下文中的
Collection实现:ConcurrentHashMap,ConcurrentSkipListMap
ConcurrentSkipListSet,CopyOnWriteArrayList和CopyOnWriteArraySet;- 当期望许多线程访问一个给定collection时,
ConcurrentHashMap通常优于同步的HashMap;
ConcurrentSkipListMap通常优于同步的TreeMap; - 当期望的读数和遍历远远大于列表的更新数时,
CopyOnWriteArrayList优于同步的ArrayList;
- 当期望许多线程访问一个给定collection时,
4.2 CountDownLatch(闭锁)
CountDownLatch是一个同步辅助类,在完成一组正在其他线程中执行的操作之前,它允许一个或多个线程一直等待;
// 测试类: 计算多线程的执行时间
public class TestCountDownLatch{
public static void main(String[] args){
final CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(10);
LatchDemo ld = new LatchDemo(latch);
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 创建10个线程
for(int i=0; i<10; i++){
new Thread(ld).start();
}
try{
latch.await();
}catch(InterruptedException e){
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗费时间为:"+(end - start));
}
}
class LatchDemo implements Runnable{
private CountDownLatch latch;
// 有参构造器
public LatchDemo(CountDownLatch latch){
this.latch = latch;
}
public void run(){
synchronized(this){
try{
// 打印50000以内的偶数
for(int i=0; i<50000; i++){
if(i % 2 == 0){
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}finally{
// 线程数量递减
latch.countDown();
}
}
}
}
5. 创建执行线程的方式三
- 相较于实现 Runnable 接口的方式,实现 Callable 接口类中的方法可以有返回值,并且可以抛出异常;
// 测试类
public class TestCallable{
public static void main(String[] args){
ThreadDemo td = new ThreadDemo();
// 执行 Callable 方式,需要 FutureTask 实现类的支持
// FutureTask 实现类用于接收运算结果, FutureTask 是 Future 接口的实现类
FutureTask<Integer> result = new FutureTask<>(td);
new Thread(result).start();
// 接收线程运算后的结果
try{
// 只有当 Thread 线程执行完成后,才会打印结果;
// 因此, FutureTask 也可用于闭锁
Integer sum = result.get();
System.out.println(sum);
}catch(InterruptedException | ExecutionException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
class ThreadDemo implements Callable<Integer>{
// 需要实现的方法
public Integer call() throws Exception{
// 计算 0~100 的和
int sum = 0;
for(int i=0; i<=100; i++){
sum += i;
}
return sum;
}
}
6. 同步锁(Lock)
// 测试类: 以卖票为例
// 使用 lock 之前
public class TestLock{
public static void main(String[] args){
Ticket ticket = new Ticket();
new Thread(ticket,"1号窗口").start();
new Thread(ticket,"2号窗口").start();
new Thread(ticket,"3号窗口").start();
}
}
class Ticket implements Runnable{
private int tick = 100;
public void run(){
while(true){
if(tick > 0){
try{
Thread.sleep(200);
}catch(InterruptedException e){
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"完成售票,余票为: "+ --tick);
}
}
}
}
// 使用 Lock
class Ticket implements Runnable{
private int tick = 100;
private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
public void run(){
while(true){
// 上锁
lock.lock();
try{
if(tick > 0){
try{
Thread.sleep(200);
}catch(InterruptedException e){
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"完成售票,余票为: "+ --tick);
}
}finally{
// 释放锁
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
}
// 练习: 程序按序交替
// 编写一个程序,开启3个线程,这三个线程的 ID 分别为 A, B, C, 每个线程将自己的 ID 在屏幕上打印10遍,
// 要求输出的结果必须按顺序显示:
// 如: ABCABCABC... 依次递归
public class TestABCAlternate{
public static void main(String[] args){
AlternateDemo ad = new AlternateDemo();
new Thread(new Runnable(){
public void run(){
for(int i=1; i<20; i++){
ad.loopA(i);
}
}
},"A").start();
new Thread(new Runnable(){
public void run(){
for(int i=1; i<20; i++){
ad.loopB(i);
}
}
},"B").start();
new Thread(new Runnable(){
public void run(){
for(int i=1; i<20; i++){
ad.loopC(i);
System.out.println("--------------------");
}
}
},"C").start();
}
}
class AlternateDemo{
private int number = 1; // 当前正在执行线程的标记
private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private Condition condition1 = lock.newCondition();
private Condition condition2 = lock.newCondition();
private Condition condition3 = lock.newCondition();
// totalLoop 表示循环第几轮
// 线程A
public void loopA(int totalLoop){
// 上锁
lock.lock();
try{
// 1. 判断
if(number != 1){
condition1.await();
}
// 2. 打印
for(int i=1; i <= 5; i++){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" "+i+" "+totalLoop);
}
// 3. 唤醒线程B
number = 2;
condition2.signal();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
// 释放锁
lock.unlock();
}
}
// 线程B
public void loopB(int totalLoop){
// 上锁
lock.lock();
try{
// 1. 判断
if(number != 2){
condition2.await();
}
// 2. 打印
for(int i=1; i <= 15; i++){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" "+i+" "+totalLoop);
}
// 3. 唤醒线程C
number = 3;
condition3.signal();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
// 释放锁
lock.unlock();
}
}
// 线程C
public void loopC(int totalLoop){
// 上锁
lock.lock();
try{
// 1. 判断
if(number != 3){
condition3.await();
}
// 2. 打印
for(int i=1; i <= 20; i++){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" "+i+" "+totalLoop);
}
// 3. 唤醒线程A
number = 1;
condition1.signal();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
// 释放锁
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
7. ReadWriteLock(读写锁)
// 测试类
public class TestReadWriteLock{
public static void main(String[] args){
ReadWriteLockDemo rw = new ReadWriteLockDemo();
// 一个线程进行写
new Thread(new Runnable(){
public void run(){
rw.set((int)(Math.random()*100));
}
},"Write:").start();
// 100个线程进行读操作
for(int i=0; i<100; i++){
new Thread(new Runnable(){
public void run(){
rw.get();
}
},"Read:").start();
}
}
}
class ReadWriteLockDemo{
private int number = 0;
private ReadWriteLock lock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
// 读
public void get(){
lock.readLock().lock(); // 上锁
try{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+number);
}finally{
lock.readLock().unlock(); // 释放锁
}
}
// 写
public void set(int number){
lock.writeLock().lock();
try{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
this.number = number;
}finally{
lock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
}
8. 线程八锁
// 测试类
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
Demo demo = new Demo();
Demo demo2 = new Demo();
new Thread(new Runnable(){
public void run(){
demo.getOne();
}
}).start();
new Thread(new Runnable(){
public void run(){
// demo2.getTwo();
demo.getTwo();
}
}).start();
}
}
class Demo{
public synchronized void getOne(){
try{
Thread.sleep(3000);
}catch(InterruptedException e){
}
System.out.println("one");
}
public synchronized void getTwo(){
System.out.println("two");
}
}
/*
* 1. 两个普通同步方法,两个线程,标准打印, 打印输出: one two
* 2. 新增 Thread.sleep() 给 getOne(), 打印输出: one two
* 3. 新增普通方法 getThree(), 打印输出: three one two
* 4. 两个普通同步方法,两个Demo对象, 两个线程,打印输出: two one
* 5. 修改 getOne() 为静态同步方法, 一个Demo对象, 打印输出: two one
* 6. 修改两个方法都为静态同步方法, 一个 Demo 对象, 打印输出: one two
* 7. 修改 getone() 为静态同步方法, 两个 Demo 对象, 打印输出: two one
* 8. 两个均为静态同步方法,两个 Demo 对象,打印输出: one two
*/
// 总结:
// 1. 非静态方法的锁默认为 this, 静态方法的锁为 "对应的Class实例";
// 2. 在某一个时刻内,只能有一个线程持有锁,无论几个方法;
9. 线程池
- 线程池提供了一个线程队列,队列中保存着所有等待状态的线程;
- 避免了创建与销毁线程的额外开销,提高了响应速度;
- 线程池的体系结构
java.util.concurrent.Executor: 负责线程的使用和调度的根接口;ExecutorService: 子接口,线程池的主要接口;ThreadPoolExecutor: 线程池的实现类;ScheduledExecutorService: 子接口,负责线程的调度;ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor: 继承了线程池的实现类,实现了负责线程调度的子接口;
- 工具类:
ExecutorsExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(): 创建固定大小的线程池;ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool(): 缓存线程池,线程池中线程的数量不固定,可以根据需求自动更改数量;ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor(): 创建单个线程池, 线程池中只有一个线程;ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(): 创建固定大小的线程,可以延时或定时的执行任务;
public class TestThreadPool{
public static void main(String[] args){
// 1. 创建线程池
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
ThreadPoolDemo tpd = new ThreadPoolDemo();
// 2. 为线程池中线程分配任务
// submit(Callable<T> task)
// submit(Runnable task)
for(int i=0; i<10; i++){
pool.submit(tpd);
}
// 3. 关闭线程池
pool.shutdown();
}
}
class ThreadPoolDemo implements Runnable{
private int i=0;
public void run(){
while(i <= 100){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" : "+ i++)
}
}
}
9.1 线程调度
public class TestScheduledThreadPool{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
// 1. 创建线程池
ScheduledExecutorService pool = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5);
// 2. 分配任务
// pool.shedule(Callalbe<T> callable, long delay, TimeUnit unit(时间单位))
for(int i=0; i < 10; i++){
Future<Integer> result = pool.schedule(new Callable<Integer>(){
public Integer call() throws Exception{
// 产生100以内的随机数
int num = new Random().nextInt(100);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ ":" + num);
return num;
}
}, 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println(result.get());
}
//3. 关闭线程池
pool.shutdown();
}
}
10 Fork/Join 框架
public class TestForkJoinPool{
public static void main(String[] args){
ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool();
ForkJoinTask<Long> task = new ForkJoinSumCalculate(0L, 100000000L);
Long sum = pool.invoke(task);
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
class ForkJoinSumCalculate extends RecursiveTask<Long>{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 24340990L;
private long start;
private long end;
private static final long THURSHOLD = 10000L; // 拆分临界值
// 有参构造器
public ForkJoinSumCalculate(long start, long end){
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
}
public Long compute(){
long length = end - start;
if(length <= THURSHOLD){
long sum = 0L;
for(long i = start; i<=end; i++){
sum += i;
}
return sum;
}else{
long middle = (start + end ) / 2;
ForkJoinSumCalculate left = new ForkJoinSumCalculate(start, middle);
left.fork(); // 进行拆分,同时压入线程队列
ForkJoinSumCalculate right = new ForkJoinSumCalculate(middle + 1, end);
right.fork(); // 进行拆分,同时压入线程队列
return left.join() + right.join();
}
}
}
参考资料