类加载
在Java代码中,类型的加载、连接与初始化过程都是在程序运行期间完成的。
类型可以是Class,Interface, 枚举等。
Java虚拟机与程序的生命周期
在如下几种情况下,Java虚拟机将结束生命周期
1)执行了System.exit() 方法
2)程序正常执行结束
3)程序在执行过程中遇到了异常或者错误而异常终止。
4) 由于操作系统出现错误导致Java虚拟机进程终止。
1.JVM运行流程,JVM基本结构
2、类加载器双亲委派模型
3、ClassLoader源码解析
4、从源码分析实现自定义类加载器
一、JVM运行流程,JVM基本结构

JVM基本结构
类加载器,运行时数据区,执行引擎,本地接口
Class Files -> ClassLoader -> 运行时数据区 -> 执行引擎 -> 本地方法库
类的装载:
加载,连接(验证,准备,解析),初始化,使用,卸载
初始化: 执行类的构造器<clinit>,为类的静态变量赋初始值
构造器:
1、static变量
2、staitc{} 语句
构造方法: 实例化的对象
二、类加载器双亲委派模型
1、为什么使用双亲委派模型
避免重复加载
2、JDK已有的类加载器
BootStrap ClassLoader JVM自己的类加载器,启动加载器。(C++) 主要加载rt.jar
Extension ClassLoader extends ClassLoader 扩展类加载器 加载%Java_home%lib/ext/*.jar
APP ClassLoader extends ClassLoader 应用加载器 -> Classpath
打印Class Loader
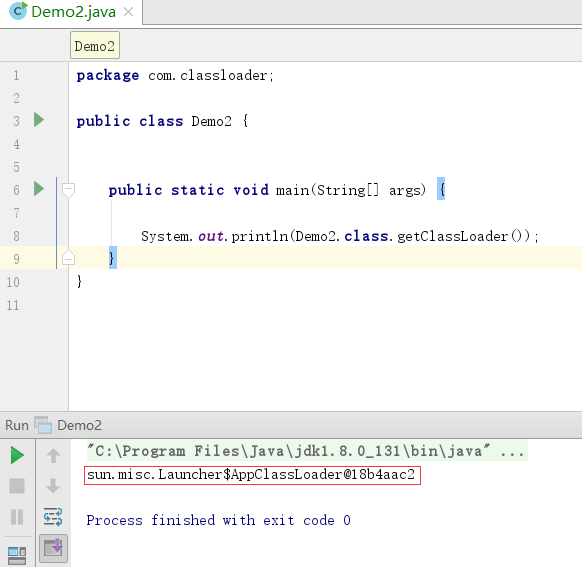
打印parent ClassLoader
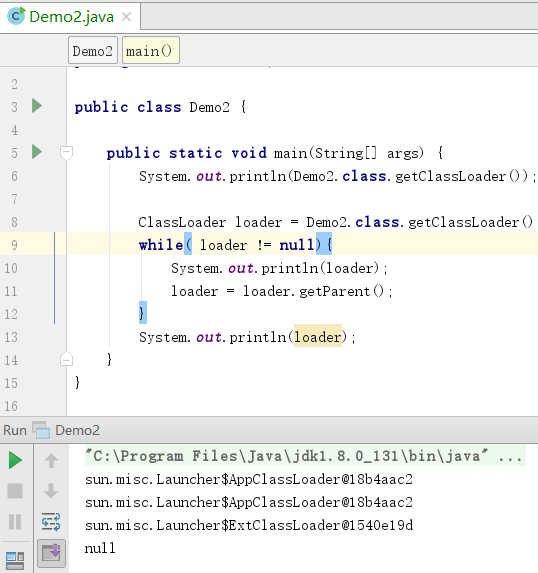
null为启动类加载器。
三、ClassLoader源码解析
ClassLoader所在的路径
1、创建关于ClassLoader的Demo
public class MyTest15 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] strings = new String[2];
System.out.println(strings.getClass());
System.out.println(strings.getClass().getClassLoader()); //启动类加载器
System.out.println("--------------------");
MyTest15[] myTest15s = new MyTest15[2];
System.out.println(myTest15s.getClass().getClassLoader()); //AppClassLoader
System.out.println("--------------------");
int[] ints = new int[2];
System.out.println(ints.getClass().getClassLoader()); //原生类型没有classLoader
}
}
打印结果:
class [Ljava.lang.String; null -------------------- sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@18b4aac2 -------------------- null
2、定位到loadClass方法

loadClass(name,false)方法
protected Class<?> loadClass(String name, boolean resolve)
throws ClassNotFoundException
{
synchronized (getClassLoadingLock(name)) {
// First, check if the class has already been loaded
Class c = findLoadedClass(name);
if (c == null) {
long t0 = System.nanoTime();
try {
if (parent != null) {
c = parent.loadClass(name, false);
} else {
c = findBootstrapClassOrNull(name);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// ClassNotFoundException thrown if class not found
// from the non-null parent class loader
}
if (c == null) {
// If still not found, then invoke findClass in order
// to find the class.
long t1 = System.nanoTime();
c = findClass(name);
// this is the defining class loader; record the stats
sun.misc.PerfCounter.getParentDelegationTime().addTime(t1 - t0);
sun.misc.PerfCounter.getFindClassTime().addElapsedTimeFrom(t1);
sun.misc.PerfCounter.getFindClasses().increment();
}
}
if (resolve) {
resolveClass(c);
}
return c;
}
}
3、双亲委派模型

如果parent不为空,则调用parent的loadClass方法。
findClass类的目的是自定义的ClassLoader

四、自定义类加载器 extends ClassLoader -> 完成自定义加载路径
1) 创建Demo.java文件,路径为D:/tmp/Demo.java

然后编译成class文件
javac Demo.java
2) 创建自定义类加载器
package com.classloader;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class MyClassLoader extends ClassLoader {
private String path; //加载的路径
private String name; //类加载器名称
public MyClassLoader(String name, String path){
super(); //让系统类加载器成为该类的父加载器
this.name = name;
this.path = path;
}
public MyClassLoader(ClassLoader parent, String name, String path){
super(parent); //显示指定父加载器
this.name = name;
this.path = path;
}
/**
* 加载自定义的类,通过自定义的ClassLoader
*/
@Override
protected Class<?> findClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException {
byte[] data = readClassFileToByteArray(name);
return this.defineClass(name, data,0, data.length);
}
/**
* 获取.class文件的字节数组
* com.classLoader.Demo ->
* D:/temp/com/classLoader/Demo.class
* @return
*/
private byte[] readClassFileToByteArray(String name) {
InputStream is = null;
byte[] returnData = null;
name = name.replaceAll("\.","/");
String filePath = this.path + name + ".class";
File file = new File(filePath);
ByteArrayOutputStream os = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
try{
is = new FileInputStream(file);
int tmp = 0;
while ((tmp = is.read()) != -1){
os.write(tmp);
}
returnData = os.toByteArray();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if(is != null){
is.close();
}
if(os != null){
os.close();
}
}catch (Exception e2){
}
}
return returnData;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return this.name;
}
}
3、使用自定义类加载器
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException {
MyClassLoader loader = new MyClassLoader("MyClassLoadName1", "D:/tmp/");
Class<?> c = loader.loadClass("Demo");
c.newInstance();
}
}
运行结果
Demo, MyClassLoadName1
4、测试父加载器
1)、工程里的Demo.java增加测试方法

2)、修改D盘下的Demo.java
增加包名
package com.classloader;
public class Demo {
public Demo(){
System.out.println("Demo, " + this.getClass().getClassLoader());
}
}
路径为,并且重新生成class文件

3) 测试文件
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException {
MyClassLoader loader = new MyClassLoader("MyClassLoadName1", "D:/tmp/");
Class<?> c = loader.loadClass("com.classloader.Demo");
c.newInstance();
}
}
运行结果:

说明使用的是父类加载器,加载的是工程里的那个Demo.class文件。
修改如下:

传入null,说明父加载器为启动加载器。
显示结果:
Demo, MyClassLoadNameChild