引自:https://www.cnblogs.com/fnlingnzb-learner/p/10752113.html
一、背景
在开发过程中,我们的软件会面对不同的运行环境,比如开发环境、测试环境、生产环境,而我们的软件在不同的环境中,有的配置可能会不一样,比如数据源配置、日志文件配置、以及一些软件运行过程中的基本配置,那每次我们将软件部署到不同的环境时,都需要修改相应的配置文件,这样来回修改,很容易出错,而且浪费劳动力。
maven提供了一种方便的解决这种问题的方案,就是profile功能。
二、profile简介
profile可以让我们定义一系列的配置信息,然后指定其激活条件。这样我们就可以定义多个profile,然后每个profile对应不同的激活条件和配置信息,从而达到不同环境使用不同配置信息的效果。
profile定义的位置
(1) 针对于特定项目的profile配置我们可以定义在该项目的pom.xml中。(下面举例是这种方式)
(2) 针对于特定用户的profile配置,我们可以在用户的settings.xml文件中定义profile。该文件在用户家目录下的“.m2”目录下。
(3) 全局的profile配置。全局的profile是定义在Maven安装目录下的“conf/settings.xml”文件中的。
Spring Boot Profile
Spring Boot Profile 有许多的功能,这里只说管理配置的内容。Spring 加载配置的顺序如下:
- Jar 包外的
application-{profile}.properties - Jar 包内的
application-{profile}.properties - Jar 包外的
application.properties - Jar 包内的
application.properties
例如,如果我们在 application.properties 中指定
spring.profiles.active = dev
则 spring 会使用 application-dev.properties 文件中的配置来覆盖 application.properties 文件中的相应配置。
三、配置动态打包
1、配置profile
在项目的profile中添加如下的profile配置:
<profiles>
<profile>
<!-- 本地开发环境 -->
<id>dev</id>
<properties>
<profiles.active>dev</profiles.active>
</properties>
<activation>
<!-- 设置默认激活这个配置 -->
<activeByDefault>true</activeByDefault>
</activation>
</profile>
<profile>
<!-- 发布环境 -->
<id>release</id>
<properties>
<profiles.active>release</profiles.active>
</properties>
</profile>
<profile>
<!-- 测试环境 -->
<id>beta</id>
<properties>
<profiles.active>beta</profiles.active>
</properties>
</profile>
</profiles>
这里定义了三个环境,分别是dev(开发环境)、beta(测试环境)、release(发布环境),其中开发环境是默认激活的(activeByDefault为true),这样如果在不指定profile时默认是开发环境,也在package的时候显示指定你要选择哪个开发环境,详情见后面。
在编译时指定 mvn clean install -Pprod 就能切换成 prod profile。
2.在 pom.xml 中定义资源过滤
目的是为了让 maven 在构建时用 profile 中指定的属性来替换 application.properties 中的内容。
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resources</directory>
<!--①-->
<excludes>
<exclude>application*.properties</exclude>
</excludes>
</resource>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resources</directory>
<!--②-->
<filtering>true</filtering>
<includes>
<include>application.properties</include>
<include>application-${profile.active}.properties</include>
</includes>
</resource>
</resources>
①中,我们通过 excludes 来将所有的 application*.properties 排除在外,这样 maven 在打包时就不会复制这些文件。毕竟我们不希望把 application-dev.properties 也包含在 prod 的 jar 包里。
②中,通过开启 filtering,maven 会将文件中的 @XX@ 替换 profile 中定义的 XX 变量/属性。另外,我们还通过 includes 来告诉 maven 根据profile 来复制对应的 properties 文件。
这里注意一个参数<filtering>true</filtering>,一定要设置成true.这样才会用对应env目录下的配置文件覆盖原来的。
其中最重要的是<filtering>true</filtering>这段,这个配置的意思是过滤上面指定属性文件中的占位符,占位符是${变量名称}这样的形式,maven会自动读取配置文件,然后解析其中的占位符,使用上面pom文件中定义的属性进行替换。
3.构建不同的包
mvn clean package -P<profile_name>
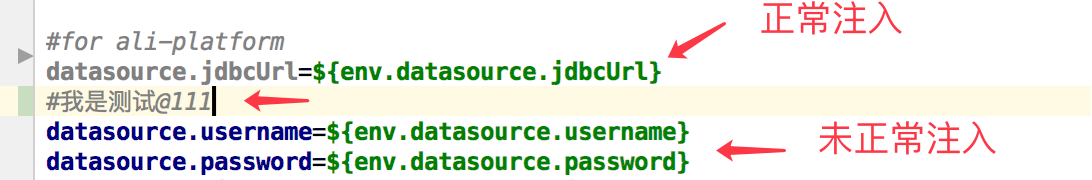
四、遇到的坑
在application.xml文件中不能出现@关键字,就算你注释了也不行。当出现@了,之后的所有环境变量将不会被注入
如: