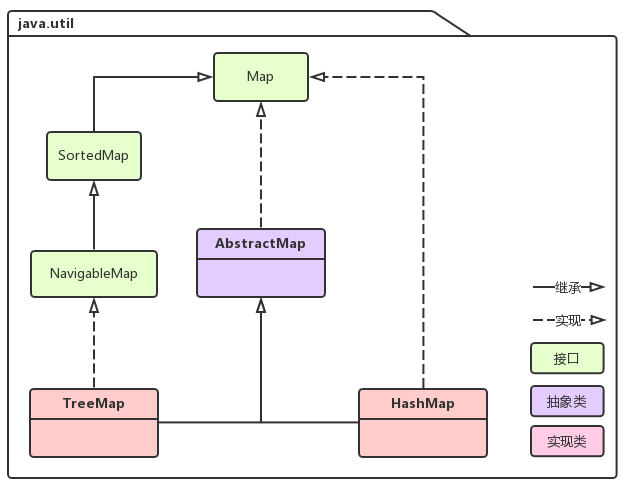
一 Map相关类图
二 Map接口
1 Map接口中的方法
| jdk |
方法名 |
简单描述 |
|
put(K,V):V |
添加value,当Key对应无值,返回null;有值则返回上一个值。(覆盖式,可以反复覆盖前一个value) |
| 8 |
putIfAbsent(K,V):V |
添加value,当Key对应无值,返回null;有值则返回上一个值。(独占式,只能赋值一次(除非调用了删除)) |
|
get(Object):V |
获取key对应的value |
| 8 |
getOrDefault(Object,V):V |
获取key对应的value,当获取不到时,返回传入的V值。 |
|
remove(Object):V |
删除key对应的value |
| 8 |
remove(Object,Object):boolean |
当传入的value与map中存的value相等,则执行删除操作 |
|
keySet():Set<K> |
返回所有key值 |
|
values():Collection<V> |
返回所有value值 |
|
entrySet():Set<Entry<K,V>> |
返回所有Entry值(下一节介绍) |
|
containsValue(Object):boolean |
判断是否包含该value |
|
containsKey(Object):boolean |
判断是否包含该value |
| 8 |
replace(K,V):V |
当该key对应有值,将value覆盖;否则,不操作。 |
| 8 |
replace(K,V value1,V value2):boolean |
当传入的value1与key对应值相等,将value2覆盖value1。 |
| 8 |
merge(K,V,BiFunction):V |
如果指定的键尚未与值关联或与 null 关联, 则将其与给定的非 null 值相关联。 |
| 8 |
compute(K,BiFunction):V |
与put相同,直接覆盖 |
| 8 |
computeIfAbsent(K,Function):V |
如果指定的键尚未与值关联或与 null 关联,使用计算值替换。 |
| 8 |
computeIfPresent(K,BiFunction):V |
如果指定的键已有绑定值则采用计算值替换 |
| 8 |
forEach |
遍历 |
2、Demo
Map<Integer, String> map = new HashMap<>();
System.out.println(map.get(1)); // null
System.out.println(map.getOrDefault(1,"1")); // "1"
// put
Map<Integer, String> map = new HashMap<>();
System.out.println(map.put(1, "1")); // null
System.out.println(map.put(1, "2")); // 1
System.out.println("map:"+map); // map:{1=2}
// putIfAbsent
Map<Integer, String> map = new HashMap<>();
System.out.println(map.putIfAbsent(1, "1")); // null
System.out.println(map.putIfAbsent(1, "2")); // 1
System.out.println("map:"+map); // map:{1=1}
Map<Integer, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(1,"1");
System.out.println(map.remove(1,"2")); // false
System.out.println(map); // {1=1}
System.out.println(map.remove(1)); // 1
System.out.println(map); // {}
Map<Integer, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(1,"1");
map.put(2,"2");
map.merge(1,"test",String::concat); // 1取到“1”,“1”.concat("test") = "1test"
map.merge(3,"3",String::concat); // 3对应null,直接返回“3”
System.out.println("map:"+map); // map:{1=1test, 2=2, 3=3}
// merge最后一个参数是BiFunction,下面三种写法结果相同
// BiFunction是二元函数,传入两个参数,返回一个结果。
map.merge(1, "test", String::concat);
map.merge(1, "test", (s, s2) -> s.concat(s2));
map.merge(1, "test", new BiFunction<String, String, String>() {
@Override
public String apply(String oldVal, String newVal) {
return oldVal.concat(newVal);
}
});
3 jdk部分源码
public interface Map<K, V> {
interface Entry<K, V> {
K getKey();
V getValue();
V setValue(V value);
// ......
}
default V getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue) {
V v;
return (((v = get(key)) != null) || containsKey(key))
? v
: defaultValue;
}
default V putIfAbsent(K key, V value) {
V v = get(key);
if (v == null) {
v = put(key, value);
}
return v;
}
default boolean remove(Object key, Object value) {
Object curValue = get(key);
if (!Objects.equals(curValue, value) ||
(curValue == null && !containsKey(key))) {
return false;
}
remove(key);
return true;
}
default V computeIfAbsent(K key,
Function<? super K, ? extends V> mappingFunction) {
Objects.requireNonNull(mappingFunction);
V v;
if ((v = get(key)) == null) {
V newValue;
if ((newValue = mappingFunction.apply(key)) != null) {
put(key, newValue);
return newValue;
}
}
return v;
}
// ... 都是比较简单的代码,不做过多介绍了
// Java8的java.util.function包可以参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/linzhanfly/p/9686941.html
}
三 SortedMap(继承Map接口)
1 SortedMap接口中的方法
| 方法 |
描述 |
| comparator():Comparator< ? super K > |
返回比较器(可能返回null) |
| subMap(K,K):SortedMap<K,V> |
截取fromKey到toKey的Map |
| headMap(K):SortedMap<K,V> |
截取小于toKey的Map |
| tailMap(K):SortedMap<K,V> |
截取大于fromKey的Map |
| fristKey():K |
最小的Key值 |
| lastKey():K |
最大的Key值 |
2 Demo
SortedMap<Integer, Character> map = new TreeMap<>();
map.put(1,'c');
map.put(3,'b');
map.put(2,'a');
System.out.println(map.keySet()); // [1, 2, 3]
System.out.println(map.values()); // 按照Key值顺序输出: [c, a, b]
SortedMap<Integer, Character> map = new TreeMap<>(
(key1, key2) -> -key1.compareTo(key2)
);
map.put(1, 'c');
map.put(3, 'b');
map.put(2, 'a');
System.out.println(map.keySet()); // [3, 2, 1]
- subMap:左闭右开 // [fromKey,toKey)
SortedMap<Integer, Character> map = new TreeMap<>();
map.put(1, 'c');
map.put(3, 'b');
map.put(2, 'a');
map.put(4, 'e');
SortedMap<Integer, Character> subMap = map.subMap(2, 4);
System.out.println(subMap); // {2=a, 3=b}
SortedMap<Integer, Character> map = new TreeMap<>();
map.put(1, 'c');
map.put(3, 'b');
map.put(2, 'a');
System.out.println("firstKey:"+map.firstKey()); // firstKey:1
System.out.println("lastKey:"+map.lastKey()); // lastKey:3
四 NavigableMap(继承SortedMap接口)
1 NavigableMap接口中的方法
| 方法 |
描述 |
| lowerKey(K):K |
寻找小于传参的Key值,找不到则返回null |
| lowerEntry(K):Entry<K,V> |
|
| higherKey(K):K |
寻找大于传参的Key值,找不到则返回null |
| higherEntry(K):Entry<K,V> |
|
| ceilingKey(K):K |
寻找大于或等于传参的Key值,找不到则返回null |
| ceilingEntry(K):Entry<K,V> |
|
| floorKey(K):K |
寻找小于或等于传参的Key值,找不到则返回null |
| floorEntry(K):Entry<K,V> |
|
| navigableKeySet():NavigableSet< K > |
顺序keySet |
| descendingKeySet():NavigableSet< K > |
倒序keySet |
| ...剩下的省略 |
|
2 Demo
NavigableMap<Integer, Character> map = new TreeMap<>();
map.put(1, 'c');
map.put(3, 'b');
map.put(2, 'a');
System.out.println(map.lowerKey(3)); // 2
System.out.println(map.floorKey(3)); // 3
System.out.println(map.higherKey(1)); // 2
System.out.println(map.ceilingKey(1)); // 1
System.out.println(map.navigableKeySet()); // [1, 2, 3]
System.out.println(map.descendingKeySet()); // [3, 2, 1]
五 AbstractMap
public abstract class AbstractMap<K,V> implements Map<K,V> {
public static class SimpleImmutableEntry<K,V> implements Entry<K,V>, java.io.Serializable{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7138329143949025153L;
private final K key;
private final V value;
public V setValue(V value) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
// 对于不可变字段的set方法可以参考这个设计
// ......
}
public abstract Set<Entry<K,V>> entrySet();
// keySet和values都使用了懒加载策略
transient Set<K> keySet;
transient Collection<V> values;
public Set<K> keySet() {
Set<K> ks = keySet;
if (ks == null) {
ks = new AbstractSet<K>() {
// ...... 基本实现方法
};
keySet = ks;
}
return ks;
}
public int size() {
return entrySet().size();
}
// 复用size方法:自己实现容器时也需要尽可能复用已有的方法,减少重复的代码。
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size() == 0;
}
// toString方法:对于容器的toString方法一般都需要遍历,遍历就涉及大量的字符串拼接,字符串拼接速度提升需要StringBuilder。
public String toString() {
Iterator<Entry<K,V>> i = entrySet().iterator();
if (! i.hasNext())
return "{}";
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append('{');
for (;;) {
Entry<K,V> e = i.next();
K key = e.getKey();
V value = e.getValue();
sb.append(key == this ? "(this Map)" : key);
sb.append('=');
sb.append(value == this ? "(this Map)" : value);
if (! i.hasNext())
return sb.append('}').toString();
sb.append(',').append(' ');
}
}
// get remove containsValue containsKey都依赖抽象方法:entrySet():Set
// Set -> Collection -> Iterable
// AbstractMap的遍历都依赖Iterable的iterator方法返回的Iterator,都采用了迭代器遍历。
public V get(Object key) {
Iterator<Entry<K,V>> i = entrySet().iterator();
if (key==null) {
while (i.hasNext()) {
Entry<K,V> e = i.next();
if (e.getKey()==null)
return e.getValue();
}
} else {
while (i.hasNext()) {
Entry<K,V> e = i.next();
if (key.equals(e.getKey()))
return e.getValue();
}
}
return null;
}
// ...没有需要注意的地方,省略了
}
六 TreeMap
1 概述
- Java版本的红黑树实现映射类
- 红黑树的前序遍历是根据值的大小排序的,即TreeMap的Key值具有有序性
- 学习过红黑树的童鞋,看这个类的实现不难
2 JDK源码
private final Comparator<? super K> comparator;
// 红黑树根节点
private transient Entry<K,V> root;
// 长度
private transient int size = 0;
// fail-fast实现字段
private transient int modCount = 0;
// 提供一些Set的操作方法:包装了一下TreeMap中的方法
private transient EntrySet entrySet;
// TreeMap的Key值具有有序性
private transient KeySet<K> navigableKeySet;
// 倒序Map
private transient NavigableMap<K,V> descendingMap;
// 节点状态常量
private static final boolean RED = false;
private static final boolean BLACK = true;
static final class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
K key;
V value;
Entry<K,V> left;
Entry<K,V> right;
Entry<K,V> parent;
boolean color = BLACK;
// 省略构造函数 getter和setter equals toString方法
}
public V put(K key, V value) {
Entry<K,V> t = root;
if (t == null) { // 根节点为空创建新节点
compare(key, key); // null值检查,TreeMap不允许key为空
root = new Entry<>(key, value, null);
size = 1;
modCount++;
return null;
}
int cmp;
Entry<K,V> parent; // 寻找插入新节点的父节点
Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator; // 自定义比较器
if (cpr != null) {
do {
parent = t;
cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key);
if (cmp < 0) t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0) t = t.right;
else return t.setValue(value);// 如果key值相等,直接覆盖value即可
} while (t != null);
}
else {
if (key == null) throw new NullPointerException();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
do {
parent = t;
cmp = k.compareTo(t.key);
if (cmp < 0) t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0) t = t.right;
else return t.setValue(value); // 如果key值相等,直接覆盖value即可
} while (t != null);
}
Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<>(key, value, parent);
if (cmp < 0) parent.left = e;
else parent.right = e;
// 节点插入后可能导致红黑树不能保持黑平衡,于是需要进行平衡调整
fixAfterInsertion(e);
size++;
modCount++;
return null;
}
private void fixAfterInsertion(Entry<K,V> x) {
x.color = RED; // 新插入的节点为红色
// 如果父亲节点和新子节点都为红色,表示破环了平衡
// 看懂下面需要了解红黑树的保持平衡的操作:左旋转 右旋转 颜色反转
while (x != null && x != root && x.parent.color == RED) {
if (parentOf(x) == leftOf(parentOf(parentOf(x)))) {
Entry<K,V> y = rightOf(parentOf(parentOf(x)));
if (colorOf(y) == RED) {
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
setColor(y, BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED);
x = parentOf(parentOf(x));
} else {
if (x == rightOf(parentOf(x))) {
x = parentOf(x);
rotateLeft(x);
}
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED);
rotateRight(parentOf(parentOf(x)));
}
} else {
Entry<K,V> y = leftOf(parentOf(parentOf(x)));
if (colorOf(y) == RED) {
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
setColor(y, BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED);
x = parentOf(parentOf(x));
} else {
if (x == leftOf(parentOf(x))) {
x = parentOf(x);
rotateRight(x);
}
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED);
rotateLeft(parentOf(parentOf(x)));
}
}
}
root.color = BLACK;
}
七 HashMap
1 概述
- 最常用的映射类,非线程安全
- hash算法:计算hash值,数组取模,得到值。时间复杂度为常数,但由于hash冲突的存在并无法做到绝对的常数级别
- hash冲突:
- 链表:长度大于8时,转化为红黑树
- 红黑树:查询效率高
- 内部维护一个Node数组:可变长数组实现存在resize操作
- 建议:请学习了hash算法和红黑树数据结构再来看jdk的源码,不然效率太低。
2Jdk源码
// 实际存放K和V的节点数组,Node实现Entry接口
transient Node<K,V>[] table;
// 采用懒加载机制,entrySet()返回值
transient Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet;
// 容器现在的大小
transient int size;
// fail-fast相关,请参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/linzhanfly/p/9571180.html
transient int modCount;
// 扩容时机:capacity * load factor
int threshold;
// 负载因子:决定容器装载到何种程度需要扩容(如:装了50%就希望扩容,则设置为0.5)
final float loadFactor;
// 默认负载因子
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16
// 最大容量值
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
// 默认负载因子
// 为什么选择0.75?请参考:https://www.jianshu.com/p/64f6de3ffcc1
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
// hash冲突的存在,不同的key值可能同一个hash值。
// hash冲突时,默认将新的key添加在链表末尾,但是随着链表的增大,查询效率越来越低(链表只能遍历查询,复杂度O(n))。
// java8为了解决这个问题,通过将链表转换成红黑树来提高查询效率(复杂度O(lgn))
// 那链表什么时候转换成红黑树?当链表长度大于TREEIFY_THRESHOLD时
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;
// 那红黑树什么时候转换成链表?当链表长度小于TREEIFY_THRESHOLD时
// 为什么TREEIFY_THRESHOLD和UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD为什么不相等?
// 因为震荡问题,假设加入某个值后,链表长度变成8,链表转换成红黑树;下一次操作又删除了该值,红黑树转换成链表。转换过程需要浪费一定的时间,具体的复杂度分析起来很复杂,以后有机会具体分析一下。
// 于是设置比TREEIFY_THRESHOLD小一点可以缓解震荡导致的复杂度飙升问题。
static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6;
// size到达threshold大小会进行扩容
// table比较小时,很容易导致扩容;所以需要限制一下链表转红黑树的最小table大小
// 如果不设置,连续的8次冲突就链表转红黑树,添加多4次,就resize了,hash也重算了,这样就不划算。
static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
this.threshold = tableSizeFor(initialCapacity);
}
// 根据容量值计算table数组所需的大小,返回值一定为2的幂次方
// 获取cap-1的二进制表达中最左边的1后面全变为1,如01000000 -> 01111111 ,最后+1 -> 10000000
static final int tableSizeFor(int cap) {
int n = cap - 1; // 01000000
n |= n >>> 1; // 01000000 移1位-> 00100000 或运算-> 01100000
n |= n >>> 2; // 01100000 移2位-> 00011000 或运算-> 01111000
n |= n >>> 4; // 01111000 移4位-> 00000111 或运算-> 01111111
n |= n >>> 8; // ...省略
n |= n >>> 16;
return (n < 0) ? 1 : (n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : n + 1;
}
// ...... 其他构造方法复用了该构造方法
// 链表节点
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
V value;
Node<K,V> next;
// ......
// hashCode和equals与key和value相关
public final int hashCode() {
return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value);
}
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this)
return true;
if (o instanceof Map.Entry) {
Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o;
if (Objects.equals(key, e.getKey()) &&
Objects.equals(value, e.getValue()))
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
// 红黑树节点
static final class TreeNode<K,V> extends LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> {
TreeNode<K,V> parent; // red-black tree links
TreeNode<K,V> left;
TreeNode<K,V> right;
TreeNode<K,V> prev; // needed to unlink next upon deletion
boolean red;
TreeNode(int hash, K key, V val, Node<K,V> next) {
super(hash, key, val, next);
}
// 循环获取根节点
final TreeNode<K,V> root() {
for (TreeNode<K,V> r = this, p;;) {
if ((p = r.parent) == null) return r;
r = p;
}
}
// 链表 -> 树
final void treeify(Node<K,V>[] tab) {
TreeNode<K,V> root = null;
for (TreeNode<K,V> x = this, next; x != null; x = next) {
next = (TreeNode<K,V>) x.next;
x.left = x.right = null;
if (root == null) {
x.parent = null;
x.red = false; // 根节点为黑
root = x;
}else {
K k = x.key;
int h = x.hash;
Class<?> kc = null;
TreeNode<K,V> p = root;
for (;;) {
int dir, ph;
K pk = p.key;
if ((ph = p.hash) > h) dir = -1;
else if (ph < h) dir = 1;
else if ((kc == null &&
(kc = comparableClassFor(k)) == null) ||
(dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) == 0)
dir = tieBreakOrder(k, pk);
TreeNode<K,V> xp = p;
if ((p = (dir <= 0) ? p.left : p.right) == null) {
x.parent = xp;
if (dir <= 0) xp.left = x;
else xp.right = x;
root = balanceInsertion(root, x); //左旋或者右旋来保持红黑树的黑平衡
break;
}
}
}
}
moveRootToFront(tab, root);
}
// 树 -> 链表
final Node<K,V> untreeify(HashMap<K,V> map) {
Node<K,V> hd = null, tl = null;
for (Node<K,V> q = this; q != null; q = q.next) {
Node<K,V> p = map.replacementNode(q, null);
if (tl == null) hd = p;
else tl.next = p;
tl = p;
}
return hd;
}
// HashMap.replacementNode方法
Node<K,V> replacementNode(Node<K,V> p, Node<K,V> next) {
return new Node<>(p.hash, p.key, p.value, next);
}
}
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value;
}
// hash值 = 高16位 低16位(高16位与低16位的异或)
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k;
// 第一个if:判断Map中有数据,并取出first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 && (first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
// hash相等与key值相等则返回
if (first.hash == hash &&
((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return first;
// 查看是否有下一个节点
if ((e = first.next) != null) {
// 红黑树查询结果
if (first instanceof TreeNode)
return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
// 链表查询结果
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
return null;
}
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
// evict字段在HashMap无实现
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
// 如果tab数组为空或者长度为0,则扩容。
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
// 没有hash冲突则直接赋值
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
// hash和key都相等,所以直接覆盖
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
// 红黑树插入新节点
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
// 链表循环插入
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
// 链表尾部则直接插入
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
// 链表 -> 红黑树
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
// 覆盖成功,跳出循环
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize(); // 扩容
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
