集合
Collection接口
概述
作用是用来存储多个数据, 集合中把每个数据叫元素
和数组的比较:
- 类型: 数组只能存相同类型的数据. 集合可以是多种数据类型
- 长度: 数组一旦创建长度就不能改变, 集合长度改变
- 遍历: 数组常用下标遍历, 方式单一. 插入, 删除操作繁琐. 集合则更加方便
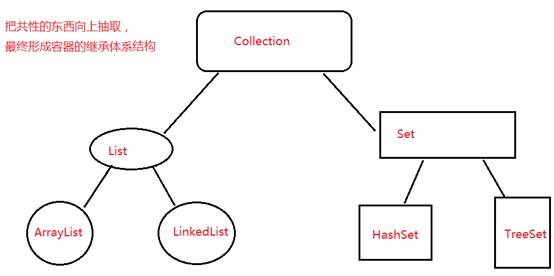
集合的继承结构:
Conllection(接口)List(接口)ArrayList(实现类)LinkedList(实现类)
Set(接口)HashSet(实现类)TreeSet(实现类)
集合的继承结构:
Collection接口常用方法 (子类通用)
| 返回值 | 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| boolean | add(E e) | 添加元素(泛型) |
| void | clear() | 清空集合, 移除集合所有元素 |
| boolean | contains(Object o) | 判断是否包含指定元素, 存在返回true, 否则返回false |
| int | hashCode() | 返回集合在内存中的哈希码 |
| boolean | isEmpty() | 是否为空, 是为true, 否则为flase |
| boolean | remove(Object o) | 移除指定元素, 移除成返回true, 否则返回false |
| int | size() | 返回集合的大小 |
| Object[] | toArray() | 把集合转为数组 |
| boolean | addAll(Collection c) | 把c集合中的所有元素都添加进来, 添加成功为true |
| boolean | containsAll(Collection c) | 如果集合包含c, 则返回true |
| boolean | removeAll(Collection c) | 删除c中包含的所有元素, 删除成功返回true |
| boolean | retainAll(Collection c) | 只保留集合中 c 包含的元素, 其余元素全部删除 |
| Iterator | iterator() | 返回一个迭代器, 用来迭代(遍历)数组(使用方法如下) |
注意: iterator() 迭代方法使用
Collection c = new ArrayList();
c.add("艾迪");
c.add("杰克");
c.add("迪迦");
c.add("泰罗");
Iterator<String> it = c.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {// hasNext() 用来判断集合中是否还有下一个元素, 有就返回true
String value = it.next(); // 获取元素'
System.out.println(value);
}
结果:
艾迪
杰克
迪迦
泰罗
测试案例:方法的使用
//这个类用来测试 collection接口的使用
public class Test5_Collection {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1、创建collection对象
Collection<String> c = new ArrayList<>();
//2、常用方法
c.add("jack");//添加元素
c.add("rose");
c.add("hanmeimei");
c.add("lilei");
// c.clear(); //清空集合
System.out.println(c.contains("jack") );//判断是否包含
System.out.println(c.equals("hanmeimei") );//判断是否相等
System.out.println(c.hashCode());//获取集合在内存中的哈希码值
System.out.println(c.isEmpty());//判断集合是否为空
System.out.println(c.remove("lilei"));//删除指定元素
System.out.println(c.size());//获取集合的长度
Object[] obs = c.toArray();//把集合中的元素放入数组中
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(obs));
//集合间的操作----
Collection<String> c2 = new ArrayList<>();
//3、常用方法
c2.add("jack");//添加元素
c2.add("rose");
c2.add("hello");
System.out.println(c.addAll(c2));//添加另一个集合
System.out.println(c.containsAll(c2));//是否包含另一个集合
System.out.println(c);
// System.out.println(c.removeAll(c2));//删除另一个集合
// System.out.println(c);
// System.out.println(c.retainAll(c2));
// System.out.println(c);
//
//4、集合元素的迭代
Iterator<String> it = c.iterator() ;
while( it.hasNext() ) {//hasNext()用来判断集合中是否还有下一个元素,有就返回true
String value = it.next() ; //next()获取迭代到的元素
System.out.println(value);
}
}
}
List (接口)
概述
有序的 collection(也称为序列)。此接口的用户可以对列表中每个元素的插入位置进行精确地控制。用户可以根据元素的整数索引(在列表中的位置)访问元素,并搜索列表中的元素。
特点:
有序, 可重复, 有索引
特有方法
| 返回值 | 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| void | add(int index, E e) | 在指定下标处插入 |
| boolean | addAll(int index, Collection c) | 向指定下标添加集合c |
| E | get(int index) | 使用下标获取元素 |
| int | indexOf(Object o) | 返回第一次出现指定元素的索引值 |
| int | lastIndexOf(Object o) | 返回最后一次出现指定元素的索引 |
| E | remove(int index) | 移除指定索引的元素, 并返回元素的值 |
| ListIterator |
listIterator() | 获取迭代对象 |
| E | set(int index, E e) | 替换指定下标的元素 |
| List |
subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) | 按下标截取集合, 包含头, 不包含尾 |
测试案例:方法的使用+索引
//这个类用来测试 List接口的使用:元素可重复 + 元素都有序 + 元素有索引
public class Test6_List {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1、创建List对象
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
//2、自己的特有方法
list.add("java");
list.add("php");
list.add("hadoop");
list.add("hadoop");
list.add(null);
list.add("hadoop");
list.add(0,"皮皮霞");//按照索引添加元素
System.out.println(list.get(1));//获取指定索引存着的元素
System.out.println(list.indexOf("hadoop"));//获取第一次出现的索引值
System.out.println(list.lastIndexOf("hadoop"));//获取最后一次出现的索引值
System.out.println(list.remove(1));//把指定索引的元素干掉
System.out.println(list.set(0,"刘沛霞"));//替换
System.out.println(list);
List<String> list2 = list.subList(1, 4);//截取子List,含头不含尾[1,4)
System.out.println(list2);
}
}
List的遍历方式:
方式一:iterator()迭代
//iterator()迭代
Iterator<String> iterator = list.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
String next = iterator.next();//获取元素指针后移
System.out.println(next);
}
方式二:listIterator()迭代
//listIterator迭代
ListIterator<String> listit = list.listIterator();
while (listit.hasNext()) {
String next = listit.next();
System.out.println(next);
}
方式三:for循环
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(list.get(i));
// list.set(i, "ppp"+i);
}
方式四:增强foreach
//增强for遍历list集合
for (String str : list) {
System.out.println(str);
}