Java IO 继承关系图
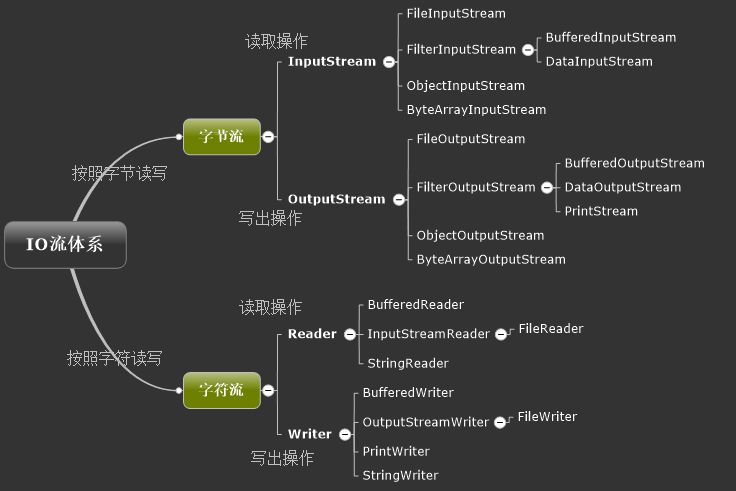
IO流常用基类:
(1)字节流
输出字节流:OutputStream:字节写入流抽象类
|--->FileOutputStream:
字节写入流
|--->BufferedOutputStream:
字节写入流缓冲区
输入字节流:InputStream:字节读取流抽象类
|--->FileInputStream:
字节读取流
|--->BufferedInputStream:
字节读取流缓冲区
(2)字符流
输出字符流:Writer:字符写入流的抽象
|--->FileWriter:
字符写入流
|--->BufferedWriter:
字符写入流缓冲区
|--->OutputStreamWriter:
字符通向字节的转换流(涉及键盘录入时用)
输入字符流:Reader: 字符读取流的抽象类
|--->FileReader:
字符读取流
|--->BufferedReader:
字符读取流缓冲区
|--->InputStreamReader:
字节通向字符的转换流(涉及键盘录入时用)
InputStreamReader
常用的构造方法:
public InputStreamReader(InputStream in)
public InputStreamReader(InputStream in, String charsetName) 创建一个InputStreamReader,使用给定的名字的编码
重要的属性:
private final StreamDecoder sd; 表示一个解码器,说明读取的数据会被转成指定的编码,若没有指定,那么将使用平台默认的编码。
重要的方法:
int read(); 读取单个字符。
int read(char[] cbuf) 从流中的0位置读取,读取cbuf长度的字符。
int read(char[] cbuf, int offset, int length) offset表示从流中哪个位置开始储存字符,length表示最大的存储个数。
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("C:\Users\Desktop\1.txt"),"gbk");
char[] cbuf = new char[10];
int len = 0;
while((len = isr.read(cbuf))>0){
System.out.print(new String(cbuf,0,len));
}
isr.close();
}
OutputStreamWriter
常用的构造方法:
public OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out) 创建使用默认字符编码的 OutputStreamWriter。
public OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out, String charsetName) 创建使用指定字符集的 OutputStreamWriter。
重要的属性:
private final StreamEncoder se; 表示一个编码器,将内存中的字符流根据指定的编码表编码成为字节储存。
重要方法:
void write(char[] cbuf,int off,int len) 写入字符数组的某一部分
void write(int c) 写入单个字符
void write(String str,int off,int len) 写入字符串的某一部分
void flash() 刷新该流的缓存
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("C:\Users\Desktop\1.txt");
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(os);
String str = "你好吗?
我很好!";
osw.write(str);
osw.close();
}
FileInputStream
常用的构造函数:
FileInputStream(File file) 创建“File对象”对应的“文件输入流”
FileInputStream(FileDescriptor fd) 创建“文件描述符”对应的“文件输入流”
FileInputStream(String path) 创建“文件(路径为path)”对应的“文件输入流”
重要方法:
int available() 返回“剩余的可读取的字节数”或者“skip的字节数”
void close() 关闭“文件输入流”
FileChannel getChannel() 返回FileChannel
final FileDescriptor getFD()返回文件描述符 int read() 返回文件输入流的下一个字节
int read(byte[] buffer, int off, int len) 读取“文件输入流”的数据并存在到buffer,从off开始存储,存储长度是len。
long skip(long n) 跳过n个字节
int read(); 读取单个字节。
int read(byte[] b)从流中的0位置读取,读取b长度的字节。
int read(byte[] b, int offset, int length) offset表示从流中哪个位置开始储存字节,length表示最大的存储个数。
FileOutputStream
常用的构造方法:
FileOutputStream(File file) 创建“File对象”对应的“文件输入流”;默认“追加模式”是false,即“写到输出的流内容”不是以追加的方式添加到文件中。
FileOutputStream(File file, boolean append) 建“File对象”对应的“文件输入流”;指定“追加模式”。
FileOutputStream(FileDescriptor fd) 创建“文件描述符”对应的“文件输入流”;默认“追加模式”是false,即“写到输出的流内容”不是以追加的方式添加到文件中。
FileOutputStream(String path) 创建“文件(路径为path)”对应的“文件输入流”;默认“追加模式”是false,即“写到输出的流内容”不是以追加的方式添加到文件中。
FileOutputStream(String path, boolean append) 创建“文件(路径为path)”对应的“文件输入流”;指定“追加模式”。
重要方法:
FileChannel getChannel() 返回FileChannel
final FileDescriptor getFD() 返回文件描述符
void write(byte[] buffer, int off, int len) 将buffer写入到“文件输出流”中,从buffer的off开始写,写入长度是len。
void write(int n) 写入字节n到“文件输出流”中
void write(byte[] b) 将b.length个字节从指定的数组写入到此输出流中
FileReader
是InputStreamReader的子类,内部一共三个方法:
public FileReader(String fileName) throws FileNotFoundException {
super(new FileInputStream(fileName));
}
public FileReader(File file) throws FileNotFoundException {
super(new FileInputStream(file));
}
public FileReader(FileDescriptor fd) {
super(new FileInputStream(fd));
}
都是通过其父类实现的,全部都是调用了父类(InputStreamReader)的方法。不能为其指定编码格式,使用平台默认的编码格式读取字符,在不要求转码的情况下,这是一个简便的写法,用于从文件中读取字符。
BufferedReader
常用的构造方法:
BufferReader(Reader in)创建一个使用默认大小输入缓冲区的缓冲字符输入流。
BufferReader(Reader in,int sz)创建一个使用指定大小的输入缓冲区的缓冲字符输入流。
重要方法:
String readLine()读取一个文本行,到达文件结尾返回null
int read() 读取单个字符,到达文件结尾返回-1
int read(char[] cbuf,int off,int len)将字符读入数组的某一部分
boolean ready() 判断该流是否已经准备好被读取
void reset()将流重置到最新的标记
void mark(int readAheadLimit)标记流中的当前位置
long skip(Long n)跳过n个字符
BufferedWriter
常用构造方法:
BufferedWriter bf = new BufferedWriter(Writer out ); 创建一个使用默认大小输出缓冲区的缓冲字符输出流。
重要方法:
void newLine() 写入一个行分隔符。
void write (int c)写入单个字符
void write(char[] cbuf,int off,int len) 写入字符数组的某一部分
void write (String s,int off,int len)写入字符串的某一部分
void close()关闭此流,但是先刷新它
实现文件的复制:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("C:\Users\Desktop\1.txt"));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("C:\Users\Desktop\2.txt"));
String str;
while((str = br.readLine())!=null){
bw.write(str);
bw.newLine();
}
br.close();
bw.close();
}
通过getEncoding()方法可以返回编码方式,默认是平台(eclipse)编码,txt文件是GBK编码,复制的文本会出现乱码,因为读取的时候是根据UTF-8读,写的时候是根据UTF-8写,这时候就不能使用FileReader的方式,要使用
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("C:\Users\Desktop\1.txt"),"gbk"));
这里的缓冲区不是减少IO操作次数,而是减少编码转换器的操作次数。这要和BufferInputStream、BufferOutputStream区别开来。
BufferInputStream
常用构造函数:
public BufferedInputStream(InputStream in); 创建一个内部缓冲区数组并将其存储在 buf 中,该buf的大小默认为8192。
BufferedInputStream(InputStream in,int size); 指定内部缓冲区的大小
重要属性:
private static int defaultBufferSize = 8192;//内置缓存字节数组的大小 8KB protected volatile byte buf[]; //内置缓存字节数组 protected int count; //当前buf中的字节总数、注意不是底层字节输入流的源中字节总数 protected int pos; //当前buf中下一个被读取的字节下标 protected int markpos = -1; //最后一次调用mark(int readLimit)方法记录的buf中下一个被读取的字节的位置 protected int marklimit; //调用mark后、在后续调用reset()方法失败之前云寻的从in中读取的最大数据量、用于限制被标记后buffer的最大值
重要方法:
int available(); //返回底层流对应的源中有效可供读取的字节数 void close(); //关闭此流、释放与此流有关的所有资源 boolean markSupport(); //查看此流是否支持mark void mark(int readLimit); //标记当前buf中读取下一个字节的下标 int read(); //读取buf中下一个字节 int read(byte[] b, int off, int len); //读取buf中下一个字节 void reset(); //重置最后一次调用mark标记的buf中的位子 long skip(long n); //跳过n个字节、 不仅仅是buf中的有效字节、也包括in的源中的字节
该类主要是提供给InputStream的没有缓冲功能的子类来使用的,经常看见有人把其和FileInputStram来一起使用,FileInputStram本身具有缓存,速度更快,直接调用底层 readBytes(byte b[], int off, int len)。