11.6
A.
书上写的示例代码已经完成了大部分工作:doit函数中的printf("%s", buf);语句打印出了请求行;read_requesthdrs函数打印出了剩下的请求报头,但是要注意书上写的是:
void read_requesthdrs(rio_t *rp)
{
char buf[MAXLINE];
Rio_readlineb(rp, buf, MAXLINE);
while(strcmp(buf, "
")){
Rio_readlineb(rp, buf, MAXLINE);
printf("%s", buf);
}
return;
}
如果按照这个打印的话,第一个请求抱头Host将无法输出,所以我们应该在while循环前输出一个报头:
void read_requesthdrs(rio_t *rp)
{
char buf[MAXLINE];
Rio_readlineb(rp, buf, MAXLINE);
printf("%s", buf); /* Host: ..... */
while(strcmp(buf, "
")){
Rio_readlineb(rp, buf, MAXLINE);
printf("%s", buf);
}
return;
}
B.
我们在A中是将请求行和请求报头输出到标准输出,在命令行启动的时候用“>”重定向到一个文件即可。
但是要注意一点:由于我们输出到文件而非一个交互设备,所以流缓冲默认是满缓冲的,如果我们在一个静态请求后按下“CRTL+C”终止tiny,那么由于缓冲内容没有输出,则文件内将没有内容,所以我们应该在read_requesthdrs函数最后加上一个fflush :
void read_requesthdrs(rio_t *rp)
{
char buf[MAXLINE];
Rio_readlineb(rp, buf, MAXLINE);
printf("%s", buf);
while(strcmp(buf, "
")) {
Rio_readlineb(rp, buf, MAXLINE);
printf("%s", buf);
}
fflush(stdout);
return;
}
关于流缓冲的问题,可以参考我之前写的这篇文章:文件描述符 流 流缓冲的一些概念与问题
运行输出:
frank@under:~/tmp$ ./a.out 15213 > line_and_headers
^C
frank@under:~/tmp$ cat line_and_headers
Accepted connection from (localhost, 45600)
GET /test.c HTTP/1.1
Host: localhost:15213
Connection: keep-alive
Cache-Control: max-age=0
Upgrade-Insecure-Requests: 1
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/64.0.3282.119 Safari/537.36
Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8
DNT: 1
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, br
Accept-Language: zh-CN,zh;q=0.9,en-US;q=0.8,en;q=0.7
frank@under:~/tmp$
C.
由B中的请求行:GET /test.c HTTP/1.1可知使用的是HTTP/1.1
D.
注意: 书上说查RFC 2616来确认各个请求报头的功能,但是有一些报头我没有在该文档中找到,根据这篇文章:
“原来的RFC 2616拆分为六个单独的协议说明,并重点对原来语义模糊的部分进行了解释,新的协议说明更易懂、易读。新的协议说明包括以下六部分:”
- RFC7230 - HTTP/1.1: Message Syntax and Routing - low-level message parsing and connection management
- RFC7231 - HTTP/1.1: Semantics and Content - methods, status codes and headers
- RFC7232 - HTTP/1.1: Conditional Requests - e.g., If-Modified-Since
- RFC7233 - HTTP/1.1: Range Requests - getting partial content
- RFC7234 - HTTP/1.1: Caching - browser and intermediary caches
- RFC7235 - HTTP/1.1: Authentication - a framework for HTTP authentication
我们应该在RFC7231中查找,而非RFC2616。 具体的介绍我就不列出了,大家可以自己在RFC7231查找详细介绍。
11.7
我电脑上倒还没有MPG格式的视频,拿一个WEBM的视频做示例——都是要将响应报头Content-type: 更改为对应的格式(这里是video/webm ):
void get_filetype(char *filename, char *filetype)
{
if (strstr(filename, ".html"))
strcpy(filetype, "text/html");
else if (strstr(filename, ".gif"))
strcpy(filetype, "image/gif");
else if (strstr(filename, ".png"))
strcpy(filetype, "image/png");
else if (strstr(filename, ".jpg"))
strcpy(filetype, "image/jpeg");
else if (strstr(filename, ".webm"))
strcpy(filetype, "video/webm");
else
strcpy(filetype, "text/plain");
}
效果如下:
11.8
根据书上8.5节的内容,我们先写一个SIGCHLD的信号处理函数handler :
void handler(int sig)
{
int olderrno = errno;
while (waitpid(-1, NULL, 0) > 0)
{
continue;
}
if (errno != ECHILD)
{
Sio_error("waitpid error");
}
errno = olderrno;
}
并serve_dynamic中使用signal将其安装 :
void serve_dynamic(int fd, char *filename, char *cgiargs)
{
if (signal(SIGCHLD, handler) == SIG_ERR)
{
unix_error("signal error");
}
char buf[MAXLINE], *emptylist[] = { NULL };
sprintf(buf, "HTTP/1.0 200 OK
");
Rio_writen(fd, buf, strlen(buf));
sprintf(buf, "Server: Tiny Web Server
");
Rio_writen(fd, buf, strlen(buf));
if (Fork() == 0) {
setenv("QUERY_STRING", cgiargs, 1);
Dup2(fd, STDOUT_FILENO);
Execve(filename, emptylist, environ);
}
//Wait(NULL);
}
经多次测试运行cgi程序未发现僵尸进程。
11.9
别忘记释放内存。
void serve_static(int fd, char *filename, int filesize)
{
int srcfd;
char *srcp, filetype[MAXLINE], buf[MAXBUF];
get_filetype(filename, filetype);
sprintf(buf, "HTTP/1.0 200 OK
");
sprintf(buf, "%sServer: Tiny Web Server
", buf);
sprintf(buf, "%sConnection: close
", buf);
sprintf(buf, "%sContent-length: %d
", buf, filesize);
sprintf(buf, "%sContent-type: %s
", buf, filetype);
Rio_writen(fd, buf, strlen(buf));
printf("Response headers:
");
printf("%s", buf);
srcfd = Open(filename, O_RDONLY, 0);
srcp = Malloc(filesize);
Rio_readn(srcfd, srcp, filesize);
Rio_writen(fd, srcp, filesize);
Free(srcp);
//srcp = Mmap(0, filesize, PROT_READ, MAP_PRIVATE, srcfd, 0);
//Close(srcfd);
//Munmap(srcp, filesize);
}
11.10
关于HTML表单的知识参考:HTML 表单
index.html:
<form action="cgi-bin/a.out" method="GET">
First Number:<br>
<input type="text" name="FirstNumber" value="">
<br><br>
Second Number:<br>
<input type="text" name="SecondNumber" value="">
<br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
由于我们不需要默认值,所以value为空。
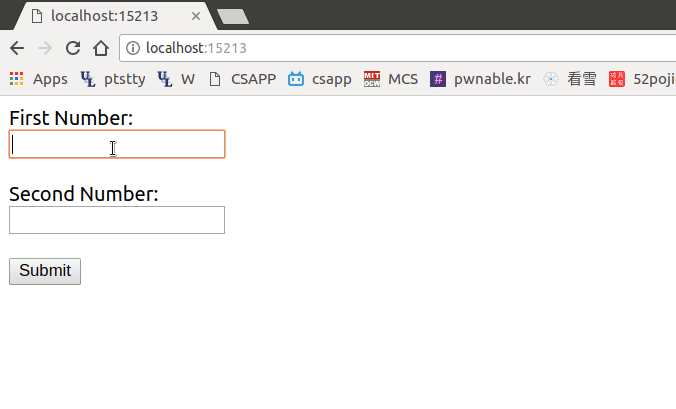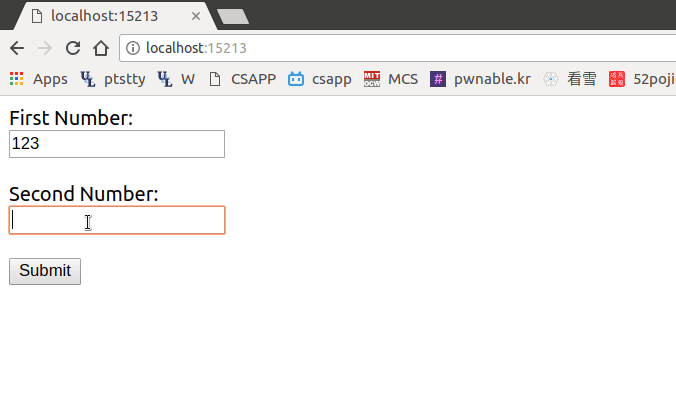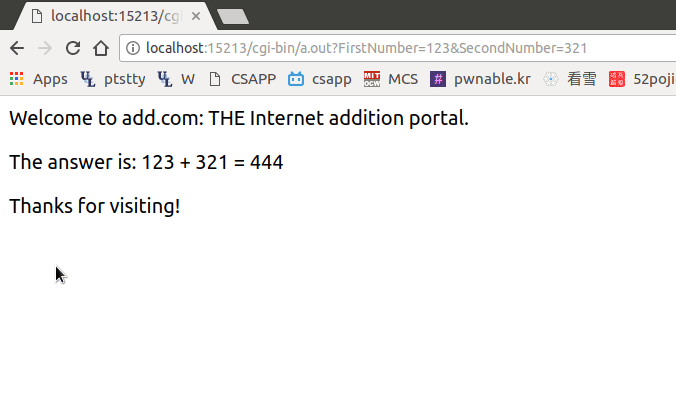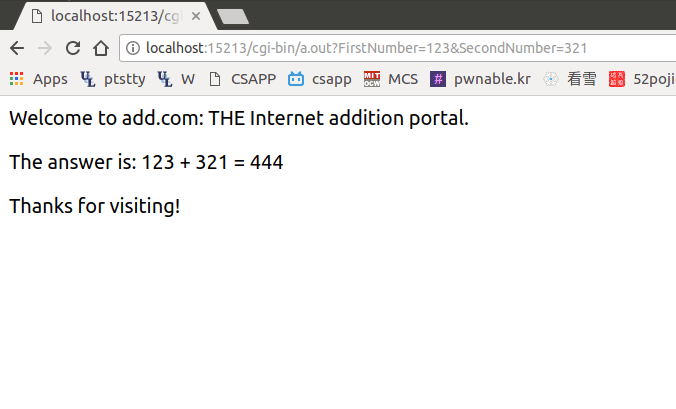
由于我们此时的GET请求是“name=value”的形式,所以应该将adder.c中取参数的部分修改为:
/* Extract the two arguments */
if ((buf = getenv("QUERY_STRING")) != NULL)
{
p = strchr(buf, '&');
*p = '�';
strcpy(arg1, buf);
strcpy(arg2, p+1);
/* 取等号后面的参数 */
p = strchr(arg1, '=');
n1 = atoi(p+1);
p = strchr(arg2, '=');
n2 = atoi(p+1);
}
运行效果:
11.11
根据RFC 7231, section 4.3.2: HEAD中的描述,HEAD方法大致描述如下:
HEAD方法与GET相同,但是HEAD并不返回消息体。在一个HEAD请求的消息响应中,HTTP投中包含的元信息应该和一个GET请求的响应消息相同。这种方法可以用来获取请求中隐含的元信息,而无需传输实体本身。这个方法经常用来测试超链接的有效性,可用性和最近修改。
一个HEAD请求响应可以被缓存,也就是说,响应中的信息可能用来更新之前缓存的实体。如果当前实体缓存实体阈值不同(可通过Content_Length、Content-MD5、ETag或Last-Modified的变化来表明),那么这个缓存被视为过期了。
所以我们只需要将处理GET方法的两个函数serve_static和serve_dynamic中增加一个如果是HEAD方法则不返回消息体的判断。而方法是在doit中判断的,所以我们设置一个标志unsigned methods = 0; 并在判断方法的语句中加上HEAD方法的判断,如果为GET,其值为0,如果为HEAD,其值为1:
if (strcasecmp(method, "GET") == 0)
{
methods = 0;
}
else if (strcasecmp(method, "HEAD") == 0)
{
methods = 1;
}
else
{
clienterror(fd, method, "501", "Not Implemented",
"Tiny does not implement this method");
return;
}
最后将函数serve_static和serve_dynamic的参数增加一个unsigned methods :
void serve_static(int fd, char *filename, int filesize, unsigned methods);
void serve_dynamic(int fd, char *filename, char *cgiargs, unsigned methods);
在其中返回消息体之前加上这样一条语句:
/* HEAD method doesn't need to send response body to client */
if (methods == 1)
return;
Telnet测试效果:
frank@under:~/tmp$ telnet localhost 15213
Trying 127.0.0.1...
Connected to localhost.
Escape character is '^]'.
HEAD / HTTP/1.0
HTTP/1.0 200 OK
Server: Tiny Web Server
Connection: close
Content-length: 241
Content-type: text/html
Connection closed by foreign host.
frank@under:~/tmp$
11.12
如果我们用POST方法传递参数的话,URI中将不含参数,而是在消息体中传递参数,例如:
index.html(将method改为POST):
<form action="cgi-bin/a.out" method="POST">
First Number:<br>
<input type="text" name="FirstNumber" value="">
<br><br>
Second Number:<br>
<input type="text" name="SecondNumber" value="">
<br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
抓包request如下:
POST /cgi-bin/a.out HTTP/1.1
Host: localhost:15213
Connection: keep-alive
Content-Length: 32
Cache-Control: max-age=0
Origin: http://localhost:15213
Upgrade-Insecure-Requests: 1
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/64.0.3282.119 Safari/537.36
Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8
DNT: 1
Referer: http://localhost:15213/
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, br
Accept-Language: zh-CN,zh;q=0.9,en-US;q=0.8,en;q=0.7
FirstNumber=123&SecondNumber=321
可以看到FirstNumber=123&SecondNumber=321放在了消息体内传递。
为了将FirstNumber=123&SecondNumber=321存入cgiargs ,我们需要在read_requesthdrs中判断是否是POST然后将请求中最后的消息体存入cgiargs。
首先,在doit中增加一个POST的method判断:
if (strcasecmp(method, "GET") == 0)
{
methods = 0;
}
else if (strcasecmp(method, "HEAD") == 0)
{
methods = 1;
}
else if (strcasecmp(method, "POST") == 0)
{
methods = 2; /* POST */
}
else
{
clienterror(fd, method, "501", "Not Implemented",
"Tiny does not implement this method");
return;
}
然后为read_requesthdrs增加两个参数:
void read_requesthdrs(rio_t *rp, char *cgiargs, unsigned methods);
在其中更据是否是POST方法来读取消息体:
void read_requesthdrs(rio_t *rp, char *cgiargs, unsigned methods)
{
char buf[MAXLINE];
Rio_readlineb(rp, buf, MAXLINE);
printf("%s", buf);
while(strcmp(buf, "
")) {
Rio_readlineb(rp, buf, MAXLINE);
printf("%s", buf);
}
fflush(stdout);
if (methods == 2){ /* POST */
Rio_readnb(rp, buf, rp->rio_cnt);
strcpy(cgiargs, buf);
}
return;
}
这里要特别注意,消息体不是以 作为结尾的,抓包如下:
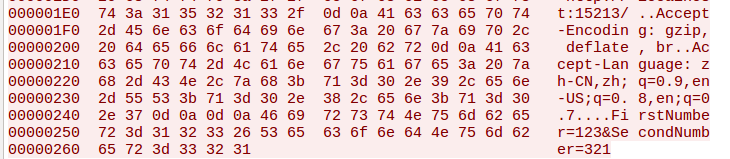
可以看到最后不是以换行符作为结尾,所以我们这里不能像之前那样使用MAXLINE作为第三个参数调用Rio这样的函数(读取函数read无法判断是否已经到达了结尾,因为缓冲区很长,表现为一直等待输入,服务器无响应),而是应该根据rp->rio_cnt读取所缓冲器剩下的所有字符:
if (methods == 2){ /* POST */
Rio_readnb(rp, buf, rp->rio_cnt);
strcpy(cgiargs, buf);
}
同时我们要更改一下parse_uri函数,因为如果是POST方法的话,read_requesthdrs就已经更新了cgiargs了,所有需要在parse_uri对方法做一个判断(也要增加一个method参数),如果是GET方法的话才对cgiargs进行更新:
int parse_uri(char *uri, char *filename, char *cgiargs, unsigned methods)
{
char *ptr;
if (!strstr(uri, "cgi-bin")) { /* Static content */
strcpy(cgiargs, "");
strcpy(filename, ".");
strcat(filename, uri);
if (uri[strlen(uri)-1] == '/')
strcat(filename, "index.html");
return 1;
}
else { /* Dynamic content */
if (methods == 0){ /* GET */
ptr = index(uri, '?');
if (ptr) {
strcpy(cgiargs, ptr+1);
*ptr = '�';
}
else
strcpy(cgiargs, "");
}
strcpy(filename, ".");
strcat(filename, uri);
return 0;
}
}
最终效果:
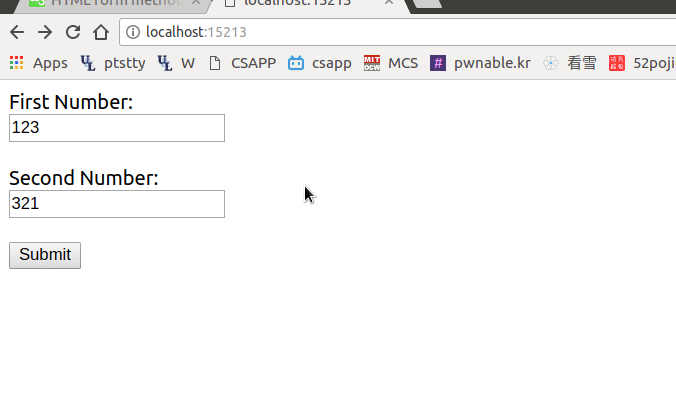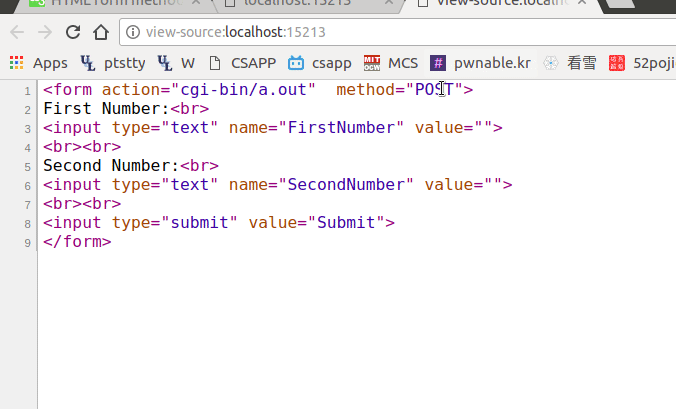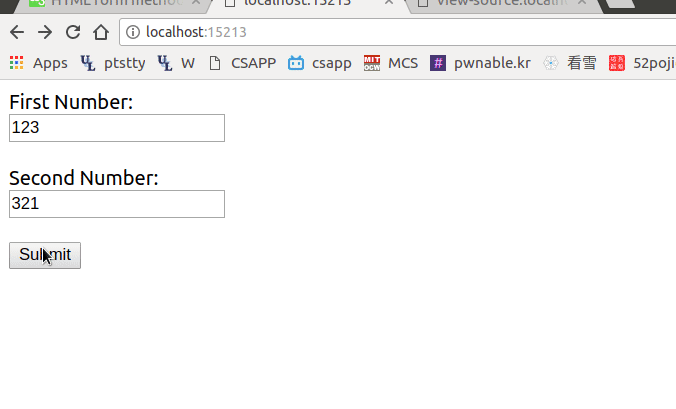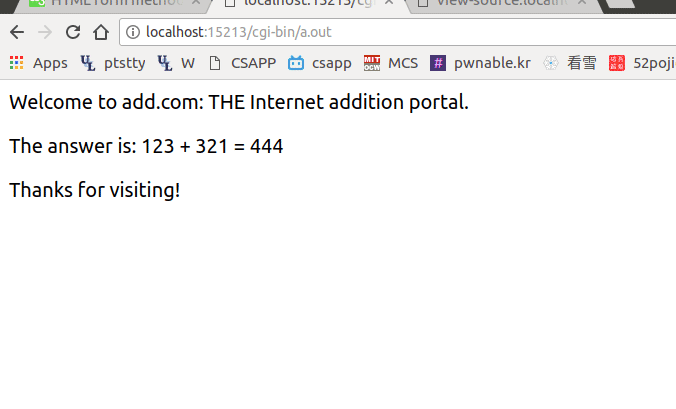
关于传递方法详细的介绍可以参考:Sending form data
11.13
这里我们直接忽略EPIPE信号(在主函数中安装):
if (Signal(SIGPIPE, SIG_IGN) == SIG_ERR)
{
unix_error("mask signal pipe error");
}
然后更换以前使用的Rio_writen ,使之能够处理EPIPE:
void Rio_writen(int fd, void *usrbuf, size_t n)
{
if (rio_writen(fd, usrbuf, n) != n)
{
unix_error("Rio_writen error");
if(errno == EPIPE)
{
unix_error("EPIPE error
Connection ended");
}
}
}
最后要注意cgi程序运行的时候也可能遇到EPIPE信号,我们要交给它自己处理:
if (Fork() == 0)
{ /* Child */
/* Real server would set all CGI vars here */
setenv("QUERY_STRING", cgiargs, 1);
Dup2(fd, STDOUT_FILENO); /* Redirect stdout to client */
if (Signal(SIGPIPE, SIG_DFL) == SIG_ERR)
{
unix_error("mask signal pipe error");
}
Execve(filename, emptylist, environ); /* Run CGI program */
}