本文将详细介绍线性布局的各种xml属性。
xml属性
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
</LinearLayout>
①android:layout_width---->设置此布局的宽度,有三种模式:
fill_parent:充满屏幕(已过时,用下面的match_parent代替)
match_parent:充满屏幕(推荐)
wrap_content:包含组件,意思就是你的组件多大,那么就占多大的空间。
②android:layout_height---->设置此布局的高度,模式同上;
③android:orientation---->此属性设置此线性布局的方式,有两个参数:
vertical:垂直布局:即子控件都在子控件的上下位置,例如
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical"> //这里选用垂直布局 <Button android:layout_width="match_parent" //宽度充满屏幕 android:layout_height="wrap_content" //高度包含组件 android:text="FirstButton" android:id="@+id/button" /> <Button android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="SecondButton" android:id="@+id/button2" /> </LinearLayout>
显示结果:
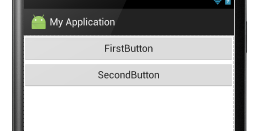
horizontal:水平布局:即子控件都在子控件的左右位置。例如:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="horizontal"> //这里设置为水平布局, <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" //宽度包含组件 android:layout_height="match_parent" //这里设置Button控件的高度充满屏幕 android:text="FirstButton" android:id="@+id/button" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:text="SecondButton" android:id="@+id/button2" /> </LinearLayout>
显示结果:

④android:baselineAligned---->此布局中的子控件是否基线对齐,其实就是设置在不在一条线上,他只有两个参数,true和false
false:若设置false,那么他里面的内容就不对齐。
true:若设置true,那么就对齐。 例如:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:baselineAligned="false" //这里设置为false android:orientation="horizontal"> <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="hello " android:textSize="24sp" /> <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="world" /> <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="hello world" android:textSize="45sp" /> </LinearLayout>
显示结果:
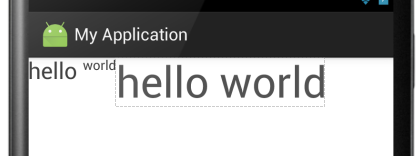
当设置为true时:
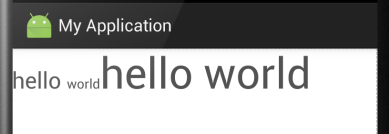
结果一目了然。
⑤android:gravity:指定布局里面的子控件的位置,几个常用参数,可以接受两个参数中间用”|“分隔开
center:控件处于布局的中心位置。
left:控件位于布局的左边。
right:控件位于布局的右边。
center|left:控件位于布局的中左位置。(也可以用center_vertical,和这个同样的作用)
官方给出的属性:
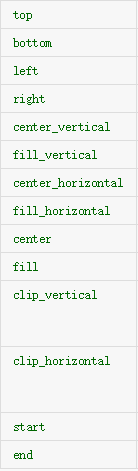
大家可以见明知义。例子:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:gravity="center|left" android:orientation="horizontal"> <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="hello " android:textSize="24sp" /> </LinearLayout>
显示结果为:
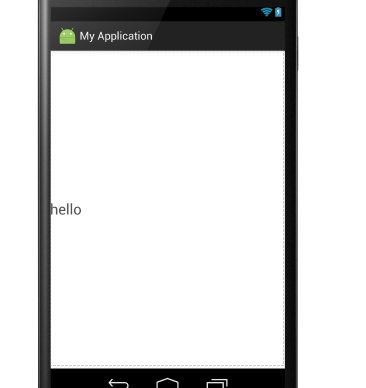
⑥android:layout_gravity:是指此子控件在布局中的位置。参数同上:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical"> <Button android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="hello " android:gravity="left" android:textSize="24sp" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="hello " android:textSize="24sp" android:layout_gravity="center" /> </LinearLayout>
显示结果:
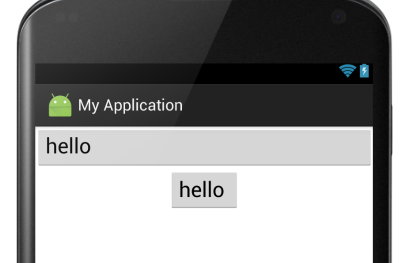
⑦android:divider:绘制子组件之间的分割线,参数可以是一个图片也可以是一个xml的shape标记,图片或者shape位于drawable下
android:showDividers:显示分割线的方式,有四种:
begging:在整体的上方添加
middle:在每个组件之间添加
end:在整体的下方添加
none:不显示
例如:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:divider="@drawable/shapee" //这里引用的shapee为一个xml文件,代码在下面 android:showDividers="middle" //这里显示方法为在每个组件之间添加 android:orientation="vertical">
shapee.xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<solid android:color="#00ff00" /> //此属性指定颜色
<size android:height="5px" /> //分割线的高度
</shape>
效果如下:
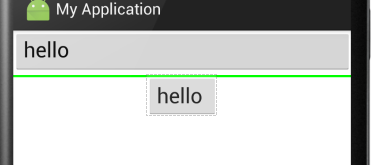
⑧android:weightSum:设定子控件中weight中的总和,其实就是控制子控件与屏幕或者其他子控件的比例,个人感觉这个比较重要,对于布局有很好的作用。
例如一下代码:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="horizontal" //布局设置为水平布局 android:weightSum="1" //设置子控件的weight总和为1 > <Button android:layout_width="0dp" //这里设置为0是为了好计算,计算公式在下面介绍 android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="0.5" //这里设置weight(权值)为0.5,也就是占用了一行的一半。 android:text="hello " android:textSize="24sp" /> <Button android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="0.4" //这里是0.4,就是40%,还有1-0.5-0.4=0.1为空白 android:text="hello " android:textSize="24sp" /> </LinearLayout>
显示结果:

计算公式: 此实例中Button的宽度计算:{ Button的width值+Button的weight*父控件width(这里是match_content,
如果父控件为200dp,那么这里就是200)/ weightSum的值 }