前言:本文爬虫的关键字眼是“美食”,实际分析时发现“零食”的销售量远远高于“美食”,因此在一开始的数据层面就已经决定了本文分析的片面性,本篇博客主要是用于记录代码和分析过程。
实际的结论请看下一篇博客(下一篇博客爬虫的关键字眼是“零食”)。
https://www.cnblogs.com/little-monkey/p/10822369.html
一、爬虫
根据崔庆才老师的爬虫视频修改而来,利用selenium进行淘宝爬取(本来想用火车采集器爬取的,尝试了一下发现没法截取淘宝网址的字段)。
selenium完全模拟人工点击操作,原理上可以爬取淘宝的所有可见内容。
爬虫代码有参考 https://www.cnblogs.com/hustcser/p/8744355.html
import re import time from selenium import webdriver from selenium.common.exceptions import TimeoutException from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By from selenium.webdriver.support.ui import WebDriverWait from selenium.webdriver.support import expected_conditions as EC from pyquery import PyQuery as pq import pymongo MONGO_URL = 'localhost' MONGO_DB = 'taobao' MONGO_TABLE = 'product2' KEYWORD = '美食' PAGE_NUM=35 #爬取页数 client=pymongo.MongoClient(MONGO_URL) db=client[MONGO_DB] browser = webdriver.Chrome() wait=WebDriverWait(browser, 10) def search(): print('正在搜素...') try: browser.get('https://s.taobao.com/search?q=%E7%BE%8E%E9%A3%9F&imgfile=&commend=all&ssid=s5-e&search_type=item&sourceId=tb.index&spm=a21bo.2017.201856-taobao-item.1&ie=utf8&initiative_id=tbindexz_20170306&sort=sale-desc&bcoffset=-30&p4ppushleft=%2C44&ntoffset=-30&fs=1&filter_tianmao=tmall&s=0') page_num=PAGE_NUM get_products() # 获取页面详情 return page_num except TimeoutException: return search() # 获取下页 def next_page(page_number): print('正在翻页%s', page_number) time.sleep(3) try: input = wait.until(EC.presence_of_element_located((By.CSS_SELECTOR, "#mainsrp-pager > div > div > div > div.form > input"))) submit = wait.until(EC.element_to_be_clickable((By.CSS_SELECTOR, '#mainsrp-pager > div > div > div > div.form > span.btn.J_Submit'))) input.clear() input.send_keys(page_number) submit.click() wait.until(EC.text_to_be_present_in_element((By.CSS_SELECTOR,'#mainsrp-pager > div > div > div > ul > li.item.active > span'),str(page_number))) get_products() except TimeoutException: next_page(page_number) # 解析页面 def get_products(): # 判断元素是否已经加载下来 wait.until(EC.presence_of_element_located((By.CSS_SELECTOR, '#mainsrp-itemlist .items .item'))) html=browser.page_source doc=pq(html) items=doc("#mainsrp-itemlist .items .item").items() for item in items: product={ # 'image': item.find('.pic .img').attr('src'), 'title': item.find('.title').text(), 'price': item.find('.price').text(), 'deal': item.find('.deal-cnt').text()[:-3], 'location': item.find('.location').text(), 'shop': item.find('.shop').text() } print(product) save_to_mongo(product) def save_to_mongo(result): try: if db[MONGO_TABLE].insert(result): print('存储到MongoDB成功',result) except Exception: print('存储到MongoDB失败',result) def main(): try: page_num=search() for i in range(2,page_num+1): next_page(i) except Exception: print('出错啦') finally: browser.close() if __name__ == '__main__': main()
注意:运行程序后会弹出淘宝登陆页面,使用手机淘宝扫描登陆,然后坐等爬取结果,最后从MongoDB中导出CSV文件即可。
结果如下:
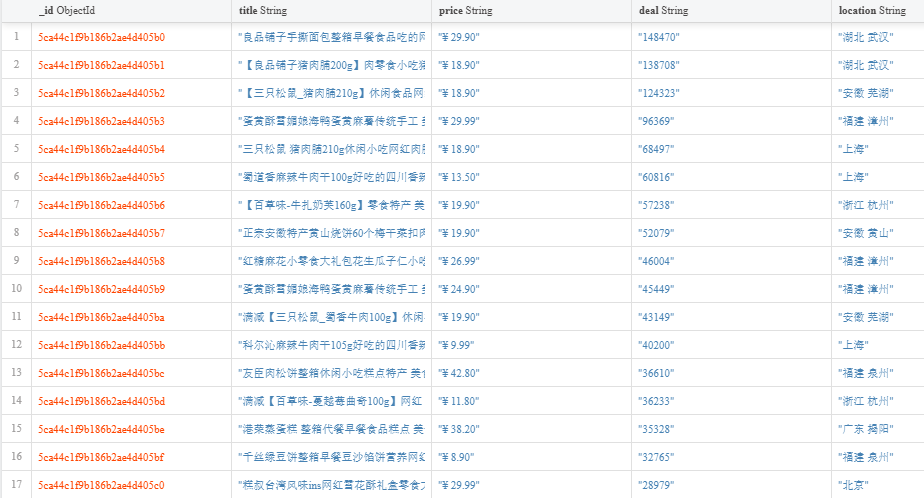
二、数据处理
data= pd.read_csv('data/淘宝美食35页.csv', encoding='utf8',engine='python') data.drop('_id',axis=1, inplace=True) #去掉id列 data['price'].replace('¥', '', regex=True, inplace=True) #去掉price列的'¥' #从location列中取出省份和城市,然后删除location列 data['province']=data.location.apply(lambda x:x.split()[0]) data['city']=data.location.apply(lambda x:x.split()[0] if len(x)<4 else x.split()[1]) data.drop('location',axis=1, inplace=True) #数据类型转化 data['price']=data.price.astype('float64') for i in ['province','city']: data[i]=data[i].astype('category')
运行结果如下:

三、数据挖掘与分析
【数据处理】
import jieba #导入整理好的待添加词语(因为jieba本身的分词功能不足以应付特定数据) add_words = pd.read_excel('data/add_words.xlsx',header=None) add_words_list = add_words[0].tolist() for w in add_words_list: # 添加词语 jieba.add_word(w , freq=1000) #导入停用词表 stopwords = [line.strip() for line in open('data/stop.csv', 'r', encoding='utf-8').readlines()] #对每个标题进行分词,使用lcut函数 title=data.title.values.tolist() #转为list title_s=[] for line in title: title_cut=jieba.lcut(line) title_s.append(title_cut) #去除冗余词Plan1:剔除停用词: title_clean = [] for line in title_s: line_clean = [] for word in line: if word not in stopwords: line_clean.append(word) title_clean.append(line_clean) #去除冗余词Plan2:直接定义,定义完后再调用lcut函数 #removes =['熟悉', '技术', '职位', '相关', '工作', '开发', '使用','能力','优先','描述','任职'] #for w in removes: # jieba.del_word(w) #去重,对title_clean中的每个list的元素进行去重,即每个标题被分割后的词语唯一,如【麻辣小鱼干香辣小鱼干】->【麻辣,香辣,小鱼干】 #去重后的title_clean_dist为二维list,即[[……],[……],……] title_clean_dist = [] for line in title_clean: line_dist = [] for word in line: if word not in line_dist: line_dist.append(word) title_clean_dist.append(line_dist) # 将 title_clean_dist 转化为一维list allwords_clean_dist = [] for line in title_clean_dist: for word in line: allwords_clean_dist.append(word) # 把列表 allwords_clean_dist 转为数据框: df_allwords_clean_dist = pd.DataFrame({'allwords': allwords_clean_dist}) # 对过滤_去重的词语 进行分类汇总: word_count = df_allwords_clean_dist.allwords.value_counts().reset_index() word_count.columns = ['word','count'] #添加列名
【词云可视化】
# 词云可视化 from PIL import Image from wordcloud import WordCloud import matplotlib.pyplot as plt txt = " ".join(allwords_clean_dist) #将list转成str,便于词云可视化 food_mask=np.array(Image.open("data/mask.png")) wc = WordCloud(font_path='data/simhei.ttf', # 设置字体 background_color="white", # 背景颜色 max_words=1000, # 词云显示的最大词数 max_font_size=100, # 字体最大值 min_font_size=5, #字体最小值 random_state=42, #随机数 collocations=False, #避免重复单词 mask=food_mask, #造型遮盖 width=1000,height=800,margin=2, #图像宽高,字间距,需要配合下面的plt.figure(dpi=xx)放缩才有效 ) wc.generate(txt) plt.figure(dpi=200) plt.imshow(wc, interpolation='catrom',vmax=1000) plt.axis("off") #隐藏坐标 plt.rcParams['figure.dpi'] = 600 plt.savefig('E:\1标题词云.png')

进一步的,进行不同关键词销量的可视化
【销量统计】
ws_sum=[] for w in word_count.word: i=0 s_list=[] for t in title_clean_dist: if w in t: s_list.append(data.deal[i]) i+=1 ws_sum.append(sum(s_list)) df_sum=pd.DataFrame({'ws_sum':ws_sum}) df_word_sum=pd.concat([word_count,df_sum],axis=1,ignore_index=True) df_word_sum.columns=['word','count','ws_sum'] #词语,出现次数,包含该词语的商品销量 df_word_sum.drop(8,axis=0,inplace=True) #删除“空格”词所在的8行 df_word_sum.sort_values('ws_sum',inplace=True,ascending=True) #升序排列 df_ws=df_word_sum.tail(40) index=np.arange(df_ws.word.size) plt.figure(figsize=(16,13)) plt.barh(index,df_ws.ws_sum,align='center') plt.yticks(index,df_ws.word,fontsize=11) #添加数据标签 for y,x in zip(index,df_ws.ws_sum): plt.text(x,y,'%.0f' %x,ha='left',va='center',fontsize=11) #ha参数有【center,left,right】,va参数有【top,bottom,center,baseline】 plt.savefig('E:\2销量词汇排行.png')
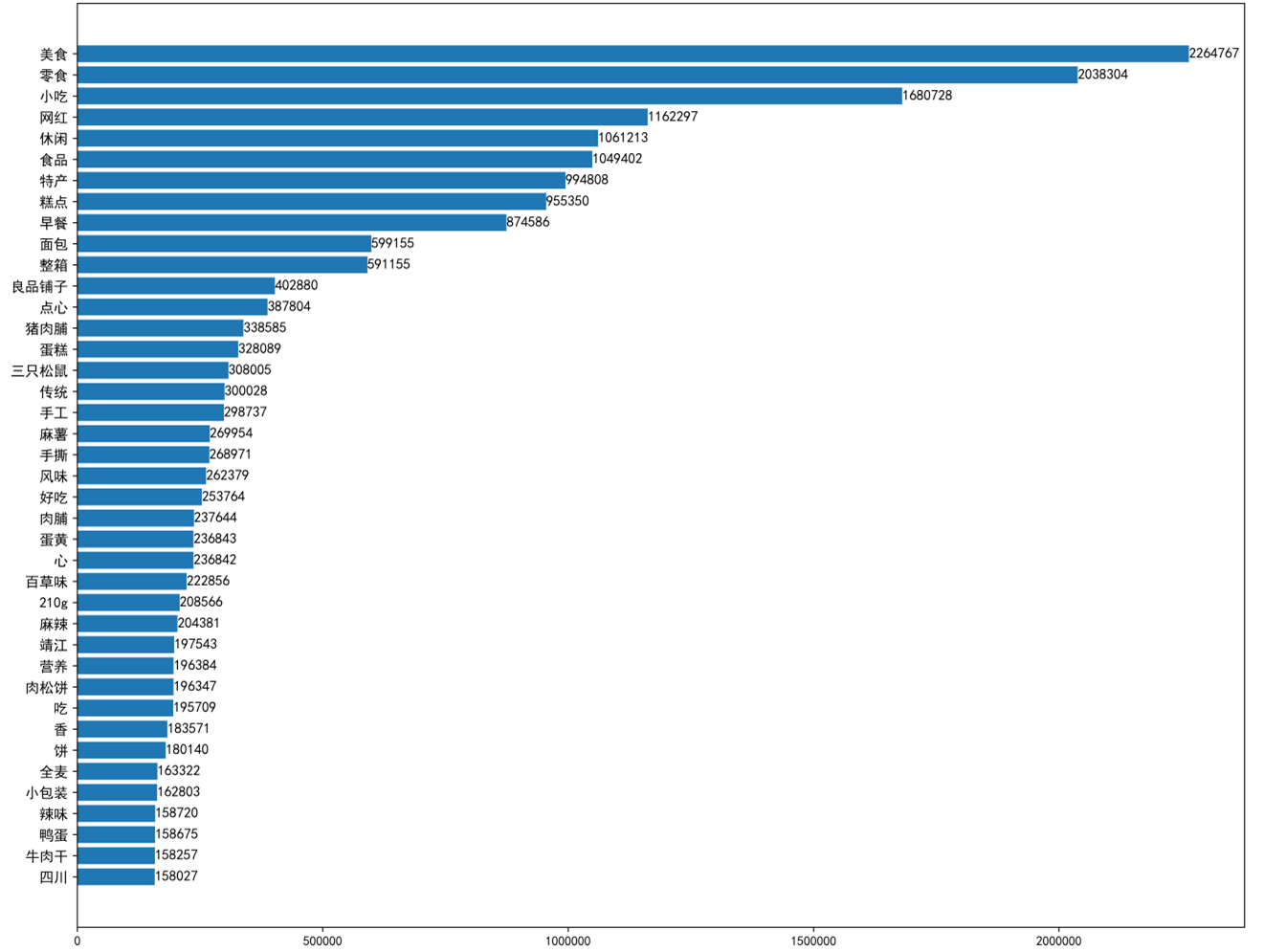
【分析1】根据淘宝标题(卖家倾向)+销量(买家倾向)分析市场情况
1、美食、零食、小吃等字眼的商品占比较高;
2、从进餐时间来看,早餐卖的最多,下午茶也有一定空间;
3、从地域来看,川渝美食领跑全国,湖南、云南、北京、厦门次之,南京、安徽、上海、黄山也有一定市场;
4、从种类来看,糕点>面包>肉脯>蛋类,看来中国人民喜欢甜点多于肉、蛋制品;
5、从风格来看,特产和网红处于第一梯队,特产卖家最多,网红销量最高,第二梯队中传统>营养,国人钟爱特产以及网红美食坐上销量宝座的深层原因,可能是宣传,即买家购买零食时更倾向于购买听说过的东西;
6、从包装来看,整箱包装最受欢迎,小包装次之,大礼包、散装、礼盒、批发虽然常见于卖家,但销量比不上整箱包装和小包装,这也和糕点、面包类畅销相关;
7、从口味来看,麻辣和香辣最受欢迎,和川渝美食地位相符;
8、从品牌来看,销量上 良品铺子>三只松鼠>百草味,三巨头领衔零食市场,已初步形成口碑。
【总结1】对美食而言,有力的宣传可以极大促进销量。川渝美食领跑全国,既和其口味【麻辣】、【香辣】有关,更和其“小吃”、“美女”、“网红”等城市标签有关;糕点、面包等精致食品广受【办公室人群】的欢迎。
同理,进行【店名分析】
#导入整理好的待添加词语(因为jieba本身的分词功能不足以应付特定数据) add_words = pd.read_excel('data/add_words.xlsx',header=None) add_words_list = add_words[0].tolist() for w in add_words_list: # 添加词语 jieba.add_word(w , freq=1000) #去除冗余词:直接定义,定义完后再调用lcut函数 removes =['来', '和', '有'] for w in removes: jieba.del_word(w) #对每个标题进行分词,使用lcut函数 shop=data.shop.values.tolist() #转为list shop_s=[] for line in shop: shop_cut=jieba.lcut(line) shop_s.append(shop_cut) shop_clean_dist = [] for line in shop_s: line_dist = [] for word in line: if word not in line_dist: line_dist.append(word) shop_clean_dist.append(line_dist) # 将 title_clean_dist 转化为一维list shop_list = [] for line in shop_clean_dist: for word in line: shop_list.append(word) txt = " ".join(shop_list) #将list转成str,便于词云可视化 sh = WordCloud(font_path='data/simhei.ttf', # 设置字体 background_color="white", # 背景颜色 max_words=100, # 词云显示的最大词数 max_font_size=100, # 字体最大值 min_font_size=5, #字体最小值 random_state=42, #随机数 collocations=False, #避免重复单词 width=600,height=400,margin=2, #图像宽高,字间距,需要配合下面的plt.figure(dpi=xx)放缩才有效 ) sh.generate(txt) plt.figure(dpi=200) plt.imshow(sh, interpolation='catrom',vmax=1000) plt.axis("off")

# 把列表 allwords_clean_dist 转为数据框: shop_list = pd.DataFrame({'allwords': shop_list}) # 对过滤_去重的词语 进行分类汇总: shop_count = shop_list.allwords.value_counts().reset_index() shop_count.columns = ['shop','count'] #添加列名 #销量统计 sh_sum=[] for w in shop_count.shop: i=0 s_list=[] for t in shop_clean_dist: if w in t: s_list.append(data.deal[i]) i+=1 sh_sum.append(sum(s_list)) df_sum=pd.DataFrame({'sh_sum':sh_sum}) df_word_sum=pd.concat([shop_count,df_sum],axis=1,ignore_index=True) df_word_sum.columns=['shop','count','shop_sum'] #店名,出现次数,该店总销量 df_word_sum.sort_values('shop_sum',inplace=True,ascending=True) #升序排列 df_sh=df_word_sum.tail(30) index=np.arange(df_sh.shop.size) plt.figure(figsize=(12,9)) plt.barh(index,df_sh.shop_sum,align='center') plt.yticks(index,df_sh.shop,fontsize=11)
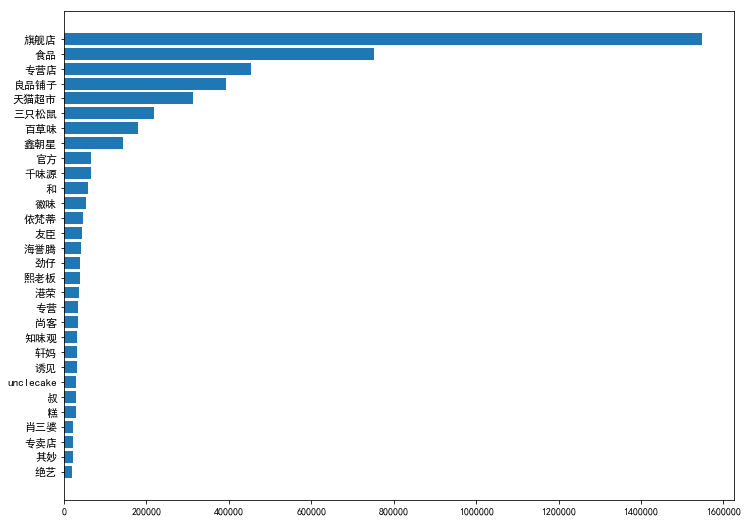
【分析2】店名分析
1、多数店名带有“旗舰店”、“食品”、“专营”等字眼;
2、良品铺子霸居榜首,虽然其商品数量不多(只有14件),但其销量高,甚至胜于天猫超市;
【总结2】店名最好带有“旗舰店”,对卖家有信服力
【价格分布】
data_p=data[data['price']<150] print('价格在150以下的商品占比:%.3f'%(len(data_p)/len(data))) plt.figure(figsize=(7,5)) plt.hist(data_p['price'],bins=25) plt.xlabel('价格',fontsize=12) plt.ylabel('商品数量',fontsize=12) plt.title('不同价格对应的商品数量分布',fontsize=12)
价格在150以下的商品占比:0.990

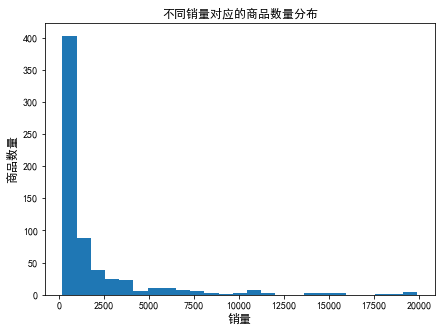
data_s=data[data['deal']<20000] data_s=data_s[data_s['deal']>200] print('销量在200~20000之间的商品占比:%.3f'%(len(data_s)/len(data))) plt.figure(figsize=(7,5)) plt.hist(data_s['deal'],bins=25) plt.xlabel('销量',fontsize=12) plt.ylabel('商品数量',fontsize=12) plt.title('不同销量对应的商品数量分布',fontsize=12)
销量在200~20000之间的商品占比:0.419
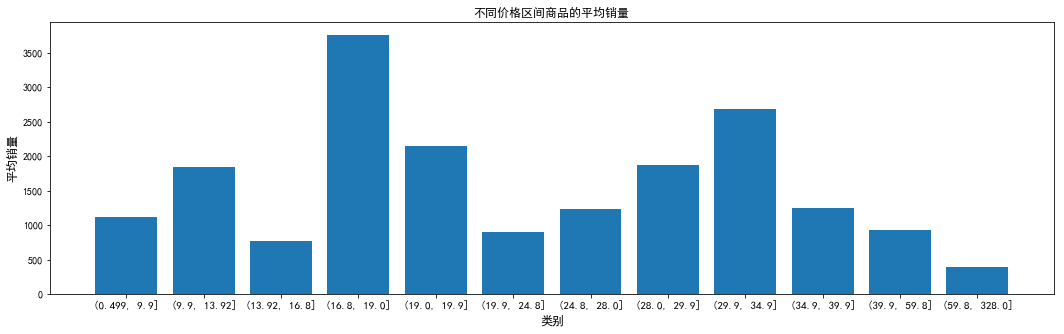
#用qcut将price分成12组 data['group']=pd.qcut(data.price,12) df_group=data.group.value_counts().reset_index() #以group列进行分类,求deal销量的均值 df_sg=data[['deal','group']].groupby('group').mean().reset_index() #绘柱形图 index=np.arange(df_sg.group.size) plt.figure(figsize=(18,5)) plt.bar(index,df_sg.deal) plt.xticks(index,df_sg.group,fontsize=11) plt.xlabel('类别',fontsize=12) plt.ylabel('平均销量',fontsize=12) plt.title('不同价格区间商品的平均销量',fontsize=12)
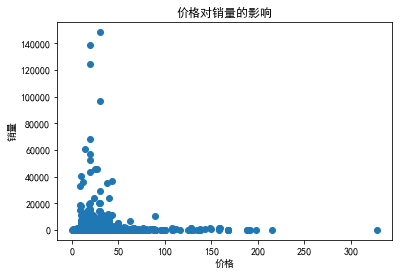
fig,ax=plt.subplots() ax.scatter(data['price'],data['deal']) ax.set_xlabel('价格') ax.set_ylabel('销量') ax.set_title('价格对销量的影响')
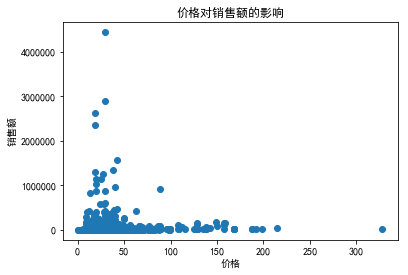
data['GMV']=data['price']*data['deal'] fig,ax=plt.subplots() ax.scatter(data['price'],data['GMV']) ax.set_xlabel('价格') ax.set_ylabel('销售额') ax.set_title('价格对销售额的影响')
【分析3】根据价格、销量、销售额分析定价影响
1、定价在25元左右的商品最多;
2、销量越高,商品越少,形成“长尾”分布;
3、【16.8,19】价格区间的销量最高,【29.9,34.9】销量次高峰;
4、价格在15~45之间的销量和销售额都不错,50元以上的零食并不畅销。
【总结3】对零食市场而言,应走“薄利多销”路线,50元以下的市场份额最大。
【地域分布】
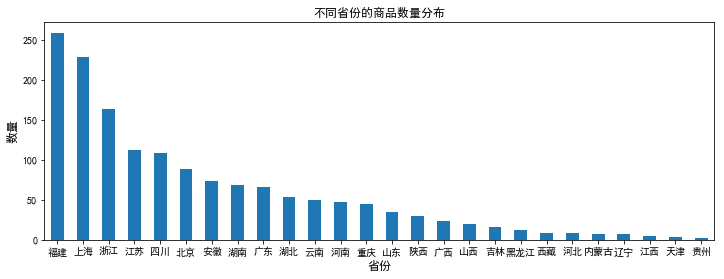
plt.figure(figsize=(12,4)) data.province.value_counts().plot(kind='bar') plt.xticks(rotation=0) #让字体横向分布 plt.xlabel('省份',fontsize=12) plt.ylabel('数量',fontsize=12) plt.title('不同省份的商品数量分布',fontsize=12)
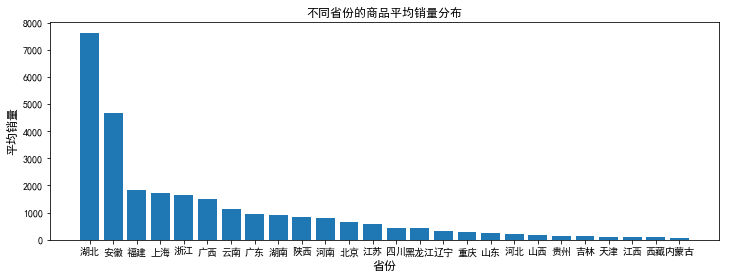
pro_sales=data.pivot_table(index='province',values='deal',aggfunc=np.mean) #分类求均值 pro_sales.sort_values('deal',inplace=True,ascending=False) pro_sales=pro_sales.reset_index() index=np.arange(pro_sales.deal.size) plt.figure(figsize=(12,4)) plt.bar(index,pro_sales.deal) plt.xticks(index,pro_sales.province,rotation=0) #让字体横向分布 plt.xlabel('省份',fontsize=12) plt.ylabel('平均销量',fontsize=12) plt.title('不同省份的商品平均销量分布',fontsize=12) pro_sales.to_excel('data/pro_sales.xlsx',index=False)
city_sales=data.pivot_table(index='city',values='deal',aggfunc=np.sum) #分城市求和 city_sales.sort_values('deal',inplace=True,ascending=False) city_sales=city_sales.reset_index() city_sales=city_sales[:30] index=np.arange(city_sales.deal.size) plt.figure(figsize=(12,4)) plt.bar(index,city_sales.deal) plt.xticks(index,city_sales.city,rotation=0) #让字体横向分布 plt.xlabel('城市',fontsize=12) plt.ylabel('销量总和',fontsize=12) plt.title('不同城市的商品销量之和',fontsize=12)
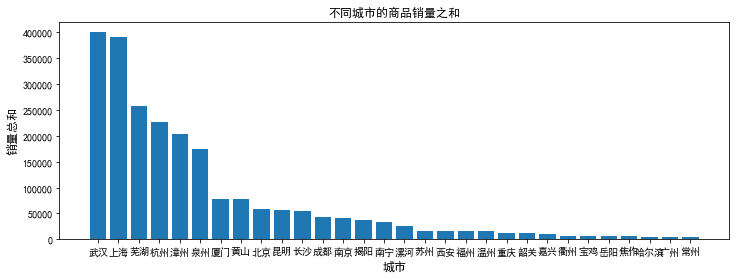

【分析4】分析地域差异
1、福建的零食商品数量最多(难道是受沙县小吃主导?),上海次之;
2、湖北虽然在售商品数量较少,但湖北的平均销量却最高。城市以武汉和上海销量最强;
3、在【分析1】中强势霸榜的川渝美食销量却一般,叫好不叫座?
4、销量高的城市大多是南方经济较发达的城市,经济能带动美食?南方零食比北方零食更畅销,猜测南方零食应该种类更加丰富。
【后记】鉴于有许多同学私信我要stop.csv(即停用词文件,这个文件可以自己设定停用词,也可以去网上找常用停用词),因此我将“stop.csv”和“淘宝美食35页”两个文件上传
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1UYr3kkFcNmjipaR9XSJeiQ
提取码:gzfq