There is a kind of balanced binary search tree named red-black tree in the data structure. It has the following 5 properties:
- (1) Every node is either red or black.
- (2) The root is black.
- (3) Every leaf (NULL) is black.
- (4) If a node is red, then both its children are black.
- (5) For each node, all simple paths from the node to descendant leaves contain the same number of black nodes.
For example, the tree in Figure 1 is a red-black tree, while the ones in Figure 2 and 3 are not.
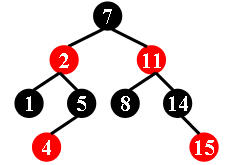 | 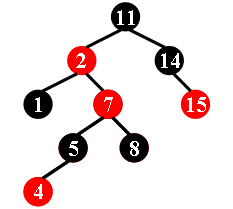 | 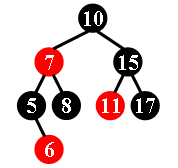 |
|---|---|---|
| Figure 1 | Figure 2 | Figure 3 |
For each given binary search tree, you are supposed to tell if it is a legal red-black tree.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains several test cases. The first line gives a positive integer K (≤30) which is the total number of cases. For each case, the first line gives a positive integer N (≤30), the total number of nodes in the binary tree. The second line gives the preorder traversal sequence of the tree. While all the keys in a tree are positive integers, we use negative signs to represent red nodes. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space. The sample input cases correspond to the trees shown in Figure 1, 2 and 3.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print in a line "Yes" if the given tree is a red-black tree, or "No" if not.
Sample Input:
3
9
7 -2 1 5 -4 -11 8 14 -15
9
11 -2 1 -7 5 -4 8 14 -15
8
10 -7 5 -6 8 15 -11 17
Sample Output:
Yes
No
No这道题目考察了红黑树的判断,我们按照二叉树插入顺序,之后判断题目中的5个条件即可
#include <iostream> using namespace std; struct node { int val; node *left, *right; node(int v): val(v), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} }; node* insert(node *n, int v) { if(!n) return new node(v); else if(abs(n->val) < abs(v)) n->left = insert(n->left, v); else n->right = insert(n->right, v); return n; } bool judge = true; int black = -1; void dfs(node *root, int blacknum) { if(!root) { if(black == -1) black = blacknum; else if(black != blacknum) judge = false; return; } if(root->val > 0) blacknum++; if(root->left && root->val < 0 && root->left->val < 0) judge = false; if(root->right && root->val < 0 && root->right->val < 0) judge = false; dfs(root->left, blacknum); dfs(root->right, blacknum); } int main() { int N, K, v; cin >> N; while(N--) { cin >> K; node *root = NULL; judge = true; black = -1; while(K--) { cin >> v; root = insert(root, v); } if(root->val < 0) judge = false; dfs(root, 0); if(judge) printf("Yes "); else printf("No "); } return 0; }