题意:给你一个有向图,点数10000,边数1000000,SCC大小不超过100(按数据范围的写法只有第三部分数据满足这个条件,不过第二部分数据并没有出现大小大于100个点的SCC,我是用数组大小为100的代码以身试法的2333)从s出发随机走,问走到t的期望步数.
首先考虑inf的情况.如果从s出发可以走到一个无法走到t的点,比如这个数据:红色点为起点,绿色点为终点,那么有1/2的概率永远也走不到(在蓝色点停下).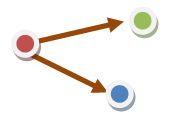
注意出现环的情况不一定是INF,因为在环上走无穷步的概率可能是无穷小。于是先缩点,把边反向找到所有不能到达t的SCC,如果从s出发有可能到达这样的一个SCC或s本身处于这样一个SCC,那么答案是INF。
接下来,我们把期望步数转化成期望经过的点数(显然经过的边数等于点数-1),那么利用期望的线性性,只需要高斯消元求出每个点的期望经过次数再加起来。但是这个范围显然不能直接做。而SCC大小小于100,提醒我们可以对每个SCC分别进行高斯消元,然后考虑SCC之间的关系。思路类似USACO一道最短路题”道路与航线”,那道题是对每个SCC分别跑dijkstra。
具体的做法:记f[i]为点i的期望经过次数,g[i]为从另一个SCC走到点i的期望次数,因为我们按拓扑序处理每个SCC,所以在处理每个SCC的时候这个SCC中每个点的g[]值都已经求出来了.接下来对SCC中每个点列一个方程.对于点x,f[x]=g[x]+sigma(f[j]/outdeg[j]),j向x有一条有向边且j和x在同一个SCC,outdeg为出度。这里j可以等于x(有自环),验证一下,这时候方程也是对的.解完这个SCC之后要用这个SCC里的点更新其他SCC的g[].注意边界g[s]=1,f[t]=1
然后码码码就好了。
#include<cstdio> #include<vector> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; int n,m,s,t; const int maxn=10005,maxm=1000005; //Graph Theory struct edge{ int to,next; }lst1[maxm],lst2[maxm],lst3[maxm];int len1=1,len2=1,len3=1; int first1[maxn],first2[maxn],first3[maxn]; void addedge1(int a,int b){ lst1[len1].to=b;lst1[len1].next=first1[a]; first1[a]=len1++; } void addedge2(int a,int b){ lst2[len2].to=b;lst2[len2].next=first2[a]; first2[a]=len2++; } void addedge3(int a,int b){ lst3[len3].to=b;lst3[len3].next=first3[a]; first3[a]=len3++; } int outdeg[maxn]; int belong[maxn],tot,sz[maxn]; vector<int> scc[maxn]; int stk[maxn],top,dfn[maxn],low[maxn],T; bool ins[maxn]; namespace Trajan{ void dfs(int x){ low[x]=dfn[x]=++T; stk[top++]=x;ins[x]=true; for(int pt=first1[x];pt;pt=lst1[pt].next){ if(!dfn[lst1[pt].to]){ dfs(lst1[pt].to); if(low[lst1[pt].to]<low[x])low[x]=low[lst1[pt].to]; }else if(ins[lst1[pt].to]&&dfn[lst1[pt].to]<low[x])low[x]=dfn[lst1[pt].to]; } if(dfn[x]==low[x]){ ++tot; do{ ins[stk[--top]]=false; belong[stk[top]]=tot; scc[tot].push_back(stk[top]); sz[tot]++; }while(stk[top]!=x); } } void tarjan(){ for(int i=1;i<=n;++i){ if(!dfn[i])dfs(i); } for(int i=1;i<=n;++i){ for(int pt=first1[i];pt;pt=lst1[pt].next){ if(belong[lst1[pt].to]!=belong[i]){ addedge2(belong[lst1[pt].to],belong[i]); addedge3(belong[i],belong[lst1[pt].to]); } } } } bool reachfromend[maxn],mustreachend[maxn]; void predfs(int x){ reachfromend[x]=true; for(int pt=first2[x];pt;pt=lst2[pt].next){ if(!reachfromend[lst2[pt].to]){ predfs(lst2[pt].to); } } } bool checkdfs(int x){ if(!reachfromend[x])return false; for(int pt=first3[x];pt;pt=lst3[pt].next){ if(mustreachend[lst3[pt].to])continue; if(!checkdfs(lst3[pt].to))return false; } return mustreachend[x]=true; } bool check(){ predfs(belong[t]); return checkdfs(belong[s]); } }; double f[maxn],g[maxn]; int map[maxn]; namespace Work{ bool done[maxn]; double F[105][105]; int rk; void Swap(int a,int b){ for(int i=0;i<=rk;++i)swap(F[a][i],F[b][i]); } void multplus(int a,int b,double times){ for(int i=0;i<=rk;++i)F[a][i]+=F[b][i]*times; } void Gauss(int n){ rk=n; for(int i=1;i<=n;++i){ if(F[i][i]==0){ for(int j=i+1;j<=n;++j){ if(F[j][i]!=0){ Swap(i,j);break; } } } for(int j=i+1;j<=n;++j)multplus(j,i,-F[j][i]/F[i][i]); } for(int i=n;i>=1;--i){ F[i][0]/=F[i][i]; for(int j=i-1;j>=1;--j){ F[j][0]-=F[j][i]*F[i][0]; } } } void build_equations(int x){ for(int i=1;i<=sz[x];++i){ for(int j=0;j<=sz[x];++j){ F[i][j]=0; } } for(int i=0;i<sz[x];++i)F[i+1][0]=-g[scc[x][i]]; for(int i=1;i<=sz[x];++i){ F[i][i]=-1;map[scc[x][i-1]]=i; if(scc[x][i-1]==t)F[i][0]=-1; } for(int i=0;i<sz[x];++i){ if(scc[x][i]==t)continue; for(int pt=first1[scc[x][i]];pt;pt=lst1[pt].next){ if(belong[lst1[pt].to]==x){ if(lst1[pt].to==t)continue; F[map[lst1[pt].to]][i+1]+=1.0/outdeg[scc[x][i]]; } } } } void dfs(int x){ for(int pt=first2[x];pt;pt=lst2[pt].next){ if(!done[lst2[pt].to])dfs(lst2[pt].to); } build_equations(x); Gauss(sz[x]); for(int i=0;i<sz[x];++i){ f[scc[x][i]]=F[i+1][0]; } for(int i=0;i<sz[x];++i){ for(int pt=first1[scc[x][i]];pt;pt=lst1[pt].next){ if(belong[lst1[pt].to]!=x){ g[lst1[pt].to]+=f[scc[x][i]]/outdeg[scc[x][i]]; } } } done[x]=true; } } int main(){ scanf("%d%d%d%d",&n,&m,&s,&t); int a,b; for(int i=1;i<=m;++i){ scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);addedge1(a,b); outdeg[a]++; } Trajan::tarjan(); if(Trajan::check()){ g[s]=1; Work::dfs(belong[t]); double ans=0; for(int i=1;i<=n;++i){//printf("%.2f ",f[i]); ans+=f[i]; }//ans:the expected number of points on the path from s to t printf("%.3f ",ans-1); }else{ printf("INF "); } return 0; }