为什么要使用PreparedStatement?
一、通过PreparedStatement提升性能
Statement主要用于执行静态SQL语句,即内容固定不变的SQL语句。Statement每执行一次都要对传入的SQL语句编译一次,效率较差。
某些情况下,SQL语句只是其中的参数有所不同,其余子句完全相同,适用于PreparedStatement。
PreparedStatement的另外一个好处就是预防sql注入攻击
PreparedStatement是接口,继承自Statement接口。
使用PreparedStatement时,SQL语句已提前编译,三种常用方法 execute、 executeQuery 和 executeUpdate 已被更改,以使之不再需要参数。
PreparedStatement 实例包含已事先编译的 SQL 语句,SQL 语句可有一个或多个 IN 参数,IN参数的值在 SQL 语句创建时未被指定。该语句为每个 IN 参数保留一个问号(“?”)作为占位符。
每个问号的值必须在该语句执行之前,通过适当的setInt或者setString 等方法提供。
由于 PreparedStatement 对象已预编译过,所以其执行速度要快于 Statement 对象。因此,多次执行的 SQL 语句经常创建为 PreparedStatement 对象,以提高效率。
通常批量处理时使用PreparedStatement。
1 //SQL语句已发送给数据库,并编译好为执行作好准备 2 PreparedStatement pstmt = con.prepareStatement( 3 "UPDATE emp SET job= ? WHERE empno = ?"); 4 //对占位符进行初始化 5 pstmt.setLong(1, "Manager"); 6 pstmt.setInt(2,1001); 7 //执行SQL语句 8 pstmt.executeUpdate();
小案例:分别向数据库插入1000条记录。分别记录执行时间,然后进行比较。
新建项目:
使用Statement的 执行效率的类INSERT3:
1 package com.cnblogs.daliu_it; 2 3 import java.sql.Connection; 4 import java.sql.PreparedStatement; 5 import java.sql.Statement; 6 7 /** 8 * 使用Statement的 执行效率 9 * 10 */ 11 public class INSERT3 { 12 13 public static void main(String[] args) { 14 Connection conn = null; 15 try { 16 conn = DBUtility.getConnection(); 17 Statement state = conn.createStatement(); 18 long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); 19 20 for (int i = 7000; i < 8000; i++) { 21 String sql = "INSERT INTO user VALUES" + "(" + i + "," 22 + "'test" + i + "'," + "'12345'," + "5000," + "'test" 23 + i + "@qq.com'" + ")"; 24 state.executeUpdate(sql); 25 } 26 System.out.println("插入完毕"); 27 long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); 28 System.out.println("耗时:" + (end - start)); 29 } catch (Exception e) { 30 System.out.println("插入数据失败"); 31 e.printStackTrace(); 32 } finally { 33 DBUtility.closeConnection(conn); 34 } 35 } 36 }
测试数据:

使用预编译PreparedStatement SQL提高执行效率的类INSERT2:
1 package com.cnblogs.daliu_it; 2 3 import java.sql.Connection; 4 import java.sql.PreparedStatement; 5 6 /** 7 * 使用预编译PreparedStatement SQL提高执行效率 8 * 9 */ 10 public class INSERT2 { 11 public static void main(String[] args) { 12 Connection conn = null; 13 try { 14 conn = DBUtility.getConnection(); 15 // Statement state= conn.createStatement(); 16 17 String sql = "INSERT INTO user VALUES(?,?,'123456',?,?)"; 18 /* 19 * 根据给定的预编译SQL语句创建一个 PreparedStatement 20 */ 21 PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql); 22 23 long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); 24 25 for (int i = 9000; i < 10000; i++) { 26 ps.setInt(1, i); 27 ps.setString(2, "test" + i); 28 ps.setInt(3, 5000); 29 ps.setString(4, "test" + i + "@qq.com"); 30 ps.executeUpdate(); 31 } 32 System.out.println("插入完毕"); 33 long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); 34 System.out.println("耗时:" + (end - start)); 35 } catch (Exception e) { 36 System.out.println("插入数据失败"); 37 e.printStackTrace(); 38 } finally { 39 DBUtility.closeConnection(conn); 40 } 41 } 42 }
测试效果:

二、通过PreparedStatement防止SQL Injection
对JDBC而言,SQL注入攻击只对Statement有效,对PreparedStatement无效,因为PreparedStatement不允许在插入参数时改变SQL语句的逻辑结构。
使用预编译的语句对象时,用户传入的任何数据不会和原SQL语句发生匹配关系,无需对输入的数据做过滤。如果用户将”or 1 = 1”传入赋值给占位符,下述SQL语句将无法执行:select * from t where username = ? and password = ?;
PreparedStatement是Statement的子类,表示预编译的SQL语句的对象。在使用PreparedStatement对象执行SQL命令时,命令被数据库编译和解析,并放入命令缓冲区。缓冲区中的预编译SQL命令可以重复使用。
1 sql = "select * from users where NAME = ? and PWD = ?"; 2 System.out.println(sql); 3 4 5 con = DBUtility.getConnection(); 6 7 //通过Statement 的改为prepareStatement 8 stmt = con.prepareStatement(sql); 9 10 11 // rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql); 12 13 stmt.setString(1, username); 14 stmt.setString(2, password); 15 rs = stmt.executeQuery();
使用PreparedStatement来执行SQL语句。在SQL语句中有2个问号,在代码中要给它们分别设置值,规则是:从左到右,对应1,2,...。
对于JDBC而言,SQL注入攻击只对Statement有效,对PreparedStatement是无效的,这是因为PreparedStatement不允许在插入时改变查询的逻辑结构。
例子:使用PreparedStatement实现用户名和密码的验证功能。
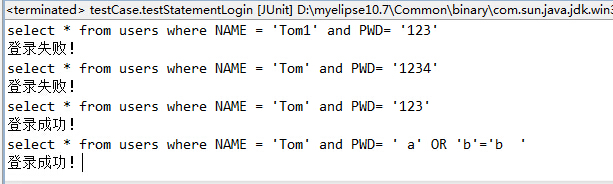
(1) 使用Statement实现用户名和密码的验证功能,并测试用户名为“Tom”、密码为“123”以及用户名为“Tom”、密码为“a' OR 'b'='b”是否能登录成功。
(2)使用PreparedStatement实现用户名和密码的验证功能,并测试用户名为“Tom”、密码为“a' OR 'b'='b”是否能登录成功。
1.新建一个java项目,配置文件,导入所需要的jar包。如下图:
2.首先创建user表:
1 2 create table users( 3 id int(4) auto_increment, 4 name varchar(50), 5 pwd varchar(50), 6 phone varchar(50) 7 ); 8 9 desc users; 10 11 select * from users; 12 13 insert into users(id,username,password)values(1,'Tom','123','110'); 14 insert into users(id,username,password)values(2,'Jerry','abc','119'); 15 insert into users(id,username,password)values(3,'Andy','456','112'); 16 17 18 select * from users;
3.连接数据库类DBUtility:
1 package com.cnblogs.daliu_it; 2 3 import java.io.IOException; 4 import java.sql.Connection; 5 import java.sql.SQLException; 6 import java.util.Properties; 7 8 import org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource; 9 /** 10 * 工具类 11 * @author daliu_it 12 * 13 */ 14 public class DBUtility { 15 private static BasicDataSource dataSource = null; 16 17 public DBUtility() { 18 } 19 public static void init() { 20 21 Properties dbProps = new Properties(); 22 // 取配置文件可以根据实际的不同修改 23 try { 24 dbProps.load(DBUtility.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream( 25 "com/cnblogs/daliu_it/db.properties")); 26 } catch (IOException e) { 27 e.printStackTrace(); 28 } 29 30 try { 31 String driveClassName = dbProps.getProperty("jdbc.driverClassName"); 32 String url = dbProps.getProperty("jdbc.url"); 33 String username = dbProps.getProperty("jdbc.username"); 34 String password = dbProps.getProperty("jdbc.password"); 35 36 String initialSize = dbProps.getProperty("dataSource.initialSize"); 37 String minIdle = dbProps.getProperty("dataSource.minIdle"); 38 String maxIdle = dbProps.getProperty("dataSource.maxIdle"); 39 String maxWait = dbProps.getProperty("dataSource.maxWait"); 40 String maxActive = dbProps.getProperty("dataSource.maxActive"); 41 42 dataSource = new BasicDataSource(); 43 dataSource.setDriverClassName(driveClassName); 44 dataSource.setUrl(url); 45 dataSource.setUsername(username); 46 dataSource.setPassword(password); 47 48 // 初始化连接数 49 if (initialSize != null) 50 dataSource.setInitialSize(Integer.parseInt(initialSize)); 51 52 // 最小空闲连接 53 if (minIdle != null) 54 dataSource.setMinIdle(Integer.parseInt(minIdle)); 55 56 // 最大空闲连接 57 if (maxIdle != null) 58 dataSource.setMaxIdle(Integer.parseInt(maxIdle)); 59 60 // 超时回收时间(以毫秒为单位) 61 if (maxWait != null) 62 dataSource.setMaxWait(Long.parseLong(maxWait)); 63 64 // 最大连接数 65 if (maxActive != null) { 66 if (!maxActive.trim().equals("0")) 67 dataSource.setMaxActive(Integer.parseInt(maxActive)); 68 } 69 } catch (Exception e) { 70 e.printStackTrace(); 71 System.out.println("创建连接池失败!请检查设置!!!"); 72 } 73 } 74 75 /** 76 * 数据库连接 77 * @return 78 * @throws SQLException 79 */ 80 public static synchronized Connection getConnection() throws SQLException { 81 if (dataSource == null) { 82 init(); 83 } 84 Connection conn = null; 85 if (dataSource != null) { 86 conn = dataSource.getConnection(); 87 } 88 return conn; 89 } 90 91 /** 92 * 关闭数据库 93 * @param conn 94 */ 95 public static void closeConnection(Connection conn){ 96 if(conn!=null){ 97 try { 98 conn.close(); 99 } catch (SQLException e) { 100 System.out.println("关闭资源失败"); 101 e.printStackTrace(); 102 } 103 } 104 } 105 106 }
4.使用Statement实现验证用户名密码是否存在的方法的类UserDAO:
1 package com.cnblogs.daliu_it; 2 3 import java.sql.Connection; 4 import java.sql.ResultSet; 5 import java.sql.SQLException; 6 import java.sql.Statement; 7 8 public class UserDAO { 9 10 /** 11 * 使用Statement实现验证用户名密码是否存在的方法 12 * 13 * @param username 14 * @param password 15 */ 16 public void login(String username, String password) { 17 18 // Statement 19 Connection con = null; 20 Statement stmt = null; 21 ResultSet rs = null; 22 23 // 定义sql语句,用来查询用户名和密码 24 String sql = null; 25 26 try { 27 sql = "select * from users where NAME = '" + username 28 + "' and PWD= '" + password + "'"; 29 30 // 检查一下sql语句是否拼写正确 31 System.out.println(sql); 32 33 // 获得数据库的连接 34 con = DBUtility.getConnection(); 35 36 stmt = con.createStatement(); 37 38 // 执行sql语句 39 rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql); 40 41 // 进行结果的遍历,并给出相应的提示 42 if (rs.next()) { 43 System.out.println("登录成功!"); 44 } else { 45 System.out.println("登录失败!"); 46 } 47 48 } catch (SQLException e) { 49 50 System.out.println("数据库访问异常!"); 51 throw new RuntimeException(e); 52 53 } finally { 54 55 // 最后关闭一下资源 56 if (con != null) { 57 DBUtility.closeConnection(con); 58 } 59 } 60 } 61 }
5.使用PreparedStatement实现验证用户名密码是否存在的方法的类 UserDAO2:
1 package com.cnblogs.daliu_it; 2 3 import java.sql.Connection; 4 import java.sql.PreparedStatement; 5 import java.sql.ResultSet; 6 import java.sql.SQLException; 7 8 public class UserDAO2 { 9 10 /** 11 * 使用PreparedStatement实现验证用户名密码是否存在的方法 12 * 13 * @param username 14 * @param password 15 */ 16 public void login(String username, String password) { 17 18 Connection con = null; 19 20 // 通过Statement 的改为prepareStatement 21 PreparedStatement stmt = null; 22 ResultSet rs = null; 23 24 String sql = null; 25 26 try { 27 // sql = "select * from users where NAME = '" + username+ 28 // "' and PWD= '" + password + "'"; 29 sql = "select * from users where NAME = ? and PWD = ?"; 30 // 使用PreparedStatement是将 "aa' or '1' = '1" 31 // 作为一个字符串赋值给问号“?”,使其作为"用户名"字段的对应值,这样来防止SQL注入。 32 33 System.out.println(sql); 34 con = DBUtility.getConnection(); 35 36 // 对于JDBC而言,SQL注入攻击只对Statement有效,对PreparedStatement是无效的,这是因为PreparedStatement不允许在插入时改变查询的逻辑结构。 37 stmt = con.prepareStatement(sql); 38 // rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql); 39 stmt.setString(1, username); 40 stmt.setString(2, password); 41 rs = stmt.executeQuery(); 42 43 // 进行结果的遍历,并给出相应的提示 44 if (rs.next()) { 45 System.out.println("登录成功!"); 46 } else { 47 System.out.println("登录失败!"); 48 } 49 50 System.out.println("执行完毕!"); 51 } catch (SQLException e) { 52 53 System.out.println("数据库访问异常!"); 54 throw new RuntimeException(e); 55 56 } finally { 57 58 // 最后关闭一下资源 59 if (con != null) { 60 DBUtility.closeConnection(con); 61 } 62 } 63 } 64 }
6.配置文件db.properties:
1 #Oracle 2 #jdbc.driverClassName=oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver 3 #jdbc.url=jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:orcl 4 #jdbc.username=root 5 #jdbc.password=123456 6 7 #Mysql 8 jdbc.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver 9 jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/csdn 10 jdbc.username=root 11 jdbc.password=123456 12 13 dataSource.initialSize=10 14 dataSource.maxIdle=20 15 dataSource.minIdle=5 16 dataSource.maxActive=50 17 dataSource.maxWait=1000
7.测试类testCase:
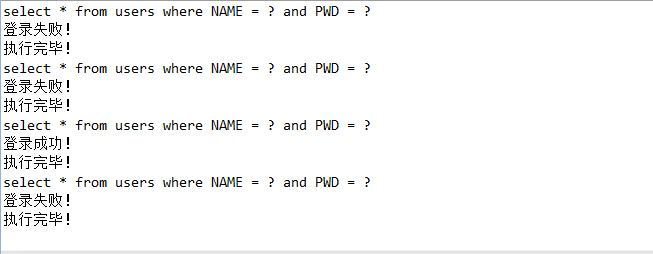
1 package com.daliu_it.test; 2 3 import java.sql.SQLException; 4 5 import org.junit.Test; 6 7 import com.cnblogs.daliu_it.DBUtility; 8 import com.cnblogs.daliu_it.UserDAO; 9 import com.cnblogs.daliu_it.UserDAO2; 10 11 public class testCase { 12 13 /** 14 * 测试是否连接 15 * 16 * @throws SQLException 17 */ 18 @Test 19 public void testgetConnection() throws SQLException { 20 DBUtility db = new DBUtility(); 21 System.out.println(db.getConnection()); 22 } 23 24 /** 25 * 测试使用Statement实现验证用户名密码是否存在的方法 26 */ 27 @Test 28 public void testStatementLogin() { 29 30 UserDAO dao = new UserDAO(); 31 // 用户名不正确 32 dao.login("Tom1", "123"); 33 // 用户名不正确 34 dao.login("Tom", "1234"); 35 // 正确 36 dao.login("Tom", "123"); 37 38 /** 39 * 这个也能登陆成功,不过这里会存在一个sql注入的问题 40 */ 41 dao.login("Tom", " a' OR 'b'='b "); 42 43 } 44 45 @Test 46 public void testPreparedStatementLogin() { 47 48 UserDAO2 dao = new UserDAO2(); 49 // 用户名不正确 50 dao.login("Tom1", "123"); 51 // 用户名不正确 52 dao.login("Tom", "1234"); 53 // 正确 54 dao.login("Tom", "123"); 55 // 测试是否还存在sql注入问题,不能登陆成功,说明我们已经解决了sql注入问题 56 dao.login("Tom", " a' OR 'b'='b "); 57 /** 58 * 实现机制不同,注入只对SQL语句的准备(编译)过程有破坏作用,而PreparedStatement已经准备好了, 59 * 执行阶段只是把输入串作为数据处理,不再需要对SQL语句进行解析、准备,因此也就避免了SQL注入问题。 60 */ 61 62 } 63 64 }
测试效果:
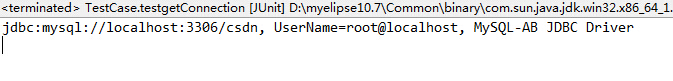
(1)连接效果:
(2)测试使用Statement实现验证用户名密码是否存在的方法
(3)测试使用PreparedStatement实现验证用户名密码是否存在的方法
原文作者:daliu_it
博文出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/liuhongfeng/p/4175765.html
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,但未经作者同意转载必须保留以上的声明且在放在文章页面明显位置。谢谢合作。