一,准备内容
在之前讲过的asp.net core 实现OAuth2.0四种模式系列中的IdentityApi客户端用到了以下配置代码
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddMvc().SetCompatibilityVersion(CompatibilityVersion.Version_2_2);
services.AddAuthentication("Bearer").AddJwtBearer(r => {
//认证地址
r.Authority = "http://localhost:5000";
//权限标识
r.Audience = "secretapi";
//是否必需HTTPS
r.RequireHttpsMetadata = false;
});
}
app.UseAuthentication();
AddJwtBearer到底起到什么作用呢。首先熟习两个概念
1,中间件(Middleware)
中间件是组装到Asp.net core应用程序管道中以处理请求和响应的软件。可以这样理解:一根管道从水源(用户)连接到家庭(资源)。水源的水是不能直接饮用的,需要重重过滤,这些过滤手段就是中间件,在处理过程中决定是否往下继续传送,可能丢弃,也可能转到其它地方。请参考我之前写的《Asp.net core之中间件》
2,身份认证执行方案(AuthenticationSchemes)
在一个启用身份认证的Asp.net core应用中可以有几个执行方案,分工不同,功能也不同。可以指定由那个方案进行身份认证,如以下代码
[HttpGet]
[Route("api/identity")]
[Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authorization.Authorize(Roles ="admin",AuthenticationSchemes ="Bearer")]
public object GetUserClaims()
指定了方案名为“Bearer”的方案来做这个Api接口的认证。这个"Bearer"是怎么来的呢,看一下services.AddAuthentication方法有几个重载,我们上面用的重载是传递一个字符串指定默认方案为“Bearer”,那么程序是如果根据"Bearer"这个方案名找到对应的执行方案的呢?
二,AddJwtBearer添加Jwt证书验证执行方案
AddJwtBearer是Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication.JwtBearer对AuthenticationBuilder的一个扩写方法,看一下源码
public static class JwtBearerExtensions
{
public static AuthenticationBuilder AddJwtBearer(this AuthenticationBuilder builder)
=> builder.AddJwtBearer(JwtBearerDefaults.AuthenticationScheme, _ => { });
public static AuthenticationBuilder AddJwtBearer(this AuthenticationBuilder builder, Action<JwtBearerOptions> configureOptions)
=> builder.AddJwtBearer(JwtBearerDefaults.AuthenticationScheme, configureOptions);
public static AuthenticationBuilder AddJwtBearer(this AuthenticationBuilder builder, string authenticationScheme, Action<JwtBearerOptions> configureOptions)
=> builder.AddJwtBearer(authenticationScheme, displayName: null, configureOptions: configureOptions);
public static AuthenticationBuilder AddJwtBearer(this AuthenticationBuilder builder, string authenticationScheme, string displayName, Action<JwtBearerOptions> configureOptions)
{
builder.Services.TryAddEnumerable(ServiceDescriptor.Singleton<IPostConfigureOptions<JwtBearerOptions>, JwtBearerPostConfigureOptions>());
return builder.AddScheme<JwtBearerOptions, JwtBearerHandler>(authenticationScheme, displayName, configureOptions);
}
}
有四个方法重载,但最后运行的是最后一个重载,最后一个重载用了builder.AddScheme方法添加方案,所以,AddJwtBearer本质上就是添加验证方案。前二个方法重载没有传“authenticationScheme"参数,使用的是JwtBearerDefaults.AuthenticationScheme这个值,我们上边用的代码是第二个重载,传了configOptions,没传authenticationScheme,JwtBearerDefaults.AuthenticationScheme这个值预设为Bearer(见以下源码),所以根据Bearer这个方案名找到的方案就是我们运行AddJwtBearer所添加的方案。
public static class JwtBearerDefaults
{
/// <summary>
/// Default value for AuthenticationScheme property in the JwtBearerAuthenticationOptions
/// </summary>
public const string AuthenticationScheme = "Bearer";
}
三,JwtBearer执行方案具体做了什么工作
上面说过AddJwtBearer本质上就是添加一个执行方案。先看下添加执行方案的关键源码
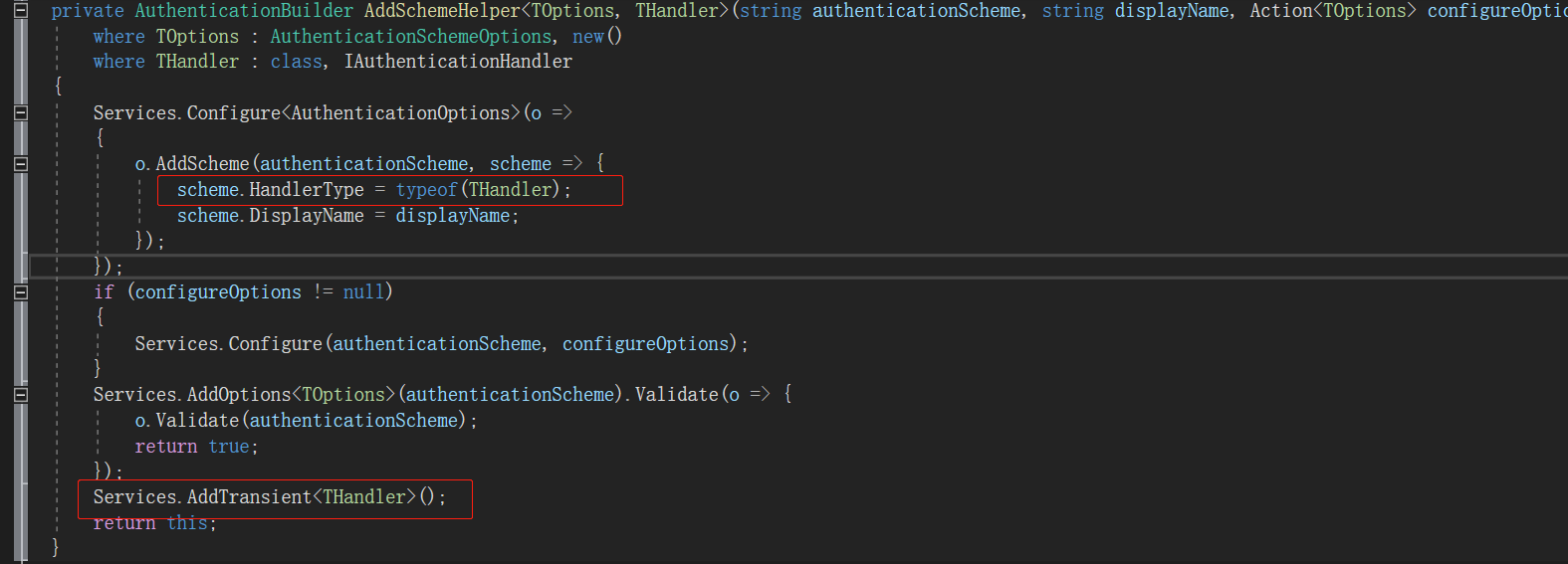
把方案的HandlerType指定为方法的第二个泛型,方便从根据方案实例化Hndler,并将这个泛型添加进了服务依赖。从AddJwtBearer源码可看到出这个泛型为:JwtBearerHandler
public static AuthenticationBuilder AddJwtBearer(this AuthenticationBuilder builder, string authenticationScheme, string displayName, Action<JwtBearerOptions> configureOptions)
{
builder.Services.TryAddEnumerable(ServiceDescriptor.Singleton<IPostConfigureOptions<JwtBearerOptions>, JwtBearerPostConfigureOptions>());
return builder.AddScheme<JwtBearerOptions, JwtBearerHandler>(authenticationScheme, displayName, configureOptions);
}
分析JwtBearerHandler源码,JwtBearerHandler主要是能干三件事
1,HandleAuthenticateAsync:获取HTTP请求头里的Authorization头。先验证是不是Bearer格式,再用JwtSecurityTokenHandler这个工具类验证Jwt数据,包括长度,格式,是否过期,签发地址等。
触发事件:1),MessageReceived:接收到请时触发。
2),TokenValidated:验证Jwt数据成功时触发。
3),AuthenticationFailed:验证Jwt数据失败时触发。
附源码
protected override async Task<AuthenticateResult> HandleAuthenticateAsync()
{
string token = null;
try
{
// Give application opportunity to find from a different location, adjust, or reject token
var messageReceivedContext = new MessageReceivedContext(Context, Scheme, Options);
// event can set the token
await Events.MessageReceived(messageReceivedContext);
if (messageReceivedContext.Result != null)
{
return messageReceivedContext.Result;
}
// If application retrieved token from somewhere else, use that.
token = messageReceivedContext.Token;
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(token))
{
string authorization = Request.Headers[HeaderNames.Authorization];
// If no authorization header found, nothing to process further
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(authorization))
{
return AuthenticateResult.NoResult();
}
if (authorization.StartsWith("Bearer ", StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase))
{
token = authorization.Substring("Bearer ".Length).Trim();
}
// If no token found, no further work possible
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(token))
{
return AuthenticateResult.NoResult();
}
}
if (_configuration == null && Options.ConfigurationManager != null)
{
_configuration = await Options.ConfigurationManager.GetConfigurationAsync(Context.RequestAborted);
}
var validationParameters = Options.TokenValidationParameters.Clone();
if (_configuration != null)
{
var issuers = new[] { _configuration.Issuer };
validationParameters.ValidIssuers = validationParameters.ValidIssuers?.Concat(issuers) ?? issuers;
validationParameters.IssuerSigningKeys = validationParameters.IssuerSigningKeys?.Concat(_configuration.SigningKeys)
?? _configuration.SigningKeys;
}
List<Exception> validationFailures = null;
SecurityToken validatedToken;
foreach (var validator in Options.SecurityTokenValidators)
{
if (validator.CanReadToken(token))
{
ClaimsPrincipal principal;
try
{
principal = validator.ValidateToken(token, validationParameters, out validatedToken);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Logger.TokenValidationFailed(ex);
// Refresh the configuration for exceptions that may be caused by key rollovers. The user can also request a refresh in the event.
if (Options.RefreshOnIssuerKeyNotFound && Options.ConfigurationManager != null
&& ex is SecurityTokenSignatureKeyNotFoundException)
{
Options.ConfigurationManager.RequestRefresh();
}
if (validationFailures == null)
{
validationFailures = new List<Exception>(1);
}
validationFailures.Add(ex);
continue;
}
Logger.TokenValidationSucceeded();
var tokenValidatedContext = new TokenValidatedContext(Context, Scheme, Options)
{
Principal = principal,
SecurityToken = validatedToken
};
await Events.TokenValidated(tokenValidatedContext);
if (tokenValidatedContext.Result != null)
{
return tokenValidatedContext.Result;
}
if (Options.SaveToken)
{
tokenValidatedContext.Properties.StoreTokens(new[]
{
new AuthenticationToken { Name = "access_token", Value = token }
});
}
tokenValidatedContext.Success();
return tokenValidatedContext.Result;
}
}
if (validationFailures != null)
{
var authenticationFailedContext = new AuthenticationFailedContext(Context, Scheme, Options)
{
Exception = (validationFailures.Count == 1) ? validationFailures[0] : new AggregateException(validationFailures)
};
await Events.AuthenticationFailed(authenticationFailedContext);
if (authenticationFailedContext.Result != null)
{
return authenticationFailedContext.Result;
}
return AuthenticateResult.Fail(authenticationFailedContext.Exception);
}
return AuthenticateResult.Fail("No SecurityTokenValidator available for token: " + token ?? "[null]");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Logger.ErrorProcessingMessage(ex);
var authenticationFailedContext = new AuthenticationFailedContext(Context, Scheme, Options)
{
Exception = ex
};
await Events.AuthenticationFailed(authenticationFailedContext);
if (authenticationFailedContext.Result != null)
{
return authenticationFailedContext.Result;
}
throw;
}
}
2,HandleChallengeAsync:验证失败时挑战验证结果,有点像网球比赛的挑战鹰眼功能。但Jwt的挑战验证极其简单,就是重新调用了一次HandleAuthenticateAsync,然后就是挑战失败后设置请求上下文的状态码为:401,也就是我们在前端访问的Response状态码,再往Http回应的Http Header上加上一个名为WWWAuthenticate的头。触发Challenge事件表示挑战失败。
附源码
protected override async Task HandleChallengeAsync(AuthenticationProperties properties)
{
var authResult = await HandleAuthenticateOnceSafeAsync();
var eventContext = new JwtBearerChallengeContext(Context, Scheme, Options, properties)
{
AuthenticateFailure = authResult?.Failure
};
// Avoid returning error=invalid_token if the error is not caused by an authentication failure (e.g missing token).
if (Options.IncludeErrorDetails && eventContext.AuthenticateFailure != null)
{
eventContext.Error = "invalid_token";
eventContext.ErrorDescription = CreateErrorDescription(eventContext.AuthenticateFailure);
}
await Events.Challenge(eventContext);
if (eventContext.Handled)
{
return;
}
Response.StatusCode = 401;
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(eventContext.Error) &&
string.IsNullOrEmpty(eventContext.ErrorDescription) &&
string.IsNullOrEmpty(eventContext.ErrorUri))
{
Response.Headers.Append(HeaderNames.WWWAuthenticate, Options.Challenge);
}
else
{
// https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6750#section-3.1
// WWW-Authenticate: Bearer realm="example", error="invalid_token", error_description="The access token expired"
var builder = new StringBuilder(Options.Challenge);
if (Options.Challenge.IndexOf(' ') > 0)
{
// Only add a comma after the first param, if any
builder.Append(',');
}
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(eventContext.Error))
{
builder.Append(" error="");
builder.Append(eventContext.Error);
builder.Append(""");
}
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(eventContext.ErrorDescription))
{
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(eventContext.Error))
{
builder.Append(",");
}
builder.Append(" error_description="");
builder.Append(eventContext.ErrorDescription);
builder.Append('"');
}
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(eventContext.ErrorUri))
{
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(eventContext.Error) ||
!string.IsNullOrEmpty(eventContext.ErrorDescription))
{
builder.Append(",");
}
builder.Append(" error_uri="");
builder.Append(eventContext.ErrorUri);
builder.Append('"');
}
Response.Headers.Append(HeaderNames.WWWAuthenticate, builder.ToString());
}
}
3,HandleForbiddenAsync,验证Jwt数据成功,但授权失败时会调用这个方法,设置Response状态码为403,直接返回不再继续往下。触发Forbidden事件。
附源码
protected override Task HandleForbiddenAsync(AuthenticationProperties properties)
{
var forbiddenContext = new ForbiddenContext(Context, Scheme, Options);
Response.StatusCode = 403;
return Events.Forbidden(forbiddenContext);
}
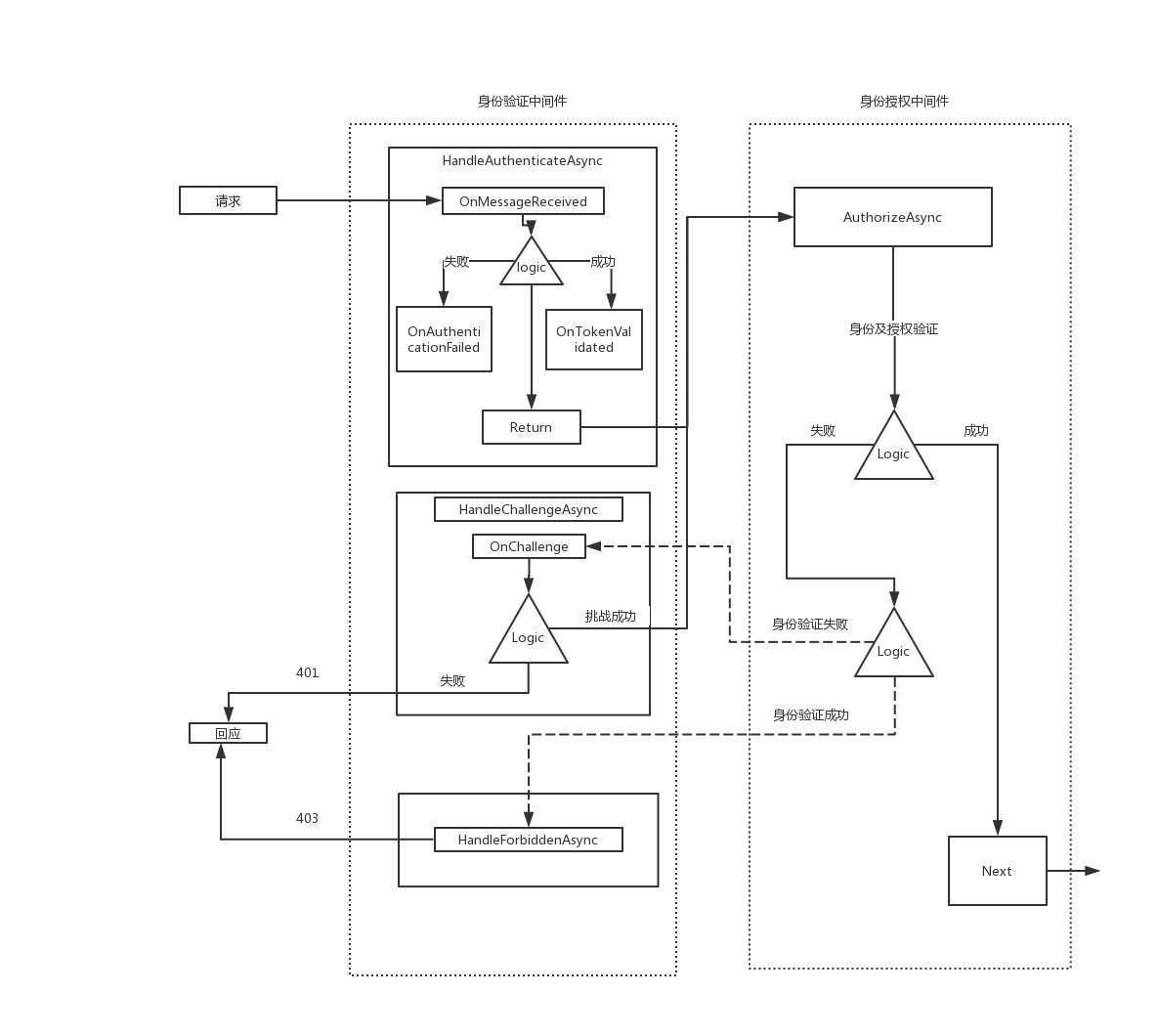
三,JwtBearer执行方案工作流程
上边说了JwtBearerHandler的三个功能,这一小节来讲讲这三个功能在什么时候开始工作的。
上面我们使用AddAuthentication,AddJwtBearer只是把这个身份验证这个功能加入到服务,好比你买了台冰箱放在家里,还没有上电使用,占了个地方而已,怎么使用呢,这里就要用到中间件,中间件就像一个即插即用的插头。启用身份验证的中间件用UseAuthentication方法。看一下这个方法的源码,看它又做了什么事。
// Copyright (c) .NET Foundation. All rights reserved.
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0. See License.txt in the project root for license information.
using System;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
namespace Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication
{
public class AuthenticationMiddleware
{
private readonly RequestDelegate _next;
public AuthenticationMiddleware(RequestDelegate next, IAuthenticationSchemeProvider schemes)
{
if (next == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(next));
}
if (schemes == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(schemes));
}
_next = next;
Schemes = schemes;
}
public IAuthenticationSchemeProvider Schemes { get; set; }
public async Task Invoke(HttpContext context)
{
context.Features.Set<IAuthenticationFeature>(new AuthenticationFeature
{
OriginalPath = context.Request.Path,
OriginalPathBase = context.Request.PathBase
});
// Give any IAuthenticationRequestHandler schemes a chance to handle the request
var handlers = context.RequestServices.GetRequiredService<IAuthenticationHandlerProvider>();
foreach (var scheme in await Schemes.GetRequestHandlerSchemesAsync())
{
var handler = await handlers.GetHandlerAsync(context, scheme.Name) as IAuthenticationRequestHandler;
if (handler != null && await handler.HandleRequestAsync())
{
return;
}
}
var defaultAuthenticate = await Schemes.GetDefaultAuthenticateSchemeAsync();
if (defaultAuthenticate != null)
{
var result = await context.AuthenticateAsync(defaultAuthenticate.Name);
if (result?.Principal != null)
{
context.User = result.Principal;
}
}
await _next(context);
}
}
}
重点是Invoke方法,看来就做了二件事
1,从当前方案集合里(可添加多个方案,目前我们只用了一个Bearer)筛选出IAuthenticationRequestHandler的实现类,执行他的HandleRequestAsync方法。
2,找到默认执行方案,执行他的AuthenticateAsync方法。
第1件事,当前我添加的Bearer方案所用的JwtBearerHandler并没有继承自IAuthenticationRequestHandler,所以这一步在当前验证方案就没起作用,我们在以后讲AddOpenIdConnect时会讲到这一步,使用OpenidConnect做身份验证时,OpenidConnect所用的OpenIdConnectHandler是RemoteAuthenticationHandler的实现,而RemoteAuthenticationHandler继承了IAuthenticationRequestHandler
public class JwtBearerHandler : AuthenticationHandler<JwtBearerOptions>
public abstract class RemoteAuthenticationHandler<TOptions> : AuthenticationHandler<TOptions>, IAuthenticationRequestHandler
第2件事,执行AuthenticateAsync方法,在JwtBearerHandler中没有这个方法,但他的父类 AuthenticationHandler<JwtBearerOptions>中是有的。在父类中执行AuthenticateAsync时如果没有设置ForwardAuthenticate(验证方案跳转),会执行HandleAuthenticateOnceAsync方法,这个方法要注意:他是一个类似于单例的调用方式,在生命周期内只会触发一次子类的HandleAuthenticateAsync方法。也就是JwtBearerHandler的HandleAuthenticateAsync方法。理解这个对后续的工作流很重要。
附源码
public async Task<AuthenticateResult> AuthenticateAsync()
{
var target = ResolveTarget(Options.ForwardAuthenticate);
if (target != null)
{
return await Context.AuthenticateAsync(target);
}
// Calling Authenticate more than once should always return the original value.
var result = await HandleAuthenticateOnceAsync();
if (result?.Failure == null)
{
var ticket = result?.Ticket;
if (ticket?.Principal != null)
{
Logger.AuthenticationSchemeAuthenticated(Scheme.Name);
}
else
{
Logger.AuthenticationSchemeNotAuthenticated(Scheme.Name);
}
}
else
{
Logger.AuthenticationSchemeNotAuthenticatedWithFailure(Scheme.Name, result.Failure.Message);
}
return result;
}
/// <summary>
/// Used to ensure HandleAuthenticateAsync is only invoked once. The subsequent calls
/// will return the same authenticate result.
/// </summary>
protected Task<AuthenticateResult> HandleAuthenticateOnceAsync()
{
if (_authenticateTask == null)
{
_authenticateTask = HandleAuthenticateAsync();
}
return _authenticateTask;
}
好了,JwtBearerHandler的三个功能,我们已经搞清一个了,他的验证功能在请求伊始就会能过身份验证中间件触发。那另二个呢,另外二个功能的触发点需要用到另一个中间件,身份授权中间件(UseAuthorization)。这个中间件不用手动Use,AddMvc和UseMvc已经把这部份工作做了。这个中间件干了什么,看下他的中间件实现源码
// Copyright (c) .NET Foundation. All rights reserved.
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0. See License.txt in the project root for license information.
using System;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authorization.Policy;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
namespace Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authorization
{
public class AuthorizationMiddleware
{
// Property key is used by other systems, e.g. MVC, to check if authorization middleware has run
private const string AuthorizationMiddlewareInvokedKey = "__AuthorizationMiddlewareInvoked";
private static readonly object AuthorizationMiddlewareInvokedValue = new object();
private readonly RequestDelegate _next;
private readonly IAuthorizationPolicyProvider _policyProvider;
public AuthorizationMiddleware(RequestDelegate next, IAuthorizationPolicyProvider policyProvider)
{
_next = next ?? throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(next));
_policyProvider = policyProvider ?? throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(policyProvider));
}
public async Task Invoke(HttpContext context)
{
if (context == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(context));
}
var endpoint = context.GetEndpoint();
// Flag to indicate to other systems, e.g. MVC, that authorization middleware was run for this request
context.Items[AuthorizationMiddlewareInvokedKey] = AuthorizationMiddlewareInvokedValue;
// IMPORTANT: Changes to authorization logic should be mirrored in MVC's AuthorizeFilter
var authorizeData = endpoint?.Metadata.GetOrderedMetadata<IAuthorizeData>() ?? Array.Empty<IAuthorizeData>();
var policy = await AuthorizationPolicy.CombineAsync(_policyProvider, authorizeData);
if (policy == null)
{
await _next(context);
return;
}
// Policy evaluator has transient lifetime so it fetched from request services instead of injecting in constructor
var policyEvaluator = context.RequestServices.GetRequiredService<IPolicyEvaluator>();
var authenticateResult = await policyEvaluator.AuthenticateAsync(policy, context);
// Allow Anonymous skips all authorization
if (endpoint?.Metadata.GetMetadata<IAllowAnonymous>() != null)
{
await _next(context);
return;
}
// Note that the resource will be null if there is no matched endpoint
var authorizeResult = await policyEvaluator.AuthorizeAsync(policy, authenticateResult, context, resource: endpoint);
if (authorizeResult.Challenged)
{
if (policy.AuthenticationSchemes.Any())
{
foreach (var scheme in policy.AuthenticationSchemes)
{
await context.ChallengeAsync(scheme);
}
}
else
{
await context.ChallengeAsync();
}
return;
}
else if (authorizeResult.Forbidden)
{
if (policy.AuthenticationSchemes.Any())
{
foreach (var scheme in policy.AuthenticationSchemes)
{
await context.ForbidAsync(scheme);
}
}
else
{
await context.ForbidAsync();
}
return;
}
await _next(context);
}
}
}
1,先进行策略验证,是不是该请求不需要授权,是的话就往下传递请求,不再执行后边的代码
2,该请求需要授权访问,请调用policyEvaluator.AuthorizeAsync进行身份及授权验证
附源码
public virtual async Task<PolicyAuthorizationResult> AuthorizeAsync(AuthorizationPolicy policy, AuthenticateResult authenticationResult, HttpContext context, object resource)
{
if (policy == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(policy));
}
var result = await _authorization.AuthorizeAsync(context.User, resource, policy);
if (result.Succeeded)
{
return PolicyAuthorizationResult.Success();
}
// If authentication was successful, return forbidden, otherwise challenge
return (authenticationResult.Succeeded)
? PolicyAuthorizationResult.Forbid()
: PolicyAuthorizationResult.Challenge();
}
如果身份和授权都验证成功,则成功,如果身份验证能过,授权没通过则禁止访问,直接回应,如果身份验证没通过就去挑战验证结果,挑战成功继续来一次来,挑战失败就直接回应了。源码中的PolicyAuthorizationResult.Forbid() 和PolicyAuthorizationResult.Challenge()具体执行的是什么方法呢?看以下源码
public virtual Task<AuthenticationScheme> GetDefaultChallengeSchemeAsync()
=> _options.DefaultChallengeScheme != null
? GetSchemeAsync(_options.DefaultChallengeScheme)
: GetDefaultSchemeAsync();
public virtual Task<AuthenticationScheme> GetDefaultForbidSchemeAsync()
=> _options.DefaultForbidScheme != null
? GetSchemeAsync(_options.DefaultForbidScheme)
: GetDefaultChallengeSchemeAsync();
然来如果没有指定特定的方案,就返回默认的方案。指定特定的Challenge方案和Forbid方案我们讲OpenIdConnect时再详细说。目前我们所用的只有一个默认方案:Bearer,所以会执行JwtBearerHandler的Challenge和Forbid方法。
如此一来,JwtBearerHandler的三种功能触发时机,作用都已经搞清楚了,我画了个图方便大家理理解