原文:https://jishuin.proginn.com/p/763bfbd32655
在本文中,我将向你展示我认为对 Python 格式化字符串 f-string 来说最重要的一些技巧。你会通过各种样例学到多种格式化字符串的方法。总的来说,就是你会看到73个关于如何完美应用 f-string 的例子。
目录一览
1. f-string 是什么?
2. 用 python 做基本的文本格式化
3. f-string 局限性
4. 如何格式化表达式
5. 如何使用f-string调试你的代码
6. 如何在不同进制下格式化数字
7. 如何使用格式化字符串常量打印出对象
8. 如何在格式化字符串常量中设置浮点数精度
9. 如何将数字格式化为百分比
10. 如何调整或者增加f-string的填充
11. 如何转义字符
12. 如何使字符串居中
13. 如何添加千位分隔符
13.1如何使用逗号作为千分位分隔符格式化数字
13.2如何使用逗号作为小数分隔符格式化数字
14.如何用科学计数法(指数计数法)格式化数字
15.在 f-string 中使用 if-else
16.如何在 f-string 中使用字典
17.如何用 f-string 拼接字符串
18.如何格式化 datetime 对象
19.如何改正 f-string 的无效语法错误
20.如何在字符串前补零
21.如何编写多行格式化字符串常量(怎样应对新行符号)
22.总结
1、python 中的 f-string 是什么?
在 Python 的历史中,字符串格式化的发展源远流长。在 python 2.6 之前,想要格式化一个字符串,你只能使用 % 这个占位符,或者string.Template 模块。不久之后,出现了更灵活更靠谱的字符串格式化方式: str.format 方法。
过去使用 % 做字符串格式化方式的代码样例:
'msg: hello world'
用string.format的样例:
'msg: hello world'
为了进一步简化格式化方法,Eric Smith 在2015年提交了 PEP 498 -- Literal String Interpolation 提案。
PEP 498 提出了一种新的字符串插值方法,该方法可以更简单便捷的使用 str.format 方法。你只需要在字符串开头加上一个字母 f,形成 f”” 的格式就可以了。
使用f-string的样例:
'msg: hello world'
这就可以了!再也不需要用 string.format 或者 % 了。不过 f-string 并不能完全替代 str.format。本文也将列举出这两者并不通用的情况。
2、基本的字符串格式化
如上文所述,使用f-string格式化字符串十分简单。唯一的要求就是给它一个有效的表达式。f-string 也可以用大写F开头或者与 r 原始字符串结合使用。但是你不能将其与 b”” 或者 ”u” 混用。

'The book The dog guide has 124 pages''The book The dog guide has 124 pages'The book The dog guide has 124 pages\n>>> print(FR"The book {book} has{num_pages} pages\n")The book The dog guide has 124 pages\n>>> print(f"The book {book} has{num_pages} pages\n")The book The dog guide has 124 pages
差不多就这些!下一节中,我会用一些例子向你展示一些你用f-string能做或不能做的事儿。
3、f-string 的限制
虽然f-string十分的便捷,但它并不能完全代替str.format。f-string在表达式出现的上下文中进行求值计算。根据PEP498,这意味着该表达式可以获取所有局部和全局变量。而且该表达式是在运行时计算的表达式。如果在 { } 之中使用的表达式无法被计算,就会跳出如下异常。
---------------------------------------------------------------------------NameError Traceback(most recent call last)<ipython-input-1in<module>----> 1 f"{name}"NameError: name 'name' is not defined
这对 str.format 来说就不是问题,你可以提前定义一个模板字符串,并在之后调用.format方法时再传递上下文信息。
'Python'{name}
另外还有个限制是,你不能在f-string中使用行内注释。
File "", line 1f"My name is {name #name}!"^SyntaxError: f-string expression part cannot include '#'
4、如何格式化一个表达式
如果不想定义变量,那你可以在大括号中使用常量。Python会计算该表达式并显示最终计算结果。
>>> f"4 * 4 is {4 * 4}"'4 * 4 is 16'
或者你可以...
'4 * 4 is 16'
5、如何使用 f-string 来调试代码
调试是f-string最常见的用途之一了。Python3.8 之前,很多人会用一种非常繁杂的hello = 42; f"hello = {hello}”来进行调试。针对此Python3.8引入了一个新功能。你可以用 f"{hello=}" 重写上面的代码,而python会显示hello=42。下面这个例子展示了在使用函数表达式时如何应用该特性,其原理与上文代码是一样的。
...: return 42...:'magic_number() = 42'
6、如何格式化数字的不同进制
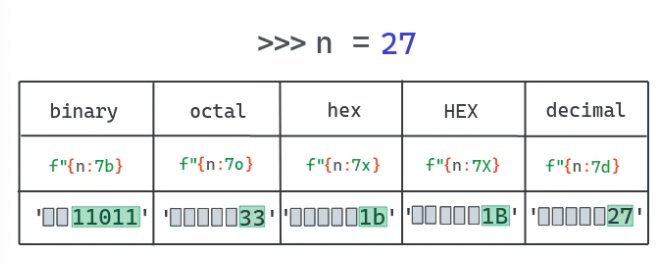
f-string 还能在不同进制下显示数字。例如,你不需要通过b来对一个int进行格式转化就可以显示其二进制结果。
>>> f'{7:b}''111'
总结一下就是你可以用f-string来格式化:
• int 到二进制
• int 到十六进制
• int 到八进制
• int 到十六进制(所有符号大写)
下面的例子使用缩进功能和进制格式化创建了一个表,可以显示数字在不同进制下的值。
"b": "bin","o": "oct","x": "hex","X": "HEX","d": "decimal"}...: for base, desc in bases.items():...: print(f"{n:5{base}}", end=' ')...: print()1 1 1 1 110 2 2 2 211 3 3 3 3100 4 4 4 4101 5 5 5 5110 6 6 6 6111 7 7 7 71000 10 8 8 81001 11 9 9 91010 12 a A 101011 13 b B 111100 14 c C 121101 15 d D 131110 16 e E 141111 17 f F 1510000 20 10 10 1610001 21 11 11 1710010 22 12 12 1810011 23 13 13 1910100 24 14 14 20
7、如何用 f-string 打印对象
你可以用f-string打印自定义对象。默认设置是,如果你向f-string表达式传递了一个对象,它将会显示该对象 __str__ 方法的返回值。不过,你也可以用显式转换操作标志来打印__repr__的值。
-
!r - 使用 repr() 将值转化为文本.
-
!s - 使用 str() 将值转化为文本.
def __init__(self, r: float = 255, g: float = 255, b: float = 255):self.r = rself.g = gself.b = bdef __str__(self) -> str:return "A RGB color"def __repr__(self) -> str:return f"Color(r={self.r}, g={self.g}, b={self.b})"# 如不加任何操作符, 会打印 __str__ 的值'A RGB color'# 用`obj!r` 的话会打印 __repr__ 的值'Color(r=123, g=32, b=255)'# 使用!s跟默认值一样'A RGB color'
Python也允许通过定义不同类型使用__format__方法控制格式化结果,下面的例子会展示所有可能情况。
def __init__(self, r: float = 255, g: float = 255, b: float = 255):self.r = rself.g = gself.b = bdef __str__(self) -> str:return "A RGB color"def __repr__(self) -> str:return f"Color(r={self.r}, g={self.g}, b={self.b})"# When no option is passed, the __str__ result is printed'A RGB color'# When `obj!r` is used, the __repr__ output is printed'Color(r=123, g=32, b=255)'# Same as the default'A RGB color'Python also allows us to control the formatting on a per-type basis through the __format__ method. The following example shows how you can do all of that.def __init__(self, r: float = 255, g: float = 255, b: float = 255):self.r = rself.g = gself.b = bdef __str__(self) -> str:return "A RGB color"def __repr__(self) -> str:return f"Color(r={self.r}, g={self.g}, b={self.b})"def __format__(self, format_spec: str) -> str:if not format_spec or format_spec == "s":return str(self)if format_spec == "r":return repr(self)if format_spec == "v":return f"Color(r={self.r}, g={self.g}, b={self.b}) - A nice RGB thing."if format_spec == "vv":return (f"Color(r={self.r}, g={self.g}, b={self.b}) "f"- A more verbose nice RGB thing.")if format_spec == "vvv":return (f"Color(r={self.r}, g={self.g}, b={self.b}) "f"- A SUPER verbose nice RGB thing.")raise ValueError(f"Unknown format code '{format_spec}' " "for object of type 'Color'")'Color(r=123, g=32, b=255) - A nice RGB thing.''Color(r=123, g=32, b=255) - A more verbose nice RGB thing.''Color(r=123, g=32, b=255) - A SUPER verbose nice RGB thing.''A RGB color''A RGB color''Color(r=123, g=32, b=255)'---------------------------------------------------------------------------ValueError Traceback (most recent call last)<ipython-input-201c0ee8dd74be> in <module>----> 1 f'{c:j}'<ipython-input-15985c4992e957> in __format__(self, format_spec)29 f"- A SUPER verbose nice RGB thing."30 )---> 31 raise ValueError(32 f"Unknown format code '{format_spec}' " "for object of type 'Color'"33 )ValueError: Unknown format code 'j' for object of type 'Color'
最后,还有个用来转义ASCII字符的a操作符。更多信息可参考:
docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#as..
"'\\xc1ei\\xf6u'"
8、如何用f-string设定浮点数精度
F-string可以像str.format那样格式化浮点数。想要实现这一点,你需要加一个 :(冒号)再加一个 .(英文句号)然后跟着小数点位数最后以f结尾。
举例来说,你可以通过如下代码打印一个浮点数精确到百分位的近似值。
'num rounded to 2 decimal palces = 4.12’
不加任何选项的话,则会打印浮点数本身的精确值。
>>> print(f'{num}')4.123956
9、如何将一个数字格式化为百分数
Python f-string方法有个非常便捷的实现格式化百分数的操作方法。方法与浮点数格式化类似,但是要用%代替结尾的f。它会将原始数值乘以100并显示成有百分符号的固定格式。精度一样也是可以设定的。
0.39080459770114945'Percentage of true positive: 39.080460%''Percentage of true positive: 39.08%'
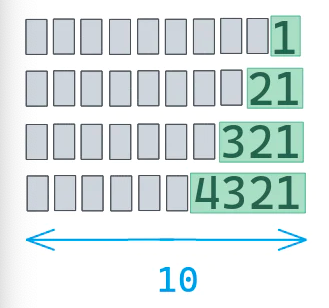
10、如何调整或者增加 f-string 的填充
你可以便捷的通过 < 或者 > 符号来调整字符串填充。

'She says hello'# Pad 10 char to the right' hello''hello '# You can omit the < for left padding'hello '
1213214321
11、如何转义符号
如果你想想打印由大括号括起来的变量名称,而不是该变量的值,那你需要双层大括号 {{}}。
'{hello} = world'
而如果你想转义双引号,就需要在引号前用反斜线 \ 做标记。
'world = "hello"'
12、如何使字符串居中

想要实现字符串居中,可以通过 var:^N 的方式。其中var是你想要打印的变量,N是字符串长度。如果N小于var的长度,会打印全部字符串。
' world ''***world***'# Extra padding is added to the right'**world***'# N shorter than len(hello)'world'
13、如何格式化千分位

F-string也允许我们自定义数字显示的格式。有个非常普遍的需求就是把数字以每3位为一个间隔使用下划线进行分隔。
'1_234_567_890'
13.1 如何使用逗号千分位分隔符数字
实际上,你可以随便用任何符号做千分位分隔符。所以用逗号做分隔符也完全没问题。
'1,234,567,890'
甚至可以一次性同时搞定既有千分位分隔符又有精度设定的浮点数。
‘2,343,552.652'
13.2 如何用空格做千分位分隔符
用空格也可以吗?
好吧,这个问题是挺棘手,不过也能实现。你可以用逗号做分隔符之后再用空格替换逗号。
'1 234 567 890'
还有个方法是设定你的本地语言环境,换成一个用空格作千位分隔符的环境比如pl_PL(波兰语环境)。更多信息可参考这个Stack Overflow链接:
https://stackoverflow.com/a/17484665
14、如何用科学计数法(指数计数法)显示一个数字
可以用 e 或者 E 字符来格式化。
'2.343553e+06''2.343553E+06''2.34e+06''2.3436E+06'
15、在 f-string 中使用 if-else
F-string也能计算稍微复杂的运算式,比如if/else
>>> b = "this is b">>> f"{a if 10 > 5 else b}"'this is a'>>> f"{a if 10 < 5 else b}"'this is b'
16、如何在 f-string 中使用字典
你可以在f-string中使用字典。唯一的要求是引起整个字符串的引号要跟内部的引号不一样。
'123'‘’123'此处有误啊应该是‘123’吧>>> f"RGB = ({color['R']},{color['G']}, {color['B']})"'RGB = (123, 145, 255)’
17、如何用 f-string 拼接字符串
合并f-string与普通字符串拼接一样,可以隐式的直接拼接,或者显式地用加号 +,或者使用 str.join 方法。
# 隐式字符串拼接'123 = 100 + 20 + 3'# 使用加号 + 的显式字符串拼接>>> f"{12}" + " != "+ f"{13}"'12 != 13'# 使用str.join的字符串拼接>>> "".join((f"{13}", f"{45}"))'13 45'>>>"#".join((f"{13}", f"{45}"))'13#45'
18、如何格式化 datetime 对象
F-string也支持datetime对象的格式化。其过程与str.format格式化日期的方法很近似。请查阅官方文档中的表格获取更多所支持格式的相关信息。

'2020-10-13 20:24:17''2020-10-23 20:24:17'
19、如何修复f-string的非法格式错误
如果用的不对,f-string会报格式错误。最常见的错误就是双引号里面套双引号。单引号也会引发相同错误。
>>>color = {"R": 123, "G": 145, "B": 255}>>> f"{color["R"]}"File"", line 1f"{color["R"]}"^SyntaxError: f-string: unmatched '['>>> f'{color['R']}'File"", line 1f'{color['R']}'^SyntaxError: f-string: unmatched '['
还有个常见错误是在旧版本python中用f-string。python3.6才引入了f-string。如果你在之前版本中使用这个方法,解释器会报格式错误 SyntaxError: invalid syntax。
File"", line 1f"this is an old version"SyntaxError: invalid syntax
看到这个错误的话,先确定当前使用的python版本。我检查的方法是在python2.7下通过调用sys.version来获取版本号。
>>> import sys;print(sys.version)2.7.18 (default, Apr 202020, 19:27:10)[GCC 8.3.0]
20、如何在字符串前补零
可以用{expr:0len} 这个方法来进行字符串补零。len是最终返回字符串的长度。还可以增加一个正负号标记。在这种情况下,用+则无论数值为正负数都将显示相应正负号。用-则只有当数值为负数时才显示负号,默认设定也是如此。更多信息可参考该链接
https://docs.python.org/3/library/string.html#format-specification-mini-language
'00042''+000000042''0000000042''0000000042''-000000042''-000000042''-000000042'
21、如何处理多行f-string(换行符的处理)
你可以用换行符\n来打印多行文本。
...: ]}\n')'R: 123\nG: 145\nB: 255\n'R: 123G: 145B: 255
还可以用三引号实现多行字符串。这样不单能增加换行符,还能有Tab。
>>> other = f"""R:{color["R"]}...: G:{color["G"]}...: B:{color["B"]}...:"""R: 123G: 145B: 255
用 Tab 的代码样例
...:this is an example...:...:^Iof color {color["R"]}...:...: ''''\nthis is an example\n\n\tof color 123\n \n'this is an exampleof color123
22、结论
本文就这些!希望大家学到了一些新奇而实用的知识。知道了如何充分利用 f-string 绝对可以让生活变得更美好。