继承的作用是减少代码冗余,通过协调来减少接口和界面。
1.派生类的定义
<1>吸收基类成员
<2>改造基类成员
一是依靠派生类的继承方式来控制基类成员的访问、二是对基类成员或成员函数的覆盖。
<3>添加新的成员
2.类的继承方式
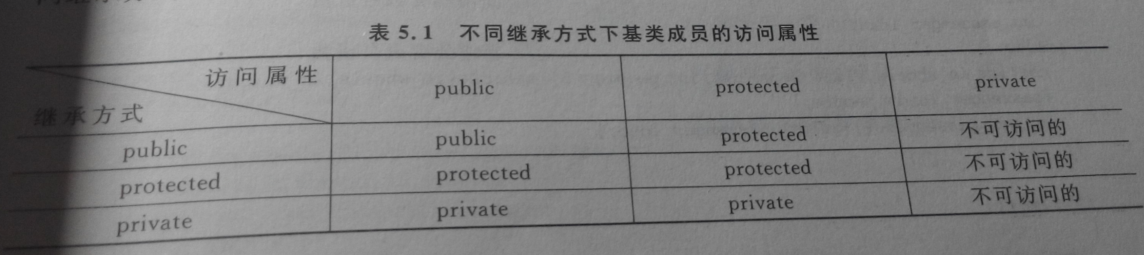
<1>.公有继承
#include <iostream> using namespace std; class vehicle { private: float weight; int wheels; public: vehicle(int in_wheels,float in_weight) { wheels=in_wheels; weight=in_weight; } int get_wheels() { return wheels; } float get_weight() { return weight; } }; class car:public vehicle { private: int passenger_load; public: car(int in_wheels,float in_weight,int people=5):vehicle(in_wheels,in_weight) { passenger_load=people; } int get_passenger() { return passenger_load; } }; int main() { car bm(4,100); cout<<bm.get_wheels()<<endl; cout<<bm.get_weight()<<endl; cout<<bm.get_passenger()<<endl; return 0; }
结果:
4
100
5
<2>.私有继承
#include <iostream> using namespace std; class vehicle { private: float weight; int wheels; public: vehicle(int in_wheels,float in_weight) { wheels=in_wheels; weight=in_weight; } int get_wheels() { return wheels; } float get_weight() { return weight; } }; class car:private vehicle { private: int passenger_load; public: car(int in_wheels,float in_weight,int people=5):vehicle(in_wheels,in_weight) { passenger_load=people; } int get_passenger() { return passenger_load; } int get_wheels() { return vehicle::get_wheels(); } int get_weight() { return vehicle::get_weight(); } }; int main() { car bm(4,100); cout<<bm.get_wheels()<<endl; cout<<bm.get_weight()<<endl; cout<<bm.get_passenger()<<endl; return 0; }
结果:
4
100
5
<3>.保护继承
#include <iostream> using namespace std; class vehicle { private: int wheels; protected: float weight; public: vehicle(int in_wheels,float in_weight) { wheels=in_wheels; weight=in_weight; } int get_wheels() { return wheels; } float get_weight() { return weight; } }; class car:protected vehicle { private: int passenger_load; public: car(int in_wheels,float in_weight,int people=5):vehicle(in_wheels,in_weight) { passenger_load=people; } int get_passenger() { return passenger_load; } int get_wheels() { return vehicle::get_wheels(); } int get_weight() { return weight; } }; int main() { car bm(4,100); cout<<bm.get_wheels()<<endl; cout<<bm.get_weight()<<endl; cout<<bm.get_passenger()<<endl; return 0; }
结果:
4
100
5
3.派生类的构造函数和析构函数


4.派生类对基类成员的继承
通过访问声明调整访问域
<1>访问声明仅仅调整名字的访问,不可为它说明任何类型;成员函数在访问声明时,也不准说明任何参数
<2>对重载函数的访问声明将调整基类中具有该名得所有函数的访问域
<3>若派生类中具有与基类同名的函数,则基类中的此函数不能在派生类中进行访问声明
5.多重继承
<1>二义性和支配原则
作用域规则、支配规则
一个派生类中的名字将优先于它的基类中相同的名字
<2>赋值兼容原则
6.虚基类



例子:
#include <iostream> using namespace std; class Furniture{ public: Furniture(){ cout<<"2333"<<endl; } void SetWeight(int i){ weight=i; } int GetWeight(){ return weight; } protected: int weight; }; class Bed:virtual public Furniture{ public: Bed(){ cout<<"2444"<<endl; } void Sleep(){ cout<<"Sleeping... "; } }; class Sofa:virtual public Furniture{ public: Sofa(){ cout<<"2555"<<endl; } void WatchTV(){ cout<<"Watch TV "; } }; class SleeerpSofa:public Bed,public Sofa{ public: SleeerpSofa():Sofa(),Bed(){ } void FoldOut(){ cout<<"Fold out the sofa. "; } }; int main(){ SleeerpSofa ss; ss.SetWeight(20); cout<<ss.GetWeight()<<endl; return 0; }
结果:
233
2444
2555
20
7.类模板
理解类模板与模板类的关系:类模板+特定的数据类型=模板类
例题:
#include <iostream> using namespace std; template<class T> class tem{ T *data; int size; public: tem(int); ~tem(){ delete []data; } T& operator[](int i){ return data[i]; } }; template<class T> tem<T>::tem(int n){ data=new T[n]; size=n; } int main(){ tem<int> x(5); int i; for(i=0;i<5;i++) x[i]=i; for(i=0;i<5;i++) cout<<x[i]<<' '; cout<<endl; return 0; }
结果:
0 1 2 3 4