设计模式对于每个人都非常有用
本片博文转载自 https://developer.ibm.com/zh/technologies/software-development/articles/os-php-designptrns
观察者模式
观察者模式为您提供了避免组件之间紧密耦合的另一种方法。该模式非常简单:一个对象通过添加一个方法(该方法允许另一个对象,即 观察者 注册自己)使本身变得可观察。当可观察的对象更改时,它会将消息发送到已注册的观察者。这些观察者使用该信息执行的操作与可观察的对象无关。结果是对象可以相互对话,而不必了解原因。
一个简单示例是系统中的用户列表。清单 4 中的代码显示一个用户列表,添加用户时,它将发送出一条消息。添加用户时,通过发送消息的日志观察者可以观察此列表。
清单 4. Observer.php
<?php
interface IObserver
{
function onChanged( $sender, $args );
}
interface IObservable
{
function addObserver( $observer );
}
class UserList implements IObservable
{
private $_observers = array();
public function addCustomer( $name )
{
foreach( $this->_observers as $obs )
$obs->onChanged( $this, $name );
}
public function addObserver( $observer )
{
$this->_observers []= $observer;
}
}
class UserListLogger implements IObserver
{
public function onChanged( $sender, $args )
{
echo( "'$args' added to user list
" );
}
}
$ul = new UserList();
$ul->addObserver( new UserListLogger() );
$ul->addCustomer( "Jack" );
?>
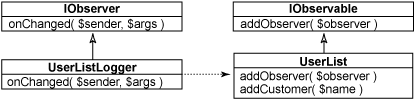
此代码定义四个元素:两个接口和两个类。 IObservable 接口定义可以被观察的对象, UserList 实现该接口,以便将本身注册为可观察。 IObserver 列表定义要通过怎样的方法才能成为观察者, UserListLogger 实现 IObserver 接口。图 4 的 UML 中展示了这些元素。
图 4. 可观察的用户列表和用户列表事件日志程序
如果在命令行中运行它,您将看到以下输出:
% php observer.php
'Jack' added to user list
%
测试代码创建 UserList ,并将 UserListLogger 观察者添加到其中。然后添加一个消费者,并将这一更改通知 UserListLogger 。
认识到 UserList 不知道日志程序将执行什么操作很关键。可能存在一个或多个执行其他操作的侦听程序。例如,您可能有一个向新用户发送消息的观察者,欢迎新用户使用该系统。这种方法的价值在于 UserList 忽略所有依赖它的对象,它主要关注在列表更改时维护用户列表并发送消息这一工作。
此模式不限于内存中的对象。它是在较大的应用程序中使用的数据库驱动的消息查询系统的基础。
命令链模式
命令链 模式以松散耦合主题为基础,发送消息、命令和请求,或通过一组处理程序发送任意内容。每个处理程序都会自行判断自己能否处理请求。如果可以,该请求被处理,进程停止。您可以为系统添加或移除处理程序,而不影响其他处理程序。清单 5 显示了此模式的一个示例。
清单 5. Chain.php
<?php
interface ICommand
{
function onCommand( $name, $args );
}
class CommandChain
{
private $_commands = array();
public function addCommand( $cmd )
{
$this->_commands []= $cmd;
}
public function runCommand( $name, $args )
{
foreach( $this->_commands as $cmd )
{
if ( $cmd->onCommand( $name, $args ) )
return;
}
}
}
class UserCommand implements ICommand
{
public function onCommand( $name, $args )
{
if ( $name != 'addUser' ) return false;
echo( "UserCommand handling 'addUser'
" );
return true;
}
}
class MailCommand implements ICommand
{
public function onCommand( $name, $args )
{
if ( $name != 'mail' ) return false;
echo( "MailCommand handling 'mail'
" );
return true;
}
}
$cc = new CommandChain();
$cc->addCommand( new UserCommand() );
$cc->addCommand( new MailCommand() );
$cc->runCommand( 'addUser', null );
$cc->runCommand( 'mail', null );
?>
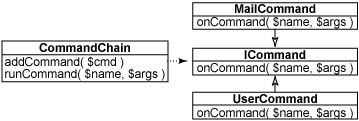
此代码定义维护 ICommand 对象列表的 CommandChain 类。两个类都可以实现 ICommand 接口 —— 一个对邮件的请求作出响应,另一个对添加用户作出响应。 图 5 给出了 UML。
图 5. 命令链及其相关命令
如果您运行包含某些测试代码的脚本,则会得到以下输出:
% php chain.php
UserCommand handling 'addUser'
MailCommand handling 'mail'
%
代码首先创建 CommandChain 对象,并为它添加两个命令对象的实例。然后运行两个命令以查看谁对这些命令作出了响应。如果命令的名称匹配 UserCommand 或 MailCommand ,则代码失败,不发生任何操作。
为处理请求而创建可扩展的架构时,命令链模式很有价值,使用它可以解决许多问题。
策略模式
我们讲述的最后一个设计模式是 策略 模式。在此模式中,算法是从复杂类提取的,因而可以方便地替换。例如,如果要更改搜索引擎中排列页的方法,则策略模式是一个不错的选择。思考一下搜索引擎的几个部分 —— 一部分遍历页面,一部分对每页排列,另一部分基于排列的结果排序。在复杂的示例中,这些部分都在同一个类中。通过使用策略模式,您可将排列部分放入另一个类中,以便更改页排列的方式,而不影响搜索引擎的其余代码。
作为一个较简单的示例,清单 6 显示了一个用户列表类,它提供了一个根据一组即插即用的策略查找一组用户的方法。
清单 6. Strategy.php
<?php
interface IStrategy
{
function filter( $record );
}
class FindAfterStrategy implements IStrategy
{
private $_name;
public function __construct( $name )
{
$this->_name = $name;
}
public function filter( $record )
{
return strcmp( $this->_name, $record ) <= 0;
}
}
class RandomStrategy implements IStrategy
{
public function filter( $record )
{
return rand( 0, 1 ) >= 0.5;
}
}
class UserList
{
private $_list = array();
public function __construct( $names )
{
if ( $names != null )
{
foreach( $names as $name )
{
$this->_list []= $name;
}
}
}
public function add( $name )
{
$this->_list []= $name;
}
public function find( $filter )
{
$recs = array();
foreach( $this->_list as $user )
{
if ( $filter->filter( $user ) )
$recs []= $user;
}
return $recs;
}
}
$ul = new UserList( array( "Andy", "Jack", "Lori", "Megan" ) );
$f1 = $ul->find( new FindAfterStrategy( "J" ) );
print_r( $f1 );
$f2 = $ul->find( new RandomStrategy() );
print_r( $f2 );
?>
此代码的 UML 如图 6 所示。
图 6. 用户列表和用于选择用户的策略
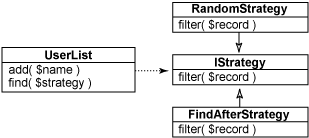
UserList 类是打包名称数组的一个包装器。它实现 find 方法,该方法利用几个策略之一来选择这些名称的子集。这些策略由 IStrategy 接口定义,该接口有两个实现:一个随机选择用户,另一个根据指定名称选择其后的所有名称。运行测试代码时,将得到以下输出:
% php strategy.php
Array
(
[0] => Jack
[1] => Lori
[2] => Megan
)
Array
(
[0] => Andy
[1] => Megan
)
%
测试代码为两个策略运行同一用户列表,并显示结果。在第一种情况中,策略查找排列在 J 后的任何名称,所以您将得到 Jack、Lori 和 Megan。第二个策略随机选取名称,每次会产生不同的结果。在这种情况下,结果为 Andy 和 Megan。
策略模式非常适合复杂数据管理系统或数据处理系统,二者在数据筛选、搜索或处理的方式方面需要较高的灵活性。
结束语