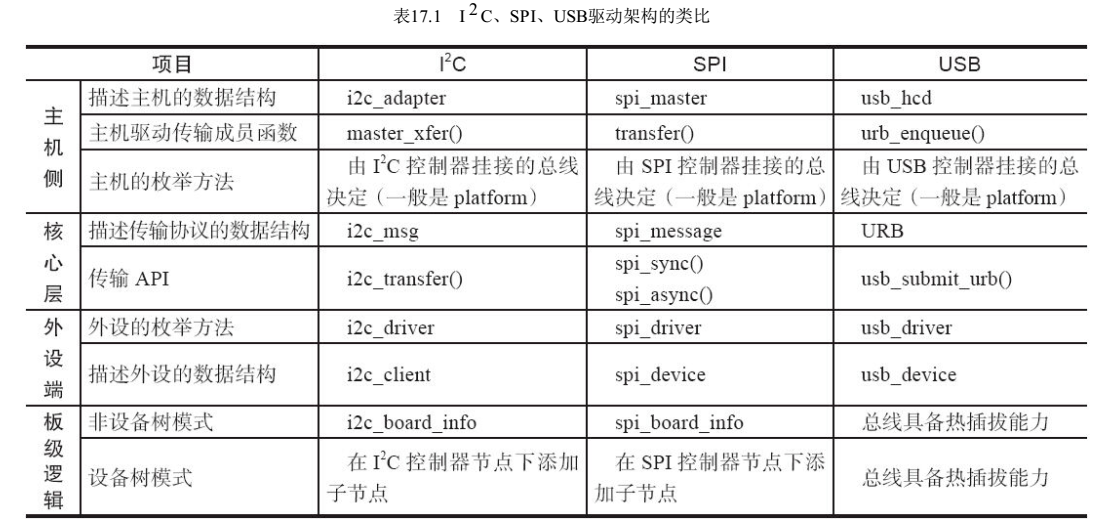
结合实际代码和书中描述,可能跟书上有一定出入。本文后续芯片相关代码参考ZYNQ。
15.1 总体结构
如下图,i2c驱动分为如下几个重要模块
- 核心层core,完成i2c总线、设备、驱动模型,对用户提供sys文件系统访问支持;为i2c内部adpter等提供注册接口。
- adpter,适配器,实际就是CPU集成的IIC控制器,有cpu控制,完成i2c物理总线操作,busses文件夹里,有各个cpu adapter的具体实现;algorithm集成到这个模块里,而且是adapter的一部分,主要实现总 线传输的标准化。
- i2c-dev,把adapter设备化,采用标准的file_operations字符设备的形式,便于用户层直接读写adapter设备文件,不是主流,一般也就是调试时用用。
- muxes,i2c切换芯片,不重点讨论。
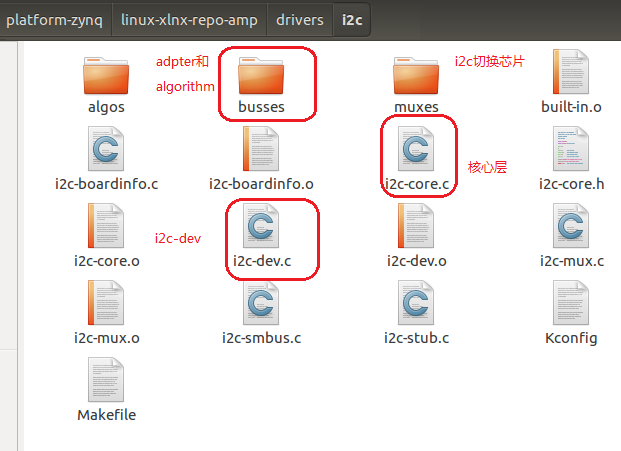
自己理解的结构图,与书中有出入,简化了。

i2c总线设备驱动模型,与platform类似,软件架构都一样。通过这种模型,最终在sysfs中创建文件,且创建文件时要填充类似file_operations类似的结构体中的读写函数,从而完成用户层到底层驱动的传递。
15.2 adapter和algorithm——最终对外提供硬件无关接口
busses/i2c-cadence.c文件是ZYNQ i2c控制器的驱动,实现i2c的adapter和algorithm。adapter采用platform机制。
先看看关键数据结构:
15.2.1 关键数据接结构
/** * struct cdns_i2c - I2C device private data structure * @membase: Base address of the I2C device * @adap: I2C adapter instance * @p_msg: Message pointer * @err_status: Error status in Interrupt Status Register * @xfer_done: Transfer complete status * @p_send_buf: Pointer to transmit buffer * @p_recv_buf: Pointer to receive buffer * @suspended: Flag holding the device's PM status * @send_count: Number of bytes still expected to send * @recv_count: Number of bytes still expected to receive * @curr_recv_count: Number of bytes to be received in current transfer * @irq: IRQ number * @input_clk: Input clock to I2C controller * @i2c_clk: Maximum I2C clock speed * @bus_hold_flag: Flag used in repeated start for clearing HOLD bit * @clk: Pointer to struct clk * @clk_rate_change_nb: Notifier block for clock rate changes */ struct cdns_i2c { void __iomem *membase; struct i2c_adapter adap; struct i2c_msg *p_msg; int err_status; struct completion xfer_done; unsigned char *p_send_buf; unsigned char *p_recv_buf; u8 suspended; unsigned int send_count; unsigned int recv_count; unsigned int curr_recv_count; int irq; unsigned long input_clk; unsigned int i2c_clk; unsigned int bus_hold_flag; struct clk *clk; struct notifier_block clk_rate_change_nb; }; /* * i2c_adapter is the structure used to identify a physical i2c bus along * with the access algorithms necessary to access it. */ struct i2c_adapter { struct module *owner; unsigned int class; /* classes to allow probing for */ const struct i2c_algorithm *algo; /* the algorithm to access the bus,实体也在此文件中定义,并在probe函数里指向此实体 */ void *algo_data; /* data fields that are valid for all devices */ struct rt_mutex bus_lock; int timeout; /* in jiffies */ int retries; struct device dev; /* the adapter device */ int nr; char name[48]; struct completion dev_released; struct mutex userspace_clients_lock; struct list_head userspace_clients; struct i2c_bus_recovery_info *bus_recovery_info; }; /** * struct i2c_algorithm - represent I2C transfer method * @master_xfer: Issue a set of i2c transactions to the given I2C adapter * defined by the msgs array, with num messages available to transfer via * the adapter specified by adap. * @smbus_xfer: Issue smbus transactions to the given I2C adapter. If this * is not present, then the bus layer will try and convert the SMBus calls * into I2C transfers instead. * @functionality: Return the flags that this algorithm/adapter pair supports * from the I2C_FUNC_* flags. * * The following structs are for those who like to implement new bus drivers: * i2c_algorithm is the interface to a class of hardware solutions which can * be addressed using the same bus algorithms - i.e. bit-banging or the PCF8584 * to name two of the most common. * * The return codes from the @master_xfer field should indicate the type of * error code that occured during the transfer, as documented in the kernel * Documentation file Documentation/i2c/fault-codes. */ struct i2c_algorithm { /* If an adapter algorithm can't do I2C-level access, set master_xfer to NULL. If an adapter algorithm can do SMBus access, set smbus_xfer. If set to NULL, the SMBus protocol is simulated using common I2C messages */ /* master_xfer should return the number of messages successfully processed, or a negative value on error */ int (*master_xfer)(struct i2c_adapter *adap, struct i2c_msg *msgs, int num); int (*smbus_xfer) (struct i2c_adapter *adap, u16 addr, unsigned short flags, char read_write, u8 command, int size, union i2c_smbus_data *data); /* To determine what the adapter supports */ u32 (*functionality) (struct i2c_adapter *); };
15.2.2 adapter的注册与注销
- adapter被组织成platform驱动形式
- 顺便理解platform的匹配机制:
- dts里有若干device的描述,linux在初始化时会把这些设备展开,形成设备列表。
- platform driver中有匹配字段of_match_table,估计注册platform驱动时(module_platform_driver),platform bus负责匹配此字段和已有的dts设备列表。
- platform driver和dev列表匹配上以后,driver中的probe就会执行,同时dev列表中的信息以probe形参struct platform_device *pdev的形式传递给probe()函数。

一般linux的iic、spi、usb等外设都是这个思路,适配器为别人提供总线,但是其本身是挂到platform总线上的。
3. adapter通过iic-core.c核心层提供的接口,注册或注销到iic总线上
- i2c_add_adapter():添加adapter数据结构,核心层里详述
- i2c_del_adapter():删除adapter设数据结构
static int cdns_i2c_probe(struct platform_device *pdev) // dts里的设备信息传递进来了 { struct resource *r_mem; struct cdns_i2c *id; int ret; id = devm_kzalloc(&pdev->dev, sizeof(*id), GFP_KERNEL); if (!id) return -ENOMEM; platform_set_drvdata(pdev, id);
xxx_adapter_hw_init(); //通常初始化iic适配器使用的硬件资源,如申请IO地址、中断号、时钟等 id->adap.dev.of_node = pdev->dev.of_node; id->adap.algo = &cdns_i2c_algo; // 把altorithm连进来 id->adap.timeout = CDNS_I2C_TIMEOUT; id->adap.retries = 3; /* Default retry value. */ id->adap.algo_data = id; id->adap.dev.parent = &pdev->dev; ret = i2c_add_adapter(&id->adap); ... } static int cdns_i2c_remove(struct platform_device *pdev) { struct cdns_i2c *id = platform_get_drvdata(pdev); i2c_del_adapter(&id->adap); xxx_adapter_hw_free(); // 硬件相关资源的free return 0; } static const struct of_device_id cdns_i2c_of_match[] = { { .compatible = "cdns,i2c-r1p10", }, { /* end of table */ } }; MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(of, cdns_i2c_of_match); static struct platform_driver cdns_i2c_drv = { .driver = { .name = DRIVER_NAME, .owner = THIS_MODULE, .of_match_table = cdns_i2c_of_match, // dts匹配的依据 .pm = &cdns_i2c_dev_pm_ops, }, .probe = cdns_i2c_probe, .remove = cdns_i2c_remove, }; module_platform_driver(cdns_i2c_drv);
iic相关的dts信息如下
iic相关dts ps7_i2c_1: ps7-i2c@e0005000 { clock-frequency = <400000>; clocks = <&clkc 39>; compatible = "cdns,i2c-r1p10"; interrupt-parent = <&ps7_scugic_0>; interrupts = <0 48 4>; reg = <0xe0005000 0x1000>; xlnx,has-interrupt = <0x0>; #address-cells = <1>; #size-cells = <0>; eeprom@52 { compatible = "at,24c512"; reg = <0x52>; }; } ;
15.2.3 i2c总线的通信方法 —— algorithm
主要需要实现i2c_algorithm结构体中的master_xfer()和functionality()函数,i2c_algorithm的作用是高度总结iic总线通信机制,把具体的适配器(不同型号)与其他通用驱动隔离开。
functionality()函数比较简单,返回支持的通信协议。
master_xfer()函数在适配器上完成i2c_msg的数据传输。
static const struct i2c_algorithm cdns_i2c_algo = { .master_xfer = cdns_i2c_master_xfer, .functionality = cdns_i2c_func, }; /** * cdns_i2c_func - Returns the supported features of the I2C driver * @adap: pointer to the i2c adapter structure * * Return: 32 bit value, each bit corresponding to a feature */ static u32 cdns_i2c_func(struct i2c_adapter *adap) { return I2C_FUNC_I2C | I2C_FUNC_10BIT_ADDR | (I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_EMUL & ~I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_QUICK) | I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_BLOCK_DATA; } /** * cdns_i2c_master_xfer - The main i2c transfer function * @adap: pointer to the i2c adapter driver instance * @msgs: pointer to the i2c message structure * @num: the number of messages to transfer * * Initiates the send/recv activity based on the transfer message received. * * Return: number of msgs processed on success, negative error otherwise */ static int cdns_i2c_master_xfer(struct i2c_adapter *adap, struct i2c_msg *msgs, int num) { int ret, count; u32 reg; struct cdns_i2c *id = adap->algo_data; /* Check if the bus is free */ if (cdns_i2c_readreg(CDNS_I2C_SR_OFFSET) & CDNS_I2C_SR_BA) return -EAGAIN; /* * Set the flag to one when multiple messages are to be * processed with a repeated start. */ if (num > 1) { id->bus_hold_flag = 1; reg = cdns_i2c_readreg(CDNS_I2C_CR_OFFSET); reg |= CDNS_I2C_CR_HOLD; cdns_i2c_writereg(reg, CDNS_I2C_CR_OFFSET); } else { id->bus_hold_flag = 0; } /* Process the msg one by one */ for (count = 0; count < num; count++, msgs++) { if (count == (num - 1)) id->bus_hold_flag = 0; ret = cdns_i2c_process_msg(id, msgs, adap); if (ret) return ret; /* Report the other error interrupts to application */ if (id->err_status) { cdns_i2c_master_reset(adap); if (id->err_status & CDNS_I2C_IXR_NACK) return -ENXIO; return -EIO; } } return num; }
15.3 core
15.3.1 i2c总线、设备、驱动模型建立和维护
创建i2c总线、设备、驱动大框架。
static int __init i2c_init(void) // linux初始化时执行
{ int retval; retval = bus_register(&i2c_bus_type); // 在sys文件夹中创建i2c总线,完成将i2c总线注册到系统,与platform总线平级,创建 /sys/i2c目录 if (retval) return retval; #ifdef CONFIG_I2C_COMPAT i2c_adapter_compat_class = class_compat_register("i2c-adapter"); // 创建类,/sys/class/i2c-adapter if (!i2c_adapter_compat_class) { retval = -ENOMEM; goto bus_err; } #endif retval = i2c_add_driver(&dummy_driver); // 注册一个dummy驱动,不知道为了啥? 在 /sys/bus/i2c/drivers目录下创建了dummy驱动 if (retval) goto class_err; return 0; class_err: #ifdef CONFIG_I2C_COMPAT class_compat_unregister(i2c_adapter_compat_class); bus_err: #endif bus_unregister(&i2c_bus_type); return retval; } static void __exit i2c_exit(void) { i2c_del_driver(&dummy_driver); #ifdef CONFIG_I2C_COMPAT class_compat_unregister(i2c_adapter_compat_class); #endif bus_unregister(&i2c_bus_type); } /* We must initialize early, because some subsystems register i2c drivers * in subsys_initcall() code, but are linked (and initialized) before i2c. */ postcore_initcall(i2c_init); // linux初始化时调用 module_exit(i2c_exit);
引出知识:driver中的probe是如何执行的?!总线match以后,总线结构体中的probe会被执行(内核代码实现的),总线probe函数会调用driver中的probe。所有总线、驱动、模型,包括platform都是这种机制。
struct bus_type i2c_bus_type = { .name = "i2c", .match = i2c_device_match, .probe = i2c_device_probe, .remove = i2c_device_remove, .shutdown = i2c_device_shutdown, .pm = &i2c_device_pm_ops, }; static int i2c_device_probe(struct device *dev) { struct i2c_client *client = i2c_verify_client(dev); struct i2c_driver *driver; int status; if (!client) return 0; driver = to_i2c_driver(dev->driver); if (!driver->probe || !driver->id_table) return -ENODEV; if (!device_can_wakeup(&client->dev)) device_init_wakeup(&client->dev, client->flags & I2C_CLIENT_WAKE); dev_dbg(dev, "probe "); acpi_dev_pm_attach(&client->dev, true); status = driver->probe(client, i2c_match_id(driver->id_table, client)); if (status) acpi_dev_pm_detach(&client->dev, true); return status; }
15.3.2 添加/删除adapter接口
// i2c/buses/i2c_cadence.c static int cdns_i2c_probe(struct platform_device *pdev) { ... ret = i2c_add_adapter(&id->adap); // 添加adapter ... } /** * i2c_add_adapter - declare i2c adapter, use dynamic bus number * @adapter: the adapter to add * Context: can sleep * * This routine is used to declare an I2C adapter when its bus number * doesn't matter or when its bus number is specified by an dt alias. * Examples of bases when the bus number doesn't matter: I2C adapters * dynamically added by USB links or PCI plugin cards. * * When this returns zero, a new bus number was allocated and stored * in adap->nr, and the specified adapter became available for clients. * Otherwise, a negative errno value is returned. */ int i2c_add_adapter(struct i2c_adapter *adapter) { struct device *dev = &adapter->dev; int id; if (dev->of_node) { id = of_alias_get_id(dev->of_node, "i2c"); if (id >= 0) { adapter->nr = id; // 从dts中自动获取i2c的adapter的个数 return __i2c_add_numbered_adapter(adapter); // 注册各adapter } } mutex_lock(&core_lock); id = idr_alloc(&i2c_adapter_idr, adapter, __i2c_first_dynamic_bus_num, 0, GFP_KERNEL); mutex_unlock(&core_lock); if (id < 0) return id; adapter->nr = id; return i2c_register_adapter(adapter); } /** * __i2c_add_numbered_adapter - i2c_add_numbered_adapter where nr is never -1 * @adap: the adapter to register (with adap->nr initialized) * Context: can sleep * * See i2c_add_numbered_adapter() for details. */ static int __i2c_add_numbered_adapter(struct i2c_adapter *adap) { int id; mutex_lock(&core_lock); id = idr_alloc(&i2c_adapter_idr, adap, adap->nr, adap->nr + 1, GFP_KERNEL); mutex_unlock(&core_lock); if (id < 0) return id == -ENOSPC ? -EBUSY : id; return i2c_register_adapter(adap); } static int i2c_register_adapter(struct i2c_adapter *adap) { int res = 0; /* Can't register until after driver model init */ if (unlikely(WARN_ON(!i2c_bus_type.p))) { res = -EAGAIN; goto out_list; } /* Sanity checks */ if (unlikely(adap->name[0] == '�')) { pr_err("i2c-core: Attempt to register an adapter with " "no name! "); return -EINVAL; } if (unlikely(!adap->algo)) { pr_err("i2c-core: Attempt to register adapter '%s' with " "no algo! ", adap->name); return -EINVAL; } rt_mutex_init(&adap->bus_lock); mutex_init(&adap->userspace_clients_lock); INIT_LIST_HEAD(&adap->userspace_clients); /* Set default timeout to 1 second if not already set */ if (adap->timeout == 0) adap->timeout = HZ; dev_set_name(&adap->dev, "i2c-%d", adap->nr); adap->dev.bus = &i2c_bus_type; adap->dev.type = &i2c_adapter_type; res = device_register(&adap->dev); if (res) goto out_list; dev_dbg(&adap->dev, "adapter [%s] registered ", adap->name); #ifdef CONFIG_I2C_COMPAT res = class_compat_create_link(i2c_adapter_compat_class, &adap->dev, adap->dev.parent); if (res) dev_warn(&adap->dev, "Failed to create compatibility class link "); #endif /* bus recovery specific initialization */ if (adap->bus_recovery_info) { struct i2c_bus_recovery_info *bri = adap->bus_recovery_info; if (!bri->recover_bus) { dev_err(&adap->dev, "No recover_bus() found, not using recovery "); adap->bus_recovery_info = NULL; goto exit_recovery; } /* Generic GPIO recovery */ if (bri->recover_bus == i2c_generic_gpio_recovery) { if (!gpio_is_valid(bri->scl_gpio)) { dev_err(&adap->dev, "Invalid SCL gpio, not using recovery "); adap->bus_recovery_info = NULL; goto exit_recovery; } if (gpio_is_valid(bri->sda_gpio)) bri->get_sda = get_sda_gpio_value; else bri->get_sda = NULL; bri->get_scl = get_scl_gpio_value; bri->set_scl = set_scl_gpio_value; } else if (!bri->set_scl || !bri->get_scl) { /* Generic SCL recovery */ dev_err(&adap->dev, "No {get|set}_gpio() found, not using recovery "); adap->bus_recovery_info = NULL; } } exit_recovery: /* create pre-declared device nodes */ of_i2c_register_devices(adap); acpi_i2c_register_devices(adap); if (adap->nr < __i2c_first_dynamic_bus_num) i2c_scan_static_board_info(adap); /* Notify drivers */ mutex_lock(&core_lock); bus_for_each_drv(&i2c_bus_type, NULL, adap, __process_new_adapter); mutex_unlock(&core_lock); return 0; out_list: mutex_lock(&core_lock); idr_remove(&i2c_adapter_idr, adap->nr); mutex_unlock(&core_lock); return res; }
15.3.3 添加/删除i2c_driver接口
向i2c_bus注册驱动,可用于匹配i2c总线上的设备,即i2c_client,例如EEPROM等
/* use a define to avoid include chaining to get THIS_MODULE */ #define i2c_add_driver(driver) i2c_register_driver(THIS_MODULE, driver) /* * An i2c_driver is used with one or more i2c_client (device) nodes to access * i2c slave chips, on a bus instance associated with some i2c_adapter. */ int i2c_register_driver(struct module *owner, struct i2c_driver *driver) { int res; /* Can't register until after driver model init */ if (unlikely(WARN_ON(!i2c_bus_type.p))) return -EAGAIN; /* add the driver to the list of i2c drivers in the driver core */ driver->driver.owner = owner; driver->driver.bus = &i2c_bus_type; /* When registration returns, the driver core * will have called probe() for all matching-but-unbound devices. */ res = driver_register(&driver->driver); if (res) return res; /* Drivers should switch to dev_pm_ops instead. */ if (driver->suspend) pr_warn("i2c-core: driver [%s] using legacy suspend method ", driver->driver.name); if (driver->resume) pr_warn("i2c-core: driver [%s] using legacy resume method ", driver->driver.name); pr_debug("i2c-core: driver [%s] registered ", driver->driver.name); INIT_LIST_HEAD(&driver->clients); /* Walk the adapters that are already present */ i2c_for_each_dev(driver, __process_new_driver); return 0; } EXPORT_SYMBOL(i2c_register_driver); /** * i2c_del_driver - unregister I2C driver * @driver: the driver being unregistered * Context: can sleep */ void i2c_del_driver(struct i2c_driver *driver) { i2c_for_each_dev(driver, __process_removed_driver); driver_unregister(&driver->driver); pr_debug("i2c-core: driver [%s] unregistered ", driver->driver.name); } EXPORT_SYMBOL(i2c_del_driver);
15.3.4 i2c传输接口
外部设备使用这些标准传输接口编写驱动。
/** * i2c_transfer - execute a single or combined I2C message * @adap: Handle to I2C bus * @msgs: One or more messages to execute before STOP is issued to * terminate the operation; each message begins with a START. * @num: Number of messages to be executed. * * Returns negative errno, else the number of messages executed. * * Note that there is no requirement that each message be sent to * the same slave address, although that is the most common model. */ int i2c_transfer(struct i2c_adapter *adap, struct i2c_msg *msgs, int num) { int ret; /* REVISIT the fault reporting model here is weak: * * - When we get an error after receiving N bytes from a slave, * there is no way to report "N". * * - When we get a NAK after transmitting N bytes to a slave, * there is no way to report "N" ... or to let the master * continue executing the rest of this combined message, if * that's the appropriate response. * * - When for example "num" is two and we successfully complete * the first message but get an error part way through the * second, it's unclear whether that should be reported as * one (discarding status on the second message) or errno * (discarding status on the first one). */ if (adap->algo->master_xfer) { #ifdef DEBUG for (ret = 0; ret < num; ret++) { dev_dbg(&adap->dev, "master_xfer[%d] %c, addr=0x%02x, " "len=%d%s ", ret, (msgs[ret].flags & I2C_M_RD) ? 'R' : 'W', msgs[ret].addr, msgs[ret].len, (msgs[ret].flags & I2C_M_RECV_LEN) ? "+" : ""); } #endif if (in_atomic() || irqs_disabled()) { ret = i2c_trylock_adapter(adap); if (!ret) /* I2C activity is ongoing. */ return -EAGAIN; } else { i2c_lock_adapter(adap); } ret = __i2c_transfer(adap, msgs, num); i2c_unlock_adapter(adap); return ret; } else { dev_dbg(&adap->dev, "I2C level transfers not supported "); return -EOPNOTSUPP; } } /** * i2c_master_send - issue a single I2C message in master transmit mode * @client: Handle to slave device * @buf: Data that will be written to the slave * @count: How many bytes to write, must be less than 64k since msg.len is u16 * * Returns negative errno, or else the number of bytes written. */ int i2c_master_send(const struct i2c_client *client, const char *buf, int count) { int ret; struct i2c_adapter *adap = client->adapter; struct i2c_msg msg; msg.addr = client->addr; msg.flags = client->flags & I2C_M_TEN; msg.len = count; msg.buf = (char *)buf; ret = i2c_transfer(adap, &msg, 1); /* * If everything went ok (i.e. 1 msg transmitted), return #bytes * transmitted, else error code. */ return (ret == 1) ? count : ret; } /** * i2c_master_recv - issue a single I2C message in master receive mode * @client: Handle to slave device * @buf: Where to store data read from slave * @count: How many bytes to read, must be less than 64k since msg.len is u16 * * Returns negative errno, or else the number of bytes read. */ int i2c_master_recv(const struct i2c_client *client, char *buf, int count) { struct i2c_adapter *adap = client->adapter; struct i2c_msg msg; int ret; msg.addr = client->addr; msg.flags = client->flags & I2C_M_TEN; msg.flags |= I2C_M_RD; msg.len = count; msg.buf = buf; ret = i2c_transfer(adap, &msg, 1); /* * If everything went ok (i.e. 1 msg received), return #bytes received, * else error code. */ return (ret == 1) ? count : ret; }
15.4 设备驱动i2c_driver和i2c_client
i2c_dirver就是i2c标准总线设备驱动模型中的驱动部分,i2c_client可理解为i2c总线上挂的外设。
1. 驱动的注册和注销
drivers/misc/eeprom/at24.c // 初始化和驱动模型 static struct i2c_driver at24_driver = { .driver = { .name = "at24", .owner = THIS_MODULE, }, .probe = at24_probe, .remove = at24_remove, .id_table = at24_ids, }; static int __init at24_init(void) { if (!io_limit) { pr_err("at24: io_limit must not be 0! "); return -EINVAL; } io_limit = rounddown_pow_of_two(io_limit); return i2c_add_driver(&at24_driver); // 匹配后,driver中的probe就能执行 } module_init(at24_init); static void __exit at24_exit(void) { i2c_del_driver(&at24_driver); } module_exit(at24_exit); // id列表 static const struct i2c_device_id at24_ids[] = { /* needs 8 addresses as A0-A2 are ignored */ { "24c00", AT24_DEVICE_MAGIC(128 / 8, AT24_FLAG_TAKE8ADDR) }, /* old variants can't be handled with this generic entry! */ { "24c01", AT24_DEVICE_MAGIC(1024 / 8, 0) }, { "24c02", AT24_DEVICE_MAGIC(2048 / 8, 0) }, /* spd is a 24c02 in memory DIMMs */ { "spd", AT24_DEVICE_MAGIC(2048 / 8, AT24_FLAG_READONLY | AT24_FLAG_IRUGO) }, { "24c04", AT24_DEVICE_MAGIC(4096 / 8, 0) }, /* 24rf08 quirk is handled at i2c-core */ { "24c08", AT24_DEVICE_MAGIC(8192 / 8, 0) }, { "24c16", AT24_DEVICE_MAGIC(16384 / 8, 0) }, { "24c32", AT24_DEVICE_MAGIC(32768 / 8, AT24_FLAG_ADDR16) }, { "24c64", AT24_DEVICE_MAGIC(65536 / 8, AT24_FLAG_ADDR16) }, { "24c128", AT24_DEVICE_MAGIC(131072 / 8, AT24_FLAG_ADDR16) }, { "24c256", AT24_DEVICE_MAGIC(262144 / 8, AT24_FLAG_ADDR16) }, { "24c512", AT24_DEVICE_MAGIC(524288 / 8, AT24_FLAG_ADDR16) }, { "24c1024", AT24_DEVICE_MAGIC(1048576 / 8, AT24_FLAG_ADDR16) }, { "at24", 0 }, { /* END OF LIST */ } }; //dts: ps7_i2c_1: ps7-i2c@e0005000 { clock-frequency = <1000000>; clocks = <&clkc 39>; compatible = "cdns,i2c-r1p10"; interrupt-parent = <&ps7_scugic_0>; interrupts = <0 48 4>; reg = <0xe0005000 0x1000>; xlnx,has-interrupt = <0x0>; #address-cells = <1>; #size-cells = <0>; eeprom@50 { compatible = "at,24c512"; reg = <0x50>; }; rtc@68 { compatible = "ds,ds1338"; reg = <0x68>; }; } ;
2. driver中的probe和remove分析
static int at24_probe(struct i2c_client *client, const struct i2c_device_id *id) { struct at24_platform_data chip; bool writable; int use_smbus = 0; struct at24_data *at24; int err; unsigned i, num_addresses; kernel_ulong_t magic; if (client->dev.platform_data) { chip = *(struct at24_platform_data *)client->dev.platform_data; } else { if (!id->driver_data) return -ENODEV; magic = id->driver_data; chip.byte_len = BIT(magic & AT24_BITMASK(AT24_SIZE_BYTELEN)); magic >>= AT24_SIZE_BYTELEN; chip.flags = magic & AT24_BITMASK(AT24_SIZE_FLAGS); /* * This is slow, but we can't know all eeproms, so we better * play safe. Specifying custom eeprom-types via platform_data * is recommended anyhow. */ chip.page_size = 1; /* update chipdata if OF is present */ at24_get_ofdata(client, &chip); chip.setup = NULL; chip.context = NULL; } if (!is_power_of_2(chip.byte_len)) dev_warn(&client->dev, "byte_len looks suspicious (no power of 2)! "); if (!chip.page_size) { dev_err(&client->dev, "page_size must not be 0! "); return -EINVAL; } if (!is_power_of_2(chip.page_size)) dev_warn(&client->dev, "page_size looks suspicious (no power of 2)! "); /* Use I2C operations unless we're stuck with SMBus extensions. */ if (!i2c_check_functionality(client->adapter, I2C_FUNC_I2C)) { if (chip.flags & AT24_FLAG_ADDR16) return -EPFNOSUPPORT; if (i2c_check_functionality(client->adapter, I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_READ_I2C_BLOCK)) { use_smbus = I2C_SMBUS_I2C_BLOCK_DATA; } else if (i2c_check_functionality(client->adapter, I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_READ_WORD_DATA)) { use_smbus = I2C_SMBUS_WORD_DATA; } else if (i2c_check_functionality(client->adapter, I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_READ_BYTE_DATA)) { use_smbus = I2C_SMBUS_BYTE_DATA; } else { return -EPFNOSUPPORT; } } if (chip.flags & AT24_FLAG_TAKE8ADDR) num_addresses = 8; else num_addresses = DIV_ROUND_UP(chip.byte_len, (chip.flags & AT24_FLAG_ADDR16) ? 65536 : 256); at24 = devm_kzalloc(&client->dev, sizeof(struct at24_data) + num_addresses * sizeof(struct i2c_client *), GFP_KERNEL); if (!at24) return -ENOMEM; mutex_init(&at24->lock); at24->use_smbus = use_smbus; at24->chip = chip; at24->num_addresses = num_addresses; /* * Export the EEPROM bytes through sysfs, since that's convenient. * By default, only root should see the data (maybe passwords etc) */ sysfs_bin_attr_init(&at24->bin); at24->bin.attr.name = "eeprom"; at24->bin.attr.mode = chip.flags & AT24_FLAG_IRUGO ? S_IRUGO : S_IRUSR; at24->bin.read = at24_bin_read; at24->bin.size = chip.byte_len; // 读写函数使用i2c-core.c提供的标准transfer接口 at24->macc.read = at24_macc_read; writable = !(chip.flags & AT24_FLAG_READONLY); if (writable) { if (!use_smbus || i2c_check_functionality(client->adapter, I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_WRITE_I2C_BLOCK)) { unsigned write_max = chip.page_size; at24->macc.write = at24_macc_write; at24->bin.write = at24_bin_write; at24->bin.attr.mode |= S_IWUSR; if (write_max > io_limit) write_max = io_limit; if (use_smbus && write_max > I2C_SMBUS_BLOCK_MAX) write_max = I2C_SMBUS_BLOCK_MAX; at24->write_max = write_max; /* buffer (data + address at the beginning) */ at24->writebuf = devm_kzalloc(&client->dev, write_max + 2, GFP_KERNEL); if (!at24->writebuf) return -ENOMEM; } else { dev_warn(&client->dev, "cannot write due to controller restrictions."); } } at24->client[0] = client; /* use dummy devices for multiple-address chips */ for (i = 1; i < num_addresses; i++) { at24->client[i] = i2c_new_dummy(client->adapter, client->addr + i); if (!at24->client[i]) { dev_err(&client->dev, "address 0x%02x unavailable ", client->addr + i); err = -EADDRINUSE; goto err_clients; } } err = sysfs_create_bin_file(&client->dev.kobj, &at24->bin); // !!! 在sysfs中创建文件,读此文件的读写,就是对EEPROM的读写,at24-bin的读写函数与i2c底层操作挂钩
if (err) goto err_clients; i2c_set_clientdata(client, at24); dev_info(&client->dev, "%zu byte %s EEPROM, %s, %u bytes/write ", at24->bin.size, client->name, writable ? "writable" : "read-only", at24->write_max); if (use_smbus == I2C_SMBUS_WORD_DATA || use_smbus == I2C_SMBUS_BYTE_DATA) { dev_notice(&client->dev, "Falling back to %s reads, " "performance will suffer ", use_smbus == I2C_SMBUS_WORD_DATA ? "word" : "byte"); } /* export data to kernel code */ if (chip.setup) chip.setup(&at24->macc, chip.context); return 0; err_clients: for (i = 1; i < num_addresses; i++) if (at24->client[i]) i2c_unregister_device(at24->client[i]); return err; } static int at24_remove(struct i2c_client *client) { struct at24_data *at24; int i; at24 = i2c_get_clientdata(client); sysfs_remove_bin_file(&client->dev.kobj, &at24->bin); for (i = 1; i < at24->num_addresses; i++) i2c_unregister_device(at24->client[i]); return 0; }
15.5 i2c-dev.c文件分析
采用file_oprations方式,组织标准字符设备驱动,对adapter进行设备化,应用层可以通过read、write函数对adapter进行直接操作。
15.6 总结
研究过i2c驱动以后,再看spi、usb等驱动框架,几乎是一样的,如下表。