ARM处理器从cortex系列开始集成NEON处理单元,该单元可以简单理解为协处理器,专门为矩阵运算等算法设计,特别适用于图像、视频、音频处理等场景,应用也很广泛。
本文先对NEON处理单元进行简要介绍,然后介绍如何在内核态下使用NEON,最后列举实例说明。
一.NEON简介
其实最好的资料就是官方文档,Cortex™-A Series Programmer’s Guide ,以下描述摘自该文档
1.1 SIMD
NEON采用SIMD架构,single instruction multy data,一条指令处理多个数据,NEON中这多个数据可以很多,而且配置灵活(8bit、16bit、32bit为单位,可多个单位数据),这是优势所在。
如下图,APU需要至少四条指令完成加操作,而NEON只需要1条,考虑到ld和st,节省的指令更多。
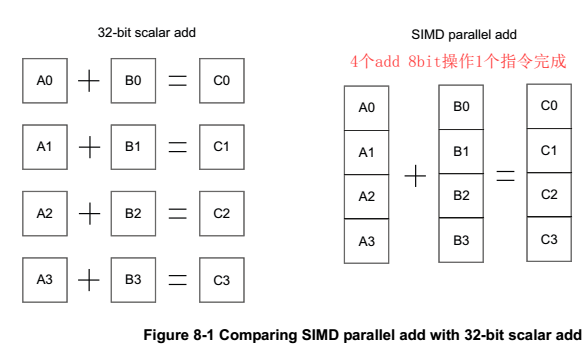
上述特性,使NEON特别适合处理块数据、图像、视频、音频等。
1.2 NEON architecture overview
NEON也是load/store架构,寄存器为64bit/128bit,可形成向量化数据,配合若干便于向量操作的指令。
1.2.1 commonality with VFP
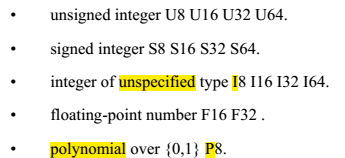
1.2.2 data type

指令中的数据类型表示,例如VMLAL.S8:
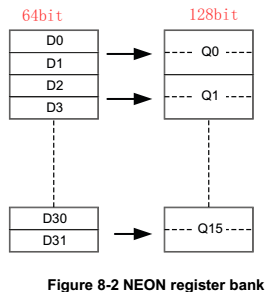
1.2.3 registers
32个64bit寄存器,D0~D31;同时可组成16个128 bit寄存器,Q0~Q15。与VFP公用。
寄存器内部的数据单位为8bit、16bit、32bit,可以根据需要灵活配置。
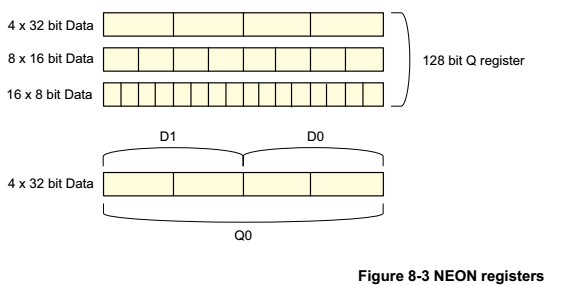
NEON的指令有Normal,Long,Wide,Narrow和Saturating variants等几种后缀,是根据操作的源src和dst寄存器的类型确定的。
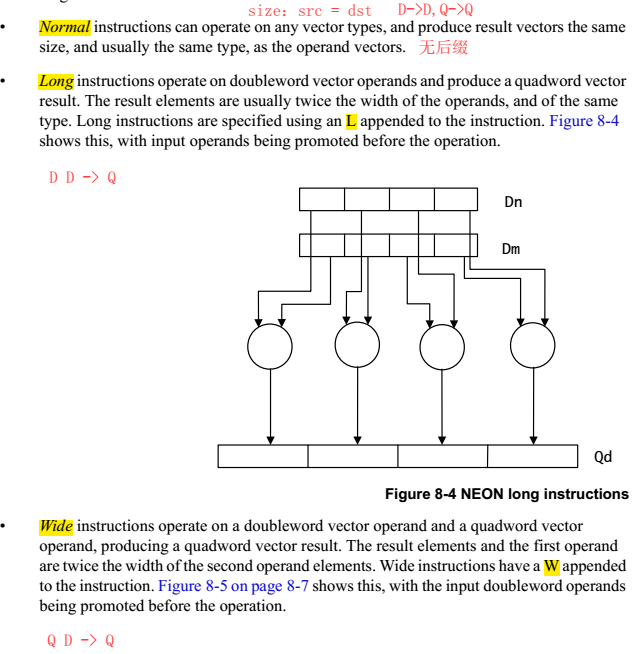
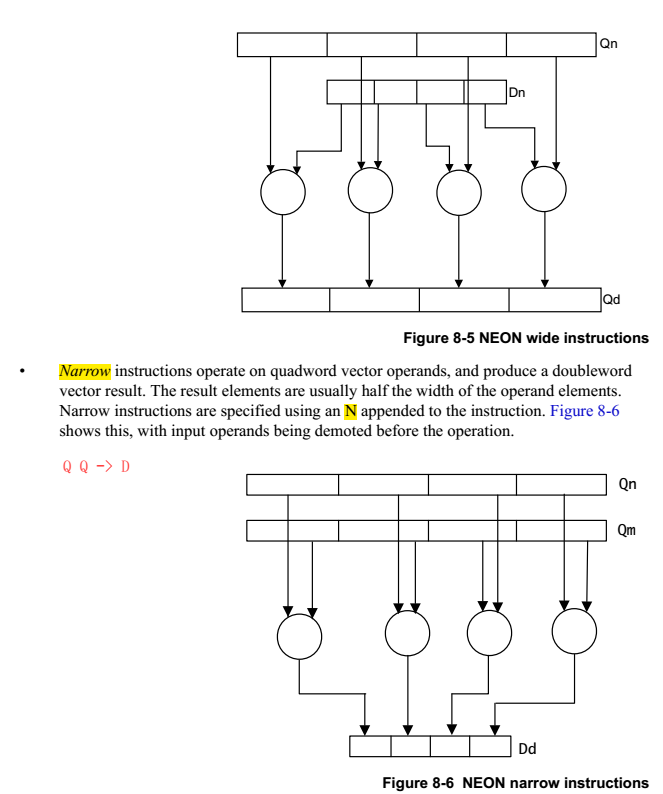
1.2.4 instruction set

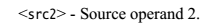
1.3 NEON 指令分类概述
指令比较多, 详细可参考Cortex™-A Series Programmer’s Guide。可大体分为:
- NEON general data processing instructions
- NEON shift instructions
- NEON logical and compare operations
- NEON arithmetic instructions
- NEON multiply instructions
- NEON load and store element and structure instructions B.8 NEON and VFP pseudo-instructions
简单罗列一下各指令
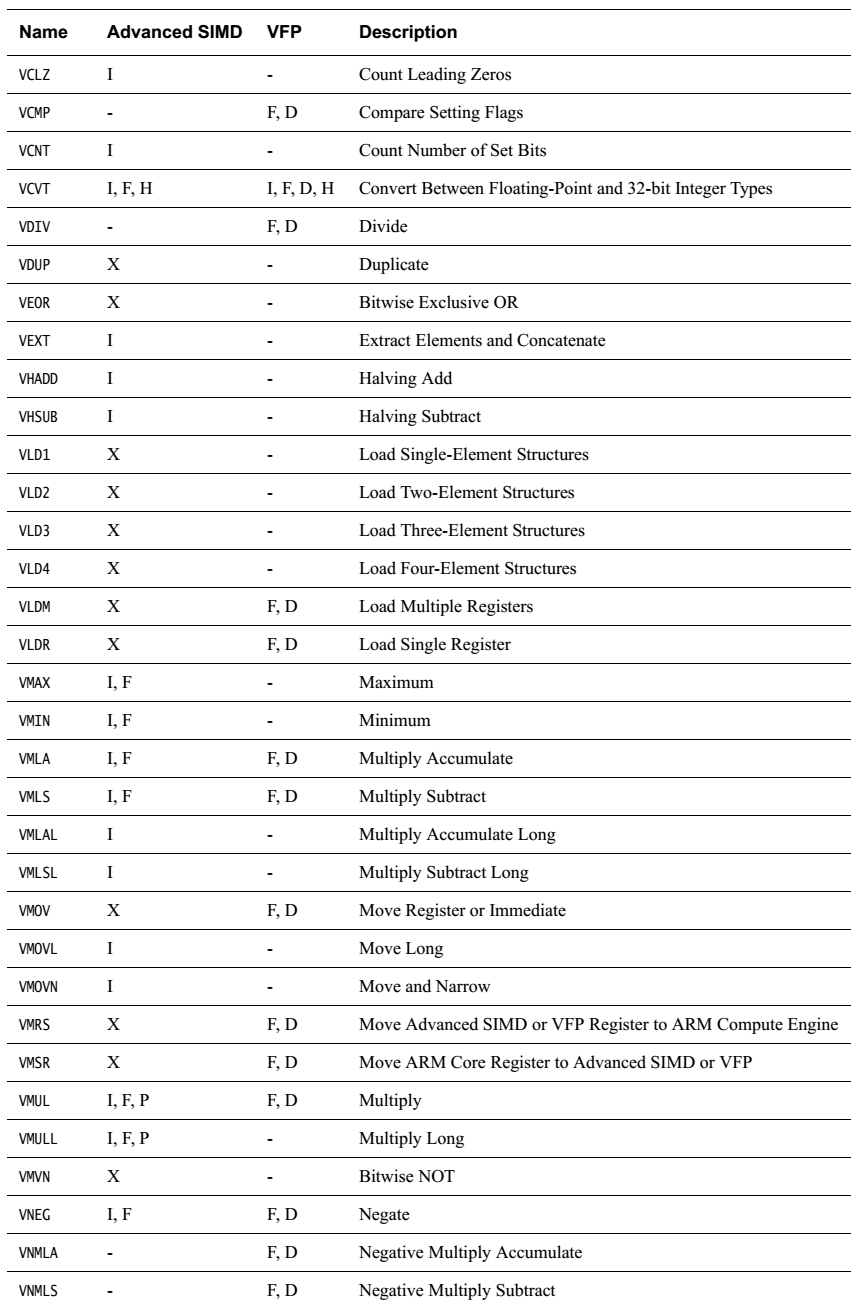
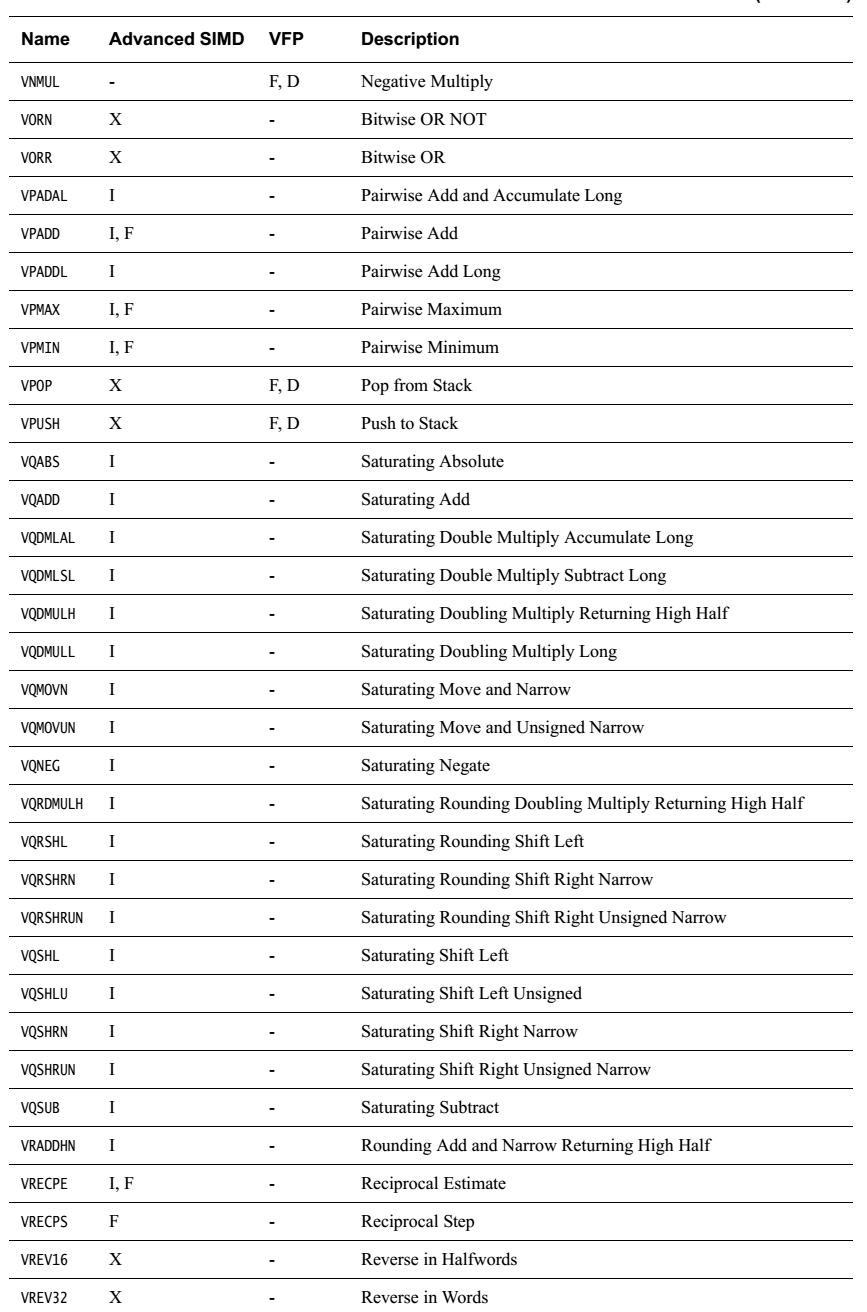

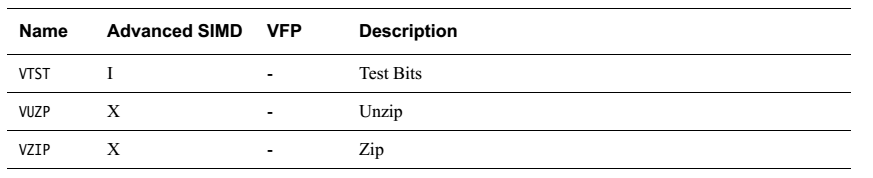
无循环左移,负数左移按右移处理。
load和store指令不太好理解,说明一下。

1.4 NEON 使用方式
1.4.1 NEON使用方式
NEON有若干种使用方式:
- C语言被编译器自动向量化,需要增加编译选项,且C语言编码时有若干注意事项。这种方式不确定性太大,没啥实用价值
- NEON汇编,可行,汇编稍微复杂一点,但是核心算法还是值得的
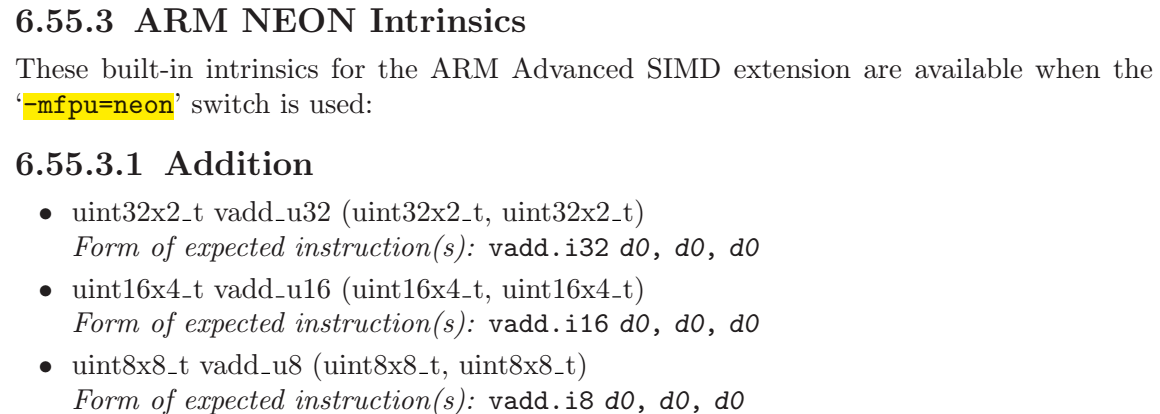
- intrinsics,gcc和armcc等编译器提供了若干与NEON对应的inline函数,可直接在C语言里调用,这些函数反汇编时会直接编程响应的NEON指令。这种方式比较实用与C语言环境,且相对简单。本文后续使用这种方式进行详细说明。
1.4.2 C语言NEON数据类型
需包含arm_neon.h头文件,该头文件在gcc目录里。都是向量数据。
typedef __builtin_neon_qi int8x8_t __attribute__ ((__vector_size__ (8))); typedef __builtin_neon_hi int16x4_t __attribute__ ((__vector_size__ (8))); typedef __builtin_neon_si int32x2_t __attribute__ ((__vector_size__ (8))); typedef __builtin_neon_di int64x1_t; typedef __builtin_neon_sf float32x2_t __attribute__ ((__vector_size__ (8))); typedef __builtin_neon_poly8 poly8x8_t __attribute__ ((__vector_size__ (8))); typedef __builtin_neon_poly16 poly16x4_t __attribute__ ((__vector_size__ (8))); typedef __builtin_neon_uqi uint8x8_t __attribute__ ((__vector_size__ (8))); typedef __builtin_neon_uhi uint16x4_t __attribute__ ((__vector_size__ (8))); typedef __builtin_neon_usi uint32x2_t __attribute__ ((__vector_size__ (8))); typedef __builtin_neon_udi uint64x1_t; typedef __builtin_neon_qi int8x16_t __attribute__ ((__vector_size__ (16))); typedef __builtin_neon_hi int16x8_t __attribute__ ((__vector_size__ (16))); typedef __builtin_neon_si int32x4_t __attribute__ ((__vector_size__ (16))); typedef __builtin_neon_di int64x2_t __attribute__ ((__vector_size__ (16))); typedef __builtin_neon_sf float32x4_t __attribute__ ((__vector_size__ (16))); typedef __builtin_neon_poly8 poly8x16_t __attribute__ ((__vector_size__ (16))); typedef __builtin_neon_poly16 poly16x8_t __attribute__ ((__vector_size__ (16))); typedef __builtin_neon_uqi uint8x16_t __attribute__ ((__vector_size__ (16))); typedef __builtin_neon_uhi uint16x8_t __attribute__ ((__vector_size__ (16))); typedef __builtin_neon_usi uint32x4_t __attribute__ ((__vector_size__ (16))); typedef __builtin_neon_udi uint64x2_t __attribute__ ((__vector_size__ (16))); typedef float float32_t; typedef __builtin_neon_poly8 poly8_t; typedef __builtin_neon_poly16 poly16_t; typedef struct int8x8x2_t { int8x8_t val[2]; } int8x8x2_t; typedef struct int8x16x2_t { int8x16_t val[2]; } int8x16x2_t; typedef struct int16x4x2_t { int16x4_t val[2]; } int16x4x2_t; typedef struct int16x8x2_t { int16x8_t val[2]; } int16x8x2_t; typedef struct int32x2x2_t { int32x2_t val[2]; } int32x2x2_t; typedef struct int32x4x2_t { int32x4_t val[2]; } int32x4x2_t; typedef struct int64x1x2_t { int64x1_t val[2]; } int64x1x2_t; typedef struct int64x2x2_t { int64x2_t val[2]; } int64x2x2_t; typedef struct uint8x8x2_t { uint8x8_t val[2]; } uint8x8x2_t; typedef struct uint8x16x2_t { uint8x16_t val[2]; } uint8x16x2_t; typedef struct uint16x4x2_t { uint16x4_t val[2]; } uint16x4x2_t; typedef struct uint16x8x2_t { uint16x8_t val[2]; } uint16x8x2_t; typedef struct uint32x2x2_t { uint32x2_t val[2]; } uint32x2x2_t; typedef struct uint32x4x2_t { uint32x4_t val[2]; } uint32x4x2_t; typedef struct uint64x1x2_t { uint64x1_t val[2]; } uint64x1x2_t; typedef struct uint64x2x2_t { uint64x2_t val[2]; } uint64x2x2_t; typedef struct float32x2x2_t { float32x2_t val[2]; } float32x2x2_t; typedef struct float32x4x2_t { float32x4_t val[2]; } float32x4x2_t; typedef struct poly8x8x2_t { poly8x8_t val[2]; } poly8x8x2_t; typedef struct poly8x16x2_t { poly8x16_t val[2]; } poly8x16x2_t; typedef struct poly16x4x2_t { poly16x4_t val[2]; } poly16x4x2_t; typedef struct poly16x8x2_t { poly16x8_t val[2]; } poly16x8x2_t; typedef struct int8x8x3_t { int8x8_t val[3]; } int8x8x3_t; typedef struct int8x16x3_t { int8x16_t val[3]; } int8x16x3_t; typedef struct int16x4x3_t { int16x4_t val[3]; } int16x4x3_t; typedef struct int16x8x3_t { int16x8_t val[3]; } int16x8x3_t; typedef struct int32x2x3_t { int32x2_t val[3]; } int32x2x3_t; typedef struct int32x4x3_t { int32x4_t val[3]; } int32x4x3_t; typedef struct int64x1x3_t { int64x1_t val[3]; } int64x1x3_t; typedef struct int64x2x3_t { int64x2_t val[3]; } int64x2x3_t; typedef struct uint8x8x3_t { uint8x8_t val[3]; } uint8x8x3_t; typedef struct uint8x16x3_t { uint8x16_t val[3]; } uint8x16x3_t; typedef struct uint16x4x3_t { uint16x4_t val[3]; } uint16x4x3_t; typedef struct uint16x8x3_t { uint16x8_t val[3]; } uint16x8x3_t; typedef struct uint32x2x3_t { uint32x2_t val[3]; } uint32x2x3_t; typedef struct uint32x4x3_t { uint32x4_t val[3]; } uint32x4x3_t; typedef struct uint64x1x3_t { uint64x1_t val[3]; } uint64x1x3_t; typedef struct uint64x2x3_t { uint64x2_t val[3]; } uint64x2x3_t; typedef struct float32x2x3_t { float32x2_t val[3]; } float32x2x3_t; typedef struct float32x4x3_t { float32x4_t val[3]; } float32x4x3_t; typedef struct poly8x8x3_t { poly8x8_t val[3]; } poly8x8x3_t; typedef struct poly8x16x3_t { poly8x16_t val[3]; } poly8x16x3_t; typedef struct poly16x4x3_t { poly16x4_t val[3]; } poly16x4x3_t; typedef struct poly16x8x3_t { poly16x8_t val[3]; } poly16x8x3_t; typedef struct int8x8x4_t { int8x8_t val[4]; } int8x8x4_t; typedef struct int8x16x4_t { int8x16_t val[4]; } int8x16x4_t; typedef struct int16x4x4_t { int16x4_t val[4]; } int16x4x4_t; typedef struct int16x8x4_t { int16x8_t val[4]; } int16x8x4_t; typedef struct int32x2x4_t { int32x2_t val[4]; } int32x2x4_t; typedef struct int32x4x4_t { int32x4_t val[4]; } int32x4x4_t; typedef struct int64x1x4_t { int64x1_t val[4]; } int64x1x4_t; typedef struct int64x2x4_t { int64x2_t val[4]; } int64x2x4_t; typedef struct uint8x8x4_t { uint8x8_t val[4]; } uint8x8x4_t; typedef struct uint8x16x4_t { uint8x16_t val[4]; } uint8x16x4_t; typedef struct uint16x4x4_t { uint16x4_t val[4]; } uint16x4x4_t; typedef struct uint16x8x4_t { uint16x8_t val[4]; } uint16x8x4_t; typedef struct uint32x2x4_t { uint32x2_t val[4]; } uint32x2x4_t; typedef struct uint32x4x4_t { uint32x4_t val[4]; } uint32x4x4_t; typedef struct uint64x1x4_t { uint64x1_t val[4]; } uint64x1x4_t; typedef struct uint64x2x4_t { uint64x2_t val[4]; } uint64x2x4_t; typedef struct float32x2x4_t { float32x2_t val[4]; } float32x2x4_t; typedef struct float32x4x4_t { float32x4_t val[4]; } float32x4x4_t; typedef struct poly8x8x4_t { poly8x8_t val[4]; } poly8x8x4_t; typedef struct poly8x16x4_t { poly8x16_t val[4]; } poly8x16x4_t; typedef struct poly16x4x4_t { poly16x4_t val[4]; } poly16x4x4_t; typedef struct poly16x8x4_t { poly16x8_t val[4]; } poly16x8x4_t;
1.4.3 gcc的NEON函数
跟NEON指令对应,详见gcc手册。
二.内核状态下使用NEON的规则
在linux里,应用态可以比较方便使用NEON instrinsic,增加头arm_neon.h头文件后直接使用。但是内核态下使用NEON有较多限制,在linux内核文档 /Documentation/arm/kernel_mode_neon.txt对此有详细说明。要点为:

还有一点特别关键:

CC [M] /work/platform-zynq/drivers/zynq_fpga_driver/mmi_neon/lcd_hw_fs8812_neon.o In file included from /home/liuwanpeng/lin/lib/gcc/arm-xilinx-linux-gnueabi/4.8.3/include/arm_neon.h:39:0, from /work/platform-zynq/drivers/zynq_fpga_driver/mmi_neon/lcd_hw_fs8812_neon.c:8: /home/liuwanpeng/lin/lib/gcc/arm-xilinx-linux-gnueabi/4.8.3/include/stdint.h:9:26: error: no include path in which to search for stdint.h # include_next <stdint.h> 没有使用-ffreestanding编译选项时,在内核态下使用出现此编译错误。
三.实例
NEON一般在图像等领域,最小处理单位就是8bit,而不是1bit,这方便的例子非常多,本文就不说明了。在实际项目中,我需要对液晶的一组数据按位操作,变换,形成新的数据,如果用传统ARM指令,掩码、移位、循环,想想效率就非常低。于是决定使用NEON的位相关指令完成上述任务。
3.1 任务说明
如下图,需要对各个bit进行转换,组成新的数据。
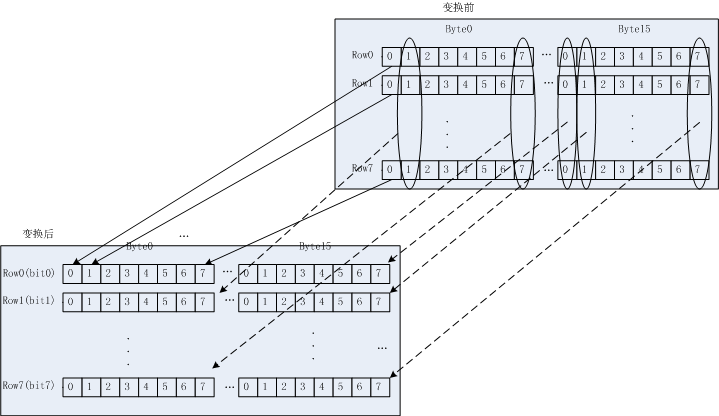
3.2 算法说明
使用vmsk、vshl、vadd等位操作完成。
3.3 kernel配置
必须配置内核支持NEON,否则kernel_neon_begin()和kernel_neon_end()等函数不会编辑进去。
make menuconfig:Floating point emulation,如下图。
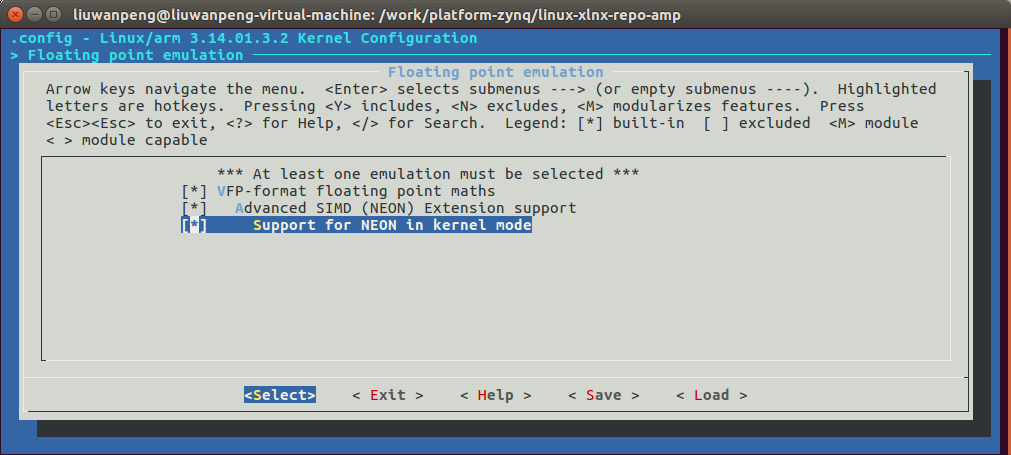
未使能“Support for NEON in kernel mode”时会报错: mmi_module_amp: Unknown symbol kernel_neon_begin (err 0) mmi_module_amp: Unknown symbol kernel_neon_end (err 0)
3.4 模块代码
由于NEON代码需要单独设置编译选项,所以单独建立了一个内核模块,makefile如下:
CFLAGS_MODULE += -O3 -mfpu=neon -mfloat-abi=softfp -ffreestanding
核心代码:
#include <linux/module.h> #include <linux/printk.h> #include <arm_neon.h> // 来自GCC的头文件,必须用-ffreestanding编译选徐昂
#define LCD_8812_ROW_BYTES 16
#define LCD_8812_PAGE_ROWS 8
#define LCD_PAGE_BYTES (LCD_8812_ROW_BYTES*LCD_8812_PAGE_ROWS)
int fs8812_cvt_buf( uint8 * dst, uint8 * src ) { uint8x16_t V_src[8]; uint8x16_t V_tmp[8]; uint8x16_t V_dst[8]; uint8x16_t V_msk; int8x16_t V_shift; int8 RSHL_bits[8] = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7}; int8 row,bit; uint8 page; uint8 * fb_page_x = NULL; // convert the frame_buf for fs8812 for( page=0;page<4;page++ ){ fb_page_x = src + page*LCD_PAGE_BYTES; for( row=0;row<LCD_8812_PAGE_ROWS;row++ ) V_src[row] = vld1q_u8( fb_page_x + row*LCD_8812_ROW_BYTES );
for( bit=0;bit<8;bit++){ V_msk = vdupq_n_u8(1<<bit); for( row=0;row<LCD_8812_PAGE_ROWS;row++){ V_tmp[row] = vandq_u8(V_src[row],V_msk); // only process the desire bit V_shift = vdupq_n_s8( RSHL_bits[row]-bit ); V_tmp[row] = vshlq_u8( V_tmp[row],V_shift ); } V_dst[bit] = vorrq_u8(V_tmp[0],V_tmp[1]); // all bit_x convert to one row V_dst[bit] |= vorrq_u8(V_tmp[2],V_tmp[3]); V_dst[bit] |= vorrq_u8(V_tmp[4],V_tmp[5]); V_dst[bit] |= vorrq_u8(V_tmp[6],V_tmp[7]); } // store to ram fb_page_x = dst + page*LCD_PAGE_BYTES; for( row=0;row<LCD_8812_PAGE_ROWS;row++ ){ vst1q_u8(fb_page_x,V_dst[row]); fb_page_x += LCD_8812_ROW_BYTES; } }
return 0; } EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(fs8812_cvt_buf);
调用模块,务必没有“-mfpu=neon -mfloat-abi=softfp ”选项
// convert the frame_buf for fs8812 kernel_neon_begin(); fs8812_cvt_buf( g_tmp_buf, frame_buf ); kernel_neon_end();