数据库操作
- 查看所有数据库
show databases;
- 1
- 查看当前使用的数据库
select database();
- 1
- 创建数据库
create databases 数据库名 charset=utf8;
- 1
5.删除数据库
drop database 数据库名
- 1
6 .使用数据句库
use database 数据库名
- 1
7.查看数据库中所有表
show tables;
- 1
表的操作
1.查看表结构
desc 表名
- 1
2.创建表结构的语法
create table table_name(
字段名 数据类型 可选的约束条件);
- 1
- 2
demo:创建班级和学生表
create table classes(
id int unsigned auto_increment primary key not null,
name varchar(10)
);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
create table students(
id int unsigned primary key auto_increment not null,
name varchar(20) default '',
age tinyint unsigned default 0,
height decimal(5,2),
gender enum('男','女','人妖','保密'),
cls_id int unsigned default 0
)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
3.修改表–添加字段
alter table 表名 add 列名 类型
demo:alter table students add birthday datetime;
- 1
- 2
4.修改表–修改字段–重命名版
alert table 表名 change 原名 新名 类型及约束
demo:alter table syudents change birthday birth datetime not null;
- 1
- 2
5.修改表–修改字段–不重命名
alter table 表名 modify 列名 类型及约束
demo : alter table students modify birth date nout noll;
- 1
- 2
6.删除表–删除字段
alter table 表名 drop 列名
demo :later table students drop birthday;
- 1
- 2
7.删除表
drop table 表名
demo:drop table students;
- 1
- 2
8.查看表的创建语句–详细过程
show create table 表名
demo : show create tabele students;
- 1
- 2
查询基本使用
1.查询所有列
select * from 表名
例:
select * from classes;
- 1
- 2
- 3
2.查询指定列
select 列1,列2,...from 表名;
例:
select id,name from classes;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
增加
说明:主键列是自动增长,但是在全列插入时需要占位,通常使用空值(0或者null) ; 字段默认值 default 来占位,插入成功后以实际数据为准
1.全列插入:值的顺序与表结构字段的顺序完全一一对应
此时 字段名列表不用填写
insert into 表名 values (...)
例:
insert into students values(0,’郭靖‘,1,'蒙古','2016-1-2');
- 1
- 2
- 3
2.部分列插入:值的顺序与给出的列顺序对应
此时需要根据实际的数据的特点 填写对应字段列表
insert into 表名 (列1,...) values(值1,...)
例:
insert into students(name,hometown,birthday) values('黄蓉','桃花岛','2016-3-2');
- 1
- 2
- 3
上面的语句一次可以向表中插入一行数据,还可以一次性插入多行数据,这样可以减少与数据库的通信
3.全列多行插入
insert into 表名 values(...),(...)...;
例:
insert into classes values(0,'python1'),(0,'python2');
- 1
- 2
- 3
4.部分列多行插入
insert into 表名(列1,...) values(值1,...),(值1,...)...;
例:
insert into students(name) values('杨康'),('杨过'),('小龙女');
- 1
- 2
- 3
修改
update 表名 set 列1=值1,列2=值2... where 条件
例:
update students set gender=0,hometown='北京' where id=5;
- 1
- 2
- 3
删除
delete from 表名 where 条件
例:
delete from students where id=5;
- 1
- 2
- 3
逻辑删除,本质就是修改操作
update students set isdelete=1 where id=1;
- 1
as关键字
1.使用 as 给字段起别名
select id as 序号, name as 名字, gender as 性别 from students;
- 1
2.可以通过 as 给表起别名
select s.id,s.name,s.gender from students as s;
- 1
条件语句查询
where后面支持多种运算符,进行条件的处理
比较运算符
逻辑运算符
模糊查询
范围查询
空判断
比较运算符
等于: =
大于: >
大于等于: >=
小于: <
小于等于: <=
不等于: != 或 <>
例1:查询编号大于3的学生
select * from students where id > 3;
- 1
例2:查询编号不大于4的学生
select * from students where id <= 4;
- 1
例3:查询姓名不是“黄蓉”的学生
select * from students where name != '黄蓉';
- 1
例4:查询没被删除的学生
select * from students where is_delete=0;
- 1
逻辑运算符
and
or
not
例5:查询编号大于3的女同学
select * from students where id > 3 and gender=0;
- 1
例6:查询编号小于4或没被删除的学生
select * from students where id < 4 or is_delete=0;
- 1
模糊查询
like
%表示任意多个任意字符
_表示一个任意字符
例7:查询姓黄的学生
select * from students where name like '黄%';
- 1
例8:查询姓黄并且“名”是一个字的学生
select * from students where name like '黄_';
- 1
例9:查询姓黄或叫靖的学生
select * from students where name like '黄%' or name like '%靖';
- 1
范围查询
范围查询分为连续范围查询和非连续范围查询
- in表示在一个非连续的范围内
例10:查询编号是1或3或8的学生
select * from students where id in(1,3,8);
- 1
- between … and …表示在一个连续的范围内
例11:查询编号为3至8的学生
select * from students where id between 3 and 8;
- 1
例12:查询编号是3至8的男生
select * from students where (id between 3 and 8) and gender=1;
- 1
空判断
判断为空
例13:查询没有填写身高的学生
select * from students where height is null;
- 1
注意: 1. null与’'是不同的 2. is null
判非空is not null
例14:查询填写了身高的学生
select * from students where height is not null;
- 1
例15:查询填写了身高的男生
select * from students where height is not null and gender=1;
- 1
- 2
优先级
优先级由高到低的顺序为:小括号,not,比较运算符,逻辑运算符
and比or先运算,如果同时出现并希望先算or,需要结合()使用
排序
排序查询语法:
select * from 表名 order by 列1 asc|desc [,列2 asc|desc,...]
- 1
语法说明:
将行数据按照列1进行排序,如果某些行 列1 的值相同时,则按照 列2 排序,以此类推
asc从小到大排列,即升序
desc从大到小排序,即降序
默认按照列值从小到大排列(即asc关键字)
例1:查询未删除男生信息,按学号降序
select * from students where gender=1 and is_delete=0 order by id desc;
- 1
例2:查询未删除学生信息,按名称升序
select * from students where is_delete=0 order by name;
- 1
例3:显示所有的学生信息,先按照年龄从大–>小排序,当年龄相同时 按照身高从高–>矮排序
select * from students order by age desc,height desc;
- 1
分页
select * from 表名 limit start=0,count
- 1
说明
从start开始,获取count条数据
start默认值为0
也就是当用户需要获取数据的前n条的时候可以直接写上 xxx limit n;
例1:查询前3行男生信息
select * from students where gender=1 limit 0,3;
- 1
关于分页的一个有趣的推导公式
已知:每页显示m条数据,当前显示第n页
求总页数:此段逻辑后面会在python项目中实现
查询总条数p1
使用p1除以m得到p2
如果整除则p2为总数页
如果不整除则p2+1为总页数
获取第n页的数据的SQL语句求解思路
第n页前有n-1页
所在第n页前已经显示的数据的总量是(n-1)*m
由于数据的下标从0开始 所以第n页前所有的网页的下标是0,1,…,(n-1)*m-1
所以第n页的数据起始下标是(n-1)*m
获取第n页数据的SQL语句
select * from students where is_delete=0 limit (n-1)*m,m
- 1
注意:在sql语句中limit后不可以直接加公式
聚合函数
总数
count(*) 表示计算总行数,括号中写星与列名,结果是相同的
例1:查询学生总数
select count(*) from students;
- 1
最大值
max(列) 表示求此列的最大值
例2:查询女生的编号最大值
select max(id) from students where gender=2;
- 1
最小值
min(列) 表示求此列的最小值
例3:查询未删除的学生最小编号
select min(id) from students where is_delete=0;
- 1
求和
sum(列) 表示求此列的和
例4:查询男生的总年龄
select sum(age) from students where gender=1;
- 1
– 平均年龄
select sum(age)/count(*) from students where gender=1;
- 1
平均值
avg(列) 表示求此列的平均值
例5:查询未删除女生的编号平均值
select avg(id) from students where is_delete=0 and gender=2;
- 1
分组
group by

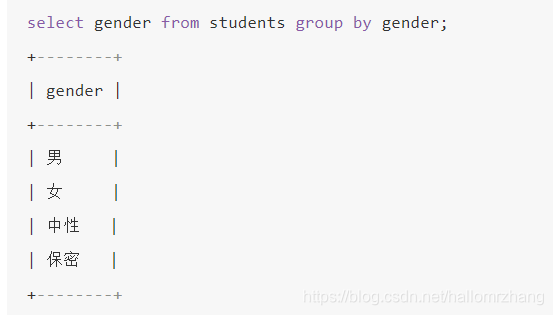
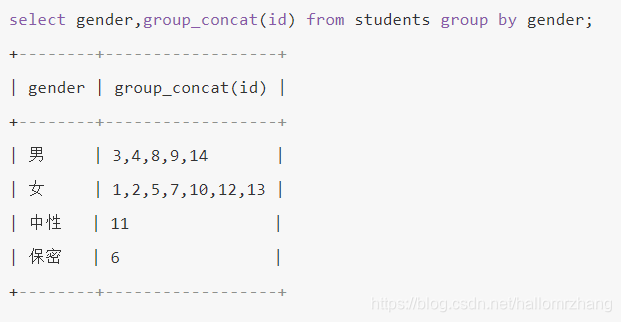
group by + group_concat()
group_concat(字段名)根据分组结果,使用group_concat()来放置每一个分组中某字段的集合

group by + 聚合函数
通过group_concat()的启发,我们既然可以统计出每个分组的某字段的值的集合,那么我们也可以通过集合函数来对这个值的集合做一些操作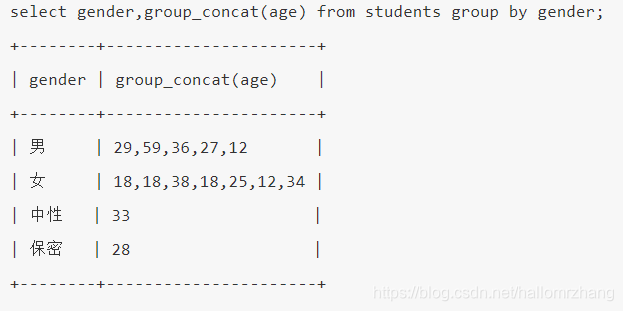


group by + having
having 条件表达式:用来过滤分组结果
having作用和where类似,但having只能用于group by 而where是用来过滤表数据
group by + with rollup
with rollup的作用是:在最后新增一行,来记录当前表中该字段对应的操作结果,一般是汇总结果。

连接查询语法
对于外连接 outer关键字可以省略
select * from 表1 inner或left或right join 表2 on 表1.列 运算符 表2.列
- 1
例1:使用内连接查询班级表与学生表
select * from students inner join classes on students.cls_id = classes.id;
- 1
例2:使用左连接查询班级表与学生表
此处使用了as为表起别名,目的是编写简单
select * from students as s left join classes as c on s.cls_id = c.id;
- 1
例3:使用右连接查询班级表与学生表
select * from students as s right join classes as c on s.cls_id = c.id;
- 1
例4:查询学生姓名及班级名称
select s.name,c.name from students as s inner join classes as c on s.cls_id = c.id;
- 1
子查询
在一个 select 语句中,嵌入了另外一个 select 语句, 那么被嵌入的 select 语句称之为子查询语句,外部那个select语句则称为主查询.
主查询和子查询的关系
子查询是嵌入到主查询中
子查询是辅助主查询的,要么充当条件,要么充当数据源
子查询是可以独立存在的语句,是一条完整的 select 语句
标量子查询
查询班级学生平均年龄
查询大于平均年龄的学生
查询班级学生的平均身高
select * from students where age > (select avg(age) from students);
- 1
列级子查询
查询还有学生在班的所有班级名字
找出学生表中所有的班级 id
找出班级表中对应的名字
select name from classes where id in (select cls_id from students);
- 1
行级子查询
需求: 查找班级年龄最大,身高最高的学生
行元素: 将多个字段合成一个行元素,在行级子查询中会使用到行元素
select * from students where (height,age) = (select max(height),max(age) from students);