目录
1 问题描述
引用自百度百科:
如果两个顶点可以相互通达,则称两个顶点强连通(strongly connected)。如果有向图G的每两个顶点都强连通,称G是一个强连通图。有向图的极大强连通子图,称为强连通分量(strongly connected components)。
当DFN(u)=Low(u)时,以u为根的搜索子树上所有节点是一个强连通分量。
2 解决方案
下面代码所使用图:
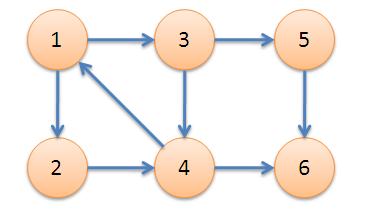
具体代码如下:
package com.liuzhen.practice; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.Stack; public class Main { public static int MAX = 100; public static int count; //用于对图中顶点遍历的次序进行计数 public static int n; public static int[] DFN = new int[MAX]; //记录图中每个节点的DFS遍历的时间戳(即次序) public static int[] Low = new int[MAX]; //记录每个顶点的所在树的根节点编号 public static boolean[] inStack = new boolean[MAX]; //用于记录当前节点是否在栈中 public static Stack<Integer> stack; public void init(int n) { count = 0; stack = new Stack<Integer>(); for(int i = 0;i <= n;i++) { DFN[i] = -1; //代表顶点i未被遍历 Low[i] = -1; inStack[i] = false; } } static class edge { public int a; //边的起点 public int b; //边的终点 edge(int a, int b) { this.a = a; this.b = b; } } public void dfs(ArrayList<edge>[] map, int start) { DFN[start] = count++; Low[start] = DFN[start]; stack.push(start); inStack[start] = true; int j = start; for(int i = 0;i < map[start].size();i++) { j = map[start].get(i).b; if(DFN[j] == -1) { //顶点j未被遍历 dfs(map, j); Low[start] = Math.min(Low[start], Low[j]); } else if(inStack[j]) { Low[start] = Math.min(Low[start], DFN[j]); } } if(DFN[start] == Low[start]) { System.out.print("强连通分量:"); do { j = stack.pop(); System.out.print(j+" "); inStack[j] = false; } while(start != j); System.out.println(); } return; } public static void main(String[] args) { Main test = new Main(); Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); n = in.nextInt(); test.init(n); int k = in.nextInt(); //有向图的边数目 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") ArrayList<edge>[] map = new ArrayList[n + 1]; for(int i = 0;i <= n;i++) map[i] = new ArrayList<edge>(); in.nextLine(); for(int i = 0;i < k;i++) { int a = in.nextInt(); int b = in.nextInt(); map[a].add(new edge(a, b)); } test.dfs(map, 1); } }
运行结果:
6 8 1 2 1 3 2 4 3 4 3 5 4 1 4 6 5 6 强连通分量:6 强连通分量:5 强连通分量:3 4 2 1
参考资料: