一:类的方法说明
类的方法分为实例方法,析构方法,构造方法,类方法,静态方法,属性方法,等等
类方法和静态方法都可以被类和类实例调用,类实例方法仅可以被类实例调用
类方法的隐含调用参数是类,而类实例方法的隐含调用参数是类的实例,静态方法没有隐含调用参数
1)实例方法:类的实例能够使用的方法。
2) 析构方法:类中使用def __init__(self)定义的方法,也就是当该类被实例化的时候就会执行该函数。那么我们就可以把要先初始化的属性放到这个函数里面
3) 构造方法:__del__”就是一个析构函数了,当使用del 删除对象时,会调用他本身的析构函数,另外当对象在某个作用域中调用完毕,在跳出其作用域的同时析构函数也会被调用一次,这样可以用来释放内存空间
4)静态方法:是一种普通函数,就位于类定义的命名空间中,它不会对任何实例类型进行操作。
使用装饰器@staticmethod定义静态方法。类对象和实例都可以调用静态方法。
只是名义上归类管理,实际上在静态方法里访问不了类的实例 中的中的任何属性
5)类方法:类方法是将类本身作为对象进行操作的方法。类方法使用@classmethod装饰器定义。类方法:只能访问类变量,不能访问实例变量
6)属性方法的作用就是通过@property把一个方法变成一个静态属性
二:示例代码
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- __author__ = 'shisanjun' class Person(object): country="中国"#类的公有属性或者类属性 def __init__(self,name,age): #构造方法,在类的实例化的时候被调用,用来初始化一些属性的时候使用 self.name=name #实例属性 self.age=age self.__salary="15000" #私有属性 def talk(self): #实例方法 print("实例方法:国家:%s,名称为:%s,年龄为:%s,薪水:%s" %(self.country,self.name,self.age,self.__salary)) #提供私有属性访问接口 def get_salary(self): return self.__salary def __del__(self): #析构方法,在实例被销毁的时候被调用 print("Person is del") #静态方法 @staticmethod def sayHi(coutry): """ print("welcome %s to china" %self.name) 会报TypeError: sayHi() missing 1 required positional argument: 'self' 只是名义上归类管理,实际上在静态方法里访问不了类的实例 中的中的任何属性。 当普通方法使用 """ print("静态方法:welcome to" ,coutry) #类方法 @classmethod def eat(self): """ print("%s eat baozi" %self.name) 报错:AttributeError: type object 'Person' has no attribute 'name' 类方法只能调用类属性(公有属性) """ print("类方法: in %s eat baozi" %self.country) #属性方法 @property def eat2(self): print("属性方法,把一个方法变成一个静态属性") p=Person("shi",23) p.talk() #访问类属性 print(Person.country) #实例属性 print(p.name) #直接访问类的私有属性会报错 #print(p.__salary) #强制访问私有属性 print(p._Person__salary) #私有属性访问2: print(p.get_salary()) #静态方法调用 p.sayHi("china") #类方法调用 p.eat() #属性方法调用 #p.eat2() 报错TypeError: 'NoneType' object is not callable,正确访问如下: #调用会出以下错误, 说NoneType is not callable, 因为eat2此时已经变成一个静态属性了, # 不是方法了, 想调用已经不需要加()号了 p.eat2
3)类属性访问,修改,删除
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- __author__ = 'shisanjun' class Flight(object): def __init__(self,name): self.flight_name=name def checking_status(self): print("checking flight %s status" %self.flight_name) return 1 @property def flight_status(self): status=self.checking_status() if status == 0 : print("flight got canceled...") elif status == 1 : print("flight is arrived...") elif status == 2: print("flight has departured already...") else: print("cannot confirm the flight status...,please check later") @flight_status.setter #修改 def flight_status(self,status): status_dic = { 0 : "canceled", 1 :"arrived", 2 : "departured" } print("�33[31;1mHas changed the flight status to �33[0m",status_dic.get(status) ) @flight_status.deleter #删除 def flight_status(self): print("status got removed...") f = Flight("CA980") f.flight_status f.flight_status = 2 #触发@flight_status.setter del f.flight_status #触发@flight_status.deleter
4)类的特殊成员方法
1.__doc__表示类的描述信息
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- __author__ = 'shisanjun' class Person(object): """ 介绍人的类 """ def sayhi(self): print("hi") p=Person() print(p.__doc__) """ 结果:介绍人的类 """
2.__module__和__class__
__module__表示当前操作对象在那个模块
__class__表示当前操作的对象的类是什么
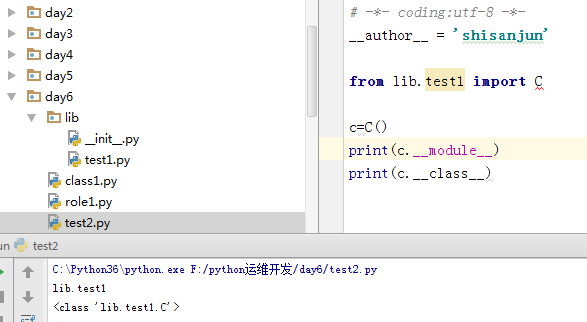
3.__init__构造方法,通过类创建对象时,自动解发执行。
4.__del__ 析构方法,当对象在内存中被释放时,自动触发执行,析构函数的调用是由解释器在进行垃圾回收时自动触发执行的
5.__call__对象后面加括号,触发执行。构造方法的执行是由创建对象触发的,即:对象 = 类名() ;而对于 __call__ 方法的执行是由对象后加括号触发的,即:对象() 或者 类()()
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- __author__ = 'shisanjun' class Person(object): """ 介绍人的类 """ def sayhi(self): print("hi") def __call__(self, *args, **kwargs): print("use __call__") p=Person() p()
6.__dict__查看类或对象中所有成员
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- __author__ = 'shisanjun' class Provice: country="china" def __init__(self,name,count): self.name=name self.count=count def func(self,*args,**kwargs): print("func") #获取类的成员,即静态字段,方法(不包括实例变量) print(Provice.__dict__) obj1=Provice("s",23) #获取实例的成员 print(obj1.__dict__) """ 结果 {'__module__': '__main__', 'country': 'china', '__init__': <function Provice.__init__ at 0x0000000002AA28C8>, 'func': <function Provice.func at 0x0000000002AA2950>, '__dict__': <attribute '__dict__' of 'Provice' objects>, '__weakref__': <attribute '__weakref__' of 'Provice' objects>, '__doc__': None} {'name': 's', 'count': 23} """
7.__str__如果类中定义了__str__访求,那么打印对象时,默认输出该方法的返回结果
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- __author__ = 'shisanjun' class Foo(object): def __str__(self): return "1111" obj=Foo() print(obj)
8.__getitem__、__setitem__、__delitem__
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- __author__ = 'shisanjun' class Foo(object): def __getitem__(self, key): print("__getitem__",key) def __setitem__(self, key, value): print("__setitem__",key,value) def __delitem__(self, key): print("__delitem",key) obj=Foo() result=obj['k1'] #触发__getitem__ obj['k2']=22 #触发__setitem__ del obj['k3'] #触发__delitem__