原因:学习ConcurrentLinkedQueue是看到akka框架的默认邮箱是使用ConcurrentLinkedQueue实现的。
1. ConcurrentLinkedQueue在java.util.concurrent包中(java 版本是1.7.0_71),类间继承关系如下:
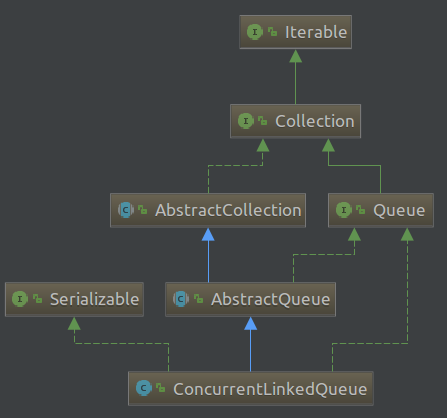
public class ConcurrentLinkedQueue<E> extends AbstractQueue<E>
implements Queue<E>, java.io.Serializable
ConcurrentLinkedQueue继承了抽象类AbstractQueue,AbstractQueue抽象类中的几个实现方法也都是利用Queue接口中的方法实现的。
Queue接口中定义的抽象方法有:
package java.util;
public interface Queue<E> extends Collection<E> {
// 向队列中插入元素e,不验证队列空间限制条件下插入一个元素。如果队列有剩余空间,直接插入;如果队列满了,就抛出IllegalStateException异常
boolean add(E e);
// 同样是向队列中插入元素e。如果队列有空间限制,同add;如果队列没有空间限制,比如ConcurrentLinkedQueue,总是可以插入进去
boolean offer(E e);
// 返回并删除队列头部的第一个元素,remove()与poll()方法的不同在于,如果队列为空,remove()方法会抛出异常,而poll()方法是返回null
E remove();
// 返回并删除队列头部的第一元素,如果队列空,返回null
E poll();
// 返回但是不删除队头元素,element()方法与peek()方法的不同在于,如果队列为空,element()方法会抛出NoSuchElementException,而peek()方法返回null
E element();
// 返回队头元素,如果队列为空,返回null
E peek();
}
队列的操作无非就是上述的插入和删除操作,从上述方法的定义来看,优先使用offer()和poll(),因为不抛异常的方法比较容易处理。
2. ConcurrentLinkedQueue是什么?
ConcurrentLinkedQueue是基于链接节点实现的无界的线程安全的先进先出的非阻塞的队列。其链接节点的结构为:
private static class Node<E> {
volatile E item;
volatile Node<E> next;
}
每一个链接节点(Node)包含节点元素(item)和指向下一个节点的引用(next)。
为了方便对ConcurrentLinkedQueue的读写操作,又定义了两个变量:头结点head;尾节点tail
// 头结点,所有后继节点都可以从head开始,使用succ()方法访问到 /** * A node from which the first live (non-deleted) node (if any) * can be reached in O(1) time. * Invariants: * - all live nodes are reachable from head via succ() * - head != null * - (tmp = head).next != tmp || tmp != head * Non-invariants: * - head.item may or may not be null. * - it is permitted for tail to lag behind head, that is, for tail * to not be reachable from head! */ private transient volatile Node<E> head; // 尾节点, /** * A node from which the last node on list (that is, the unique * node with node.next == null) can be reached in O(1) time. * Invariants: * - the last node is always reachable from tail via succ() * - tail != null * Non-invariants: * - tail.item may or may not be null. * - it is permitted for tail to lag behind head, that is, for tail * to not be reachable from head! * - tail.next may or may not be self-pointing to tail. */ private transient volatile Node<E> tail;
头尾节点的注释中都提到了succ()方法,succ()方法是什么呢?
// succ()方法是返回节点p的后继节点。如果节点p的后继节点指向自己,则返回头结点。这种情况是如何发生的?(节点p已经不在链表中了?)
final Node<E> succ(Node<E> p) {
Node<E> next = p.next;
return (p == next) ? head : next;
}
succ()方法主要用途有什么?
(1). size(), 求队列大小
// 返回队列中元素个数,可以看到元素个数是int类型, 如果元素个数超过了Integer.MAX_VALUE的话,也只能返回Integer.MAX_VALUE
// 另外,这个方法返回的值是不精确的。
public int size() {
int count = 0;
// 从第一个节点开始遍历,如果节点不为null,统计节点个数,然后使用succ()方法获取下一个节点
for (Node<E> p = first(); p != null; p = succ(p))
if (p.item != null)
// Collection.size() spec says to max out
if (++count == Integer.MAX_VALUE)
break;
return count;
}
(2). contains()方法中succ()的用法与求队列大小类似
public boolean contains(Object o) {
if (o == null) return false;
for (Node<E> p = first(); p != null; p = succ(p)) {
E item = p.item;
if (item != null && o.equals(item))
return true;
}
return false;
}
3. ConcurrentLinkedQueue的构造函数为:
public ConcurrentLinkedQueue() {
head = tail = new Node<E>(null);
}
从构造函数看,ConcurrentLinkedQueue的头结点是包含null元素的一个节点,并且初始条件下head节点指向tail节点。
接下来看下head和tail是如何在offer()和poll()方法中怎么使用的。
// 插入元素到队尾
public boolean offer(E e) {
// 检查元素e是否为null,如果为null,抛出NullPointerException
checkNotNull(e);
// 创建新节点newNode
final java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentLinkedQueue.Node<E>
newNode = new java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentLinkedQueue.Node<E>(e);
// 首先赋值tail给t (t = tail),赋值t给p (p = t)
// 然后执行死循环for(;;)
for (java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentLinkedQueue.Node<E> t = tail, p = t;;) {
// 将p的next赋值给q, p.next -> q
java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentLinkedQueue.Node<E> q = p.next;
// 如果q为null,表示p是尾节点
if (q == null) {
// p是尾节点,将新节点newNode赋值给p的next,p.next -> e(newNode)
// 这个赋值过程是使用CAS来实现的,CAS比较并交换,意思就是如果newNode != null,则交换他们
if (p.casNext(null, newNode)) {
// 如果p != t,即p != t = tail,表示t(= tail)不是尾节点
if (p != t)
// 将t置为尾节点,该操作允许失败,因此t(= tail)并不总是尾节点
// 因此需要执行for(;;),先找到尾节点
casTail(t, newNode); // Failure is OK.
return true;
}
// Lost CAS race to another thread; re-read next
}
else if (p == q)
// 如果p == q, 说明尾节点tail已经不在链表中了,
// 这种情况下,跳转到head,因为从head开始所有的节点都可达
p = (t != (t = tail)) ? t : head;
else
// 如果p == q且q == null,p指向q,即p跳转到下一个元素
p = (p != t && t != (t = tail)) ? t : q;
}
}
public E poll() {
// 跳出for(;;)循环的标志位
restartFromHead:
for (;;) {
// 首先赋值head给h (h = head),赋值h给p (p = h),并定义变量q
// 然后执行死循环for(;;)
for (java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentLinkedQueue.Node<E> h = head, p = h, q;;) {
// 获取p的元素值,即头节点的元素值
E item = p.item;
// 如果元素值不为null,并将p的元素置null
// casItem(item, null)意思是如果item != null,则交换两者
// 交换之后,item就从队列中被移除了
if (item != null && p.casItem(item, null)) {
if (p != h) // 如果p不是指向h (head),更新head的值
updateHead(h, ((q = p.next) != null) ? q : p);
return item;
}
else if ((q = p.next) == null) { // 说明元素为空
updateHead(h, p);
return null;
}
else if (p == q)
continue restartFromHead;
else
p = q;
}
}
}
4. 生产者消费者使用ConcurrentLinkedQueue
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentLinkedQueue;
public class ProducerAndConsumer {
private static ConcurrentLinkedQueue queue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue();
static class Producer extends Thread {
String name;
public Producer(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
queue.offer(i);
System.out.println(name + " : " + i);
try {
Thread.sleep(1 * 1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
static class Consumer extends Thread {
String name;
public Consumer(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void run() {
for (;;) {
Object item = queue.poll();
System.out.println(name + " : " + item);
try {
Thread.sleep(1 * 1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Producer("p1").start();
new Producer("p2").start();
new Consumer("c1").start();
// new Consumer("c2").start();
}
}