一、 Annotation 概述;
Annotatio从jdk1.5开始产生;他是代码里面的特殊标记,可以在编译、类加载、运行时被读取,并执行相应的处理。
可以修饰包、类、构造器、 成员变量、参数、局部变量的声明;
框架 = 注解+反射+设计模式
二、注解示例
1. 文档注解:
- @auth 标明该模块的作者,多个作者用,分割
- @version 表明该类模块的版本
- @see 参考转向,也就是相关主题;
- @since 从哪个版本开始增加的;
- @param 对方法中某些参数的说明,如果没有参数就不能写
- @return 对返回值的说明,如果方法的返回值类型就void就不能写
- @exception 对方法可能抛出的一场进行说明,如果方法没有又throws 显示抛出异常,就不能写其中
例如:

1 /** 2 * 3 * @author joy 4 * @Description: 5 * @date: 2021年3月25日 上午10:06:39 6 */ 7 public class Day22Annotation10 { 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 @SuppressWarnings("unused") 10 int a = 0; 11 } 12 }
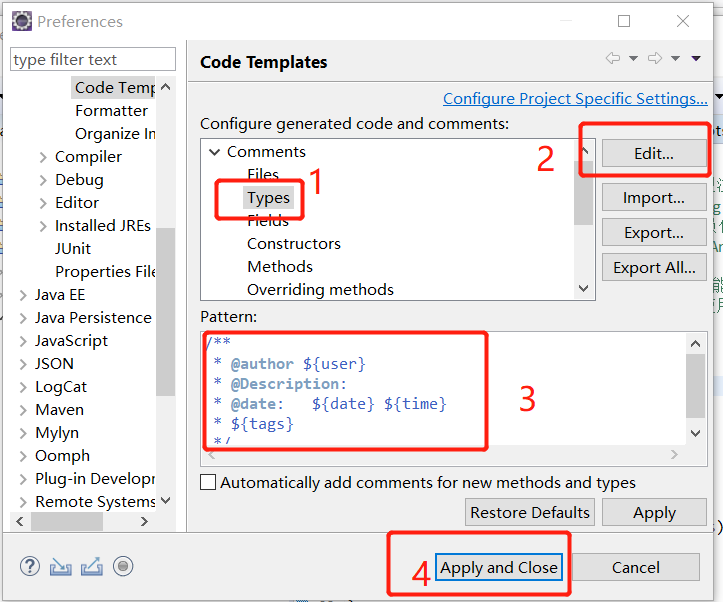
补充:eclipse配置:
1 windows-->preference 2 Java-->Code Style-->Code Templates 3 Comments-->Type
在右侧选择Comments,将其中的Type项,然后选右边的"Edit",进入编辑模式:
/**
* @author ${user}
* @Description:
* @date: ${date} ${time}
* ${tags}
*/
最后 apply and close;
2.三个基本注解:
- @override 限定重写父类方法 如下Student 中的 work 方法(如下代码),如果student中写错了work(如下图),则编译报错;若没有加override注解,那么如果work方法不会在编译的时候被校验; 若work在写的时候写成了wok()则也不会报错;如果写了override 则会报错,显示没有重写方法;
- @Deprecated 用于表示所修饰的元素(类、方法等)已过时;通常时因为所修饰的结构危险或存在更好的选择;
- @SuppressWarnIngs:抑制编译警告
1 public class Day22Annotation10 { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 Student student = new Student("aa",1); 4 student.work();//学生走了 5 } 6 } 7 class Person{ 8 private String name; 9 private int age; 10 11 public String getName() { 12 return name; 13 } 14 15 public void setName(String name) { 16 this.name = name; 17 } 18 19 public int getAge() { 20 return age; 21 } 22 23 public void setAge(int age) { 24 this.age = age; 25 } 26 public Person(String name, int age) { 27 super(); 28 this.name = name; 29 this.age = age; 30 } 31 32 public void work() { 33 System.out.println("人走了"); 34 } 35 public void eat() { 36 System.out.println("人吃饭"); 37 } 38 } 39 class Student extends Person{ 40 41 public Student(String name, int age) { 42 super(name, age); 43 // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub 44 } 45 46 @Override 47 public void work() { 48 System.out.println("学生走了"); 49 } 50 }

三、自定义注解:参照SupressWarnlngs;
1.注解声明:@interface
2.内部成员定义,通常使用 value表示
3.可使用成员的默认值,使用default定义
4.如果自定义注解没有成员,表明是一个标识作用;
如果注解有成员,在使用注解时,需要指定成员的值,若有默认值,则不需要指定;
自定义注解必须配上注解的信息处理流程(反射)才有意义;
通常指明Retention和Target
1 public @interface MyAnnotation { 2 3 String value() default "hello"; 4 }
1 @MyAnnotation//@MyAnnotation(value="hi") 2 class Student extends Person{ 3 4 public Student(String name, int age) { 5 super(name, age); 6 // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub 7 } 8 9 @Override 10 public void work() { 11 System.out.println("学生走了"); 12 } 13 }
四、JDK中的4种元注解:
1.Retention:
只能定义Annotation的生命周期,
RetentionPolicy3种状态:SOURCE(编译时抛弃注解) CLASS(编译时保留注解) RUNTIME(执行时保留注解,只有该状态时,反射才能调)
eg.@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIOME)
2.Target
只能定义Annotation的使用类型;(如下代码)
类型:FIELD METHOD PARAMETER CONSTRUCTOR LOCAL_VARIABLE..
例如@Target({FIELD,CONSTRUCTOR});说明该注解只能用在属性和构造器上,比如该注释写在方法前那就不行,会报错;如下代码;
元注释的作用:修改时其他 annotation的annotation
元数据:对现有数据的修饰的数据;eg.String name = "joy";这里,String和name 就是元数据;
1 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) 2 @Target({TYPE, FIELD, PARAMETER,CONSTRUCTOR, ElementType.TYPE_PARAMETER,ElementType.TYPE_USE}) 3 public @interface MyAnnotation { 4 5 String value() default "hello"; 6 }

3.Documented 被他修饰的Annotation类将被javadouc 工具提取成文档
4.Inherited 被他修饰的Annotation将具有继承性
五、通过反射获取注解信息;
六、jdk8种注解的新特性:可重复注解、类型注解
1.可重复注解;可以加多个不同类型的注解 eg.Repeatable(MyAnotations.class);
①在MyAnnotation上声明@Repeatable,成员值为MyAnotations.class
②MyAnotation的Rarget 和 Retention和MyAnotations相同;
1 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) 2 @Target({ElementType.TYPE,ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR, ElementType.TYPE_PARAMETER,ElementType.TYPE_USE}) 3 public @interface MyAnnotations { 4 5 MyAnnotation[] value(); 6 }
1 @Repeatable(MyAnnotations.class) 2 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) 3 @Target({ElementType.TYPE,ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR, ElementType.TYPE_PARAMETER,ElementType.TYPE_USE}) 4 public @interface MyAnnotation { 5 6 String value() default "hello"; 7 }
可重复注解实例:
@MyAnnotation(value="hi") @MyAnnotation class Student extends Person{ public Student(String name, int age) { super(name, age); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } @Override public void work() { System.out.println("学生走了"); } }
2.类型注解(可以修饰泛型)
ElementType.TYPE_PARRAMETER 表示该注解能写在类型变量的声明语句种(如泛型声明)
ElementType.TYPE_USE 表示该注解能写在使用类型的任何语句中;
类型注解(可以修饰泛型)实例:
class Generic<@MyAnnotation T>{ public void show() throws RuntimeException{ int num = (@MyAnnotation int )10l; } }
class Generic<@MyAnnotation T>这里的@MyAnnotation,是因为设置了@Target({ElementType.TYPE,ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR, ElementType.TYPE_PARAMETER})
@Target设置了ElementType.TYPE_PARAMETER;所以@MyAnnotation这里不报错;
int num = (@MyAnnotation int )10l;@Target设置了ElementType.TYPE_USE;所以这里(@MyAnnotation int )10l不报错;
否则 报错;
