synchronized 声明方法的弊端
比如A线程调用同步方法执行一个很长时间的任务,那么B线程则必须等待比较长的时间。
示例:
public class SyncMethod { public static void main(String[] args) { Task task = new Task(); MyThread1 thread1 = new MyThread1(task); MyThread2 thread2 = new MyThread2(task); thread1.start(); thread2.start(); try { Thread.sleep(10000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } long beginTime = CommonUtils.beginTime1; if (CommonUtils.beginTime2 < CommonUtils.beginTime1) { beginTime = CommonUtils.beginTime2; } long endTime = CommonUtils.endTime1; if (CommonUtils.endTime2 > CommonUtils.endTime1) { endTime = CommonUtils.endTime2; } System.out.println("耗时:" + ((endTime - beginTime) / 1000)); } static class Task { private String getData1; private String getData2; synchronized public void doLongTimeTask() { try { System.out.println("begin task"); Thread.sleep(3000); getData1 = "长时间处理任务后从远程返回的值 1 threadName = " + Thread.currentThread().getName(); getData2 = "长时间处理任务后从远程返回的值 2 threadName = " + Thread.currentThread().getName(); System.out.println(getData1); System.out.println(getData2); System.out.println("end task"); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } static class CommonUtils { public static long beginTime1; public static long endTime1; public static long beginTime2; public static long endTime2; } static class MyThread1 extends Thread { private Task task; public MyThread1(Task task) { super(); this.task = task; } @Override public void run() { super.run(); CommonUtils.beginTime1 = System.currentTimeMillis(); task.doLongTimeTask(); CommonUtils.endTime1 = System.currentTimeMillis(); } } static class MyThread2 extends Thread { private Task task; public MyThread2(Task task) { this.task = task; } @Override public void run() { super.run(); CommonUtils.beginTime2 = System.currentTimeMillis(); task.doLongTimeTask(); CommonUtils.endTime2 = System.currentTimeMillis(); } } }
运行结果如图:

使用 synchronized 块改造成一半异步,一半同步
示例:
public class SyncMethod { public static void main(String[] args) { Task task = new Task(); MyThread1 thread1 = new MyThread1(task); MyThread2 thread2 = new MyThread2(task); thread1.start(); thread2.start(); try { Thread.sleep(10000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } long beginTime = CommonUtils.beginTime1; if (CommonUtils.beginTime2 < CommonUtils.beginTime1) { beginTime = CommonUtils.beginTime2; } long endTime = CommonUtils.endTime1; if (CommonUtils.endTime2 > CommonUtils.endTime1) { endTime = CommonUtils.endTime2; } System.out.println("耗时:" + ((endTime - beginTime) / 1000)); } static class Task { private String getData1; private String getData2; public void doLongTimeTask() { try { System.out.println("begin task"); Thread.sleep(3000); synchronized (this) { getData1 = "长时间处理任务后从远程返回的值 1 threadName = " + Thread.currentThread().getName(); getData2 = "长时间处理任务后从远程返回的值 2 threadName = " + Thread.currentThread().getName(); System.out.println(getData1); System.out.println(getData2); } System.out.println("end task"); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } static class CommonUtils { public static long beginTime1; public static long endTime1; public static long beginTime2; public static long endTime2; } static class MyThread1 extends Thread { private Task task; public MyThread1(Task task) { super(); this.task = task; } @Override public void run() { super.run(); CommonUtils.beginTime1 = System.currentTimeMillis(); task.doLongTimeTask(); CommonUtils.endTime1 = System.currentTimeMillis(); } } static class MyThread2 extends Thread { private Task task; public MyThread2(Task task) { this.task = task; } @Override public void run() { super.run(); CommonUtils.beginTime2 = System.currentTimeMillis(); task.doLongTimeTask(); CommonUtils.endTime2 = System.currentTimeMillis(); } } }
运行结果如图:

synchronized 代码块间的同步性
在使用同步 synchronized(this) 代码块时需要注意的是,当一个线程访问 object 的一个 synchronized(this) 同步代码块时,其他线程对同一个 object 中的所有其他 synchronized(this) 同步代码块的访问将被阻塞(言外之意是,非同步代码块,还是能被异步访问),
所以 synchronized 锁定的是当前对象
示例:
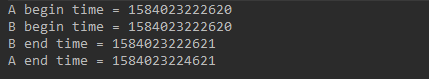
public class SyncBlock { public static void main(String[] args) { ObjectService service = new ObjectService(); ThreadA threadA = new ThreadA(service); ThreadB threadB = new ThreadB(service); threadA.setName("a"); threadB.setName("b"); threadA.start(); threadB.start(); } static class ObjectService { public void serviceMethodA() { try { synchronized (this) { System.out.println("A begin time = " + System.currentTimeMillis()); Thread.sleep(2000); System.out.println("A end time = " + System.currentTimeMillis()); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public void serviceMethodB() { System.out.println("B begin time = " + System.currentTimeMillis()); System.out.println("B end time = " + System.currentTimeMillis()); } } static class ThreadA extends Thread { private ObjectService service; public ThreadA(ObjectService service) { this.service = service; } @Override public void run() { super.run(); service.serviceMethodA(); } } static class ThreadB extends Thread { private ObjectService service; public ThreadB(ObjectService service) { this.service = service; } @Override public void run() { super.run(); service.serviceMethodB(); } } }
运行结果如图: