对于一棵普通的二叉查找树而言,在进行多次的插入或删除后,容易让树失去平衡,导致树的深度不是O(logN),而接近O(N),这样将大大减少对树的查找效率。一种解决办法就是要有一个称为平衡的附加的结构条件:任何节点的深度均不得过深。有一种最古老的平衡查找树,即AVL树。
AVL树是带有平衡条件的二叉查找树。平衡条件是每个节点的左子树和右子树的高度最多差1的二叉查找树(空树的高度定义为-1)。相比于普通的二叉树,AVL树的节点需要增加一个变量保存节点高度。AVL树的节点声明如下:
typedef struct TreeNode *AvlTree; typedef struct TreeNode *Position; struct TreeNode { int Data; AvlTree Left; AvlTree Right; int Height; //保存节点高度 };
只有一个节点的树显然是AVL树,之后我们向其插入节点。然而在插入过程中可能破坏AVL树的特性,因此我们需要对树进行简单的修正,即AVL树的旋转。
设a节点在插入下一个节点后会失去平衡,这种插入可能出现四种情况:
1. 对a的左儿子的左子树进行一次插入。(左-左)
2. 对a的左儿子的右子树进行一次插入。(左-右)
3. 对a的右儿子的左子树进行一次插入。(右-左)
4. 对a的右儿子的右子树进行一次插入。(右-右)
情形1和4,情形2和3分别是关于A节点的镜像对称,故在理论上是两种情况,而编程具体实现还是需要考虑四种。
单旋转--情形1和4:
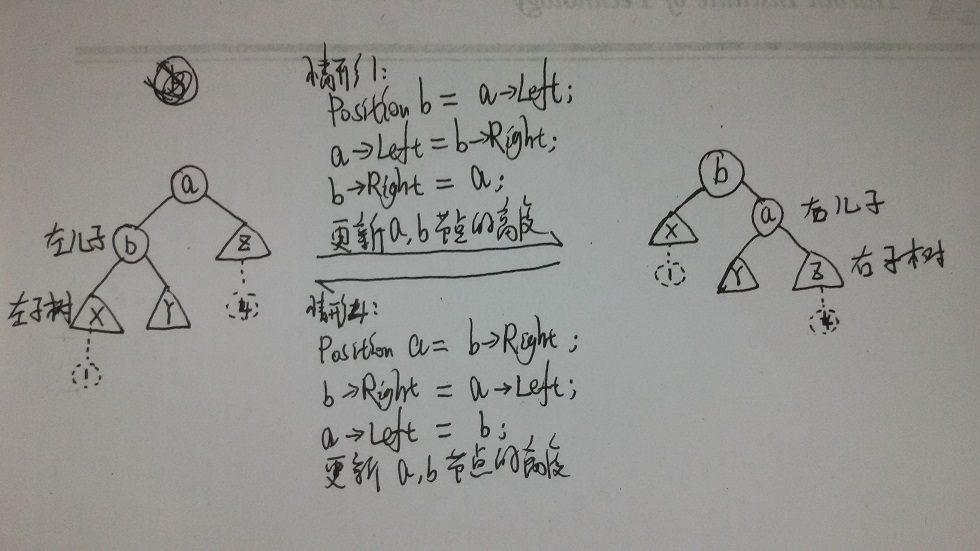
双旋转--情形2和3:
情形2和3就是向上图中的子树Y插入一个节点,由上图可知,无论是左单旋还是右单旋都无法改变子树Y的高度。解决办法是再将子树Y分解成根节点和相应的左子树和右子树,然后对相应的节点做相应的旋转,如下图:
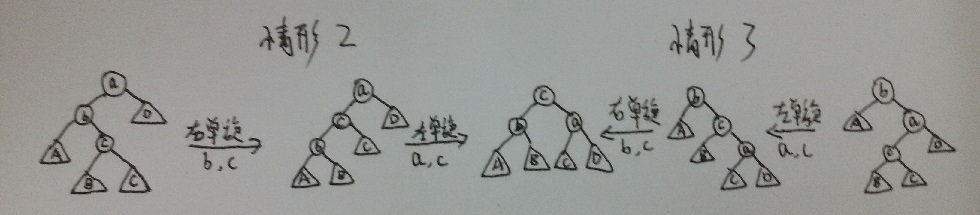
下面一个题即是考察AVL树的旋转:题目来源:http://www.patest.cn/contests/mooc-ds/04-%E6%A0%914
An AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree. In an AVL tree, the heights of the two child subtrees of any node differ by at most one; if at any time they differ by more than one, rebalancing is done to restore this property. Figures 1-4 illustrate the rotation rules.




Now given a sequence of insertions, you are supposed to tell the root of the resulting AVL tree.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (<=20) which is the total number of keys to be inserted. Then N distinct integer keys are given in the next line. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print ythe root of the resulting AVL tree in one line.
Sample Input 1:
5 88 70 61 96 120
Sample Output 1:
70
Sample Input 2:
7 88 70 61 96 120 90 65
Sample Output 2:
88
题目大意是先输入一个整数N,然后依次输入N个节点的值,以此建立AVL树,最后输出AVL树的根节点的值。
代码如下:
#include <cstdio> #include <cstdlib> typedef struct TreeNode *AvlTree; typedef struct TreeNode *Position; struct TreeNode { int Data; AvlTree Left; AvlTree Right; int Height; }; AvlTree Insert(int x, AvlTree T); //插入新节点,必要时调整 Position SingleRotateWithLeft(Position a); //左单旋 Position SingleRotateWithRight(Position b); //右单旋 Position DoubleRotateWithLeft(Position a); //左右旋 Position DoubleRotateWithRight(Position b); //右左旋 int Max(int x1, int x2); //返回两个int中较大的 int Height(Position P); //返回一个节点的高度 int main() { int n, x; AvlTree T = NULL; scanf("%d", &n); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { scanf("%d", &x); T = Insert(x, T); } printf("%d ", T->Data); //打印根节点的值 return 0; } AvlTree Insert(int x, AvlTree T) { if (T == NULL) { T = (AvlTree)malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode)); T->Data = x; T->Left = T->Right = NULL; T->Height = 0; } else if (x < T->Data) //向左子树插入 { T->Left = Insert(x, T->Left); if (Height(T->Left) - Height(T->Right) == 2) //需调整 { if (x < T->Left->Data) T = SingleRotateWithLeft(T); else T = DoubleRotateWithLeft(T); } } else if (x > T->Data) //向右子树插入 { T->Right = Insert(x, T->Right); if (Height(T->Right) - Height(T->Left) == 2) //需调整 { if (x > T->Right->Data) T = SingleRotateWithRight(T); else T = DoubleRotateWithRight(T); } } /*else值为x的节点已经存在树中,无需插入*/ /*更新节点高度*/ T->Height = Max(Height(T->Left), Height(T->Right)) + 1; return T; } Position SingleRotateWithLeft(Position a) { Position b = a->Left; a->Left = b->Right; b->Right = a; //更新a, b节点高度 a->Height = Max(Height(a->Left), Height(a->Right)) + 1; b->Height = Max(Height(b->Left), Height(b->Right)) + 1; return b; /*新的根节点*/ } Position SingleRotateWithRight(Position b) { Position a = b->Right; b->Right = a->Left; a->Left = b; //更新a,b节点高度 a->Height = Max(Height(a->Left), Height(a->Right)) + 1; b->Height = Max(Height(b->Left), Height(b->Right)) + 1; return a; /*新的根节点*/ } Position DoubleRotateWithLeft(Position a) { a->Left = SingleRotateWithRight(a->Left); return SingleRotateWithLeft(a); } Position DoubleRotateWithRight(Position b) { b->Right = SingleRotateWithLeft(b->Right); return SingleRotateWithRight(b); } int Max(int x1, int x2) { return (x1 > x2) ? x1 : x2; } int Height(Position P) { if (P == NULL) //空节点高度为-1 return -1; return P->Height; }
需要注意的细节是我们需要快速得到一个节点(包括空节点)的高度,所以我们需要些一个函数来处理空节点(空指针)的情况,而不是简单的Position->Height。