一、iterator属性
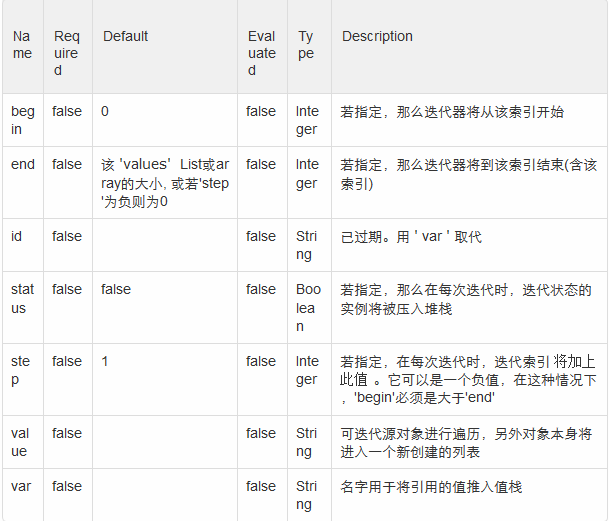
iterator标签主要是用于迭代输出集合元素,如list set map 数组等,在使用标签的时候有三个属性值得我们关注
- value属性:可选的属性,value属性是指一个被迭代的集合,使用ognl表达式指定,如果为空的话默认就是ValueStack栈顶的集合.
2.id属性:可选属性, 是指集合元素的id
3.status属性:可选属性,该属性在迭代时会产生一个IteratorStatus对象,该对象可以判断当前元素的位置,包含了以下属性方法:
int getCount(); 迭代元素个数
int getIndex(); 迭代元素当前索引
boolean getFirst(); 是否为第一个
boolean getEven(); 是否为偶
boolean getLast(); 是否最后一个
bolean getOdd(); 是否为奇
由于iteratorstatus对象并不是ognl的根对象因此访问需要加上 #访问如下例子:
<s:iterator value=”{’dd’,'bb’,'cc’}” status=”st”>
<s:if test=”#st.odd”>
<s:property value=”#st.index”/>
</s:if>
</s:iterator>此外:iterator也可以迭代map对象,map对象中有几对key-value 就迭代几次,分别使用
<s:property value=”key”/>
<s:property value=”value”/>输出即可.
案例如下(Struts2标签):实现奇偶行不同颜色显示
JSP中结果集显示如下:
<s:iterator value="resultList" status="status">
<tr class="<s:if test="#status.even">row-even</s:if><s:else>row-odd</s:else>">
<td>
<s:property value=""/>
</td>
</tr>
</s:iterator>样式表可以参考:
.row-even{background-color:#def7c2;}
.row-odd{background-color:#c8e7a6;}除了使用#status.even判断是否偶数行外,还有其他几个属性可以使用:
1)status.odd 是否奇数行
2)status.count 当前行数
3)status.index 当前行的序号,从0开始
4)[#status.count=#status.index+1]
5)status.first 是否第一行
6)status.last 是否最后一行
7)status.modules(int) 当前行数取模
二、iterator的使用解析
1:jsp页面定义元素写法 数组或list
<s:iterator value="{'1','2','3','4','5'}" id='number'>
<s:property value='#number'/>A
</s:iterator>打印结果为: 1A2A3A4A5A
2:索引的用法
如果指定了status,每次的迭代数据都有IteratorStatus的实例,它有以下几个方法
int getCount()返回当前迭代了几个元素
int getIndex()返回当前元素索引
boolean isEven()当然的索引是否偶数
boolean isFirst()当前是否第一个元素
boolean isLast()
boolean isOdd()当前元素索引是否奇数
现在的索引是奇数为:
当前元素值:
3:遍历map
value可以直接定义为:
value=”#{“1”:”a”,”2”:”b”}”
每个元素以都好隔开。元素之间的key和value 冒号隔开
value也可以是数据栈里面的java.util.Map对象
遍历写法如下:
<s:iterator value="map" id="id" status="st">
key : <s:property value='key'/>
value:<s:property vlaue='value'/>
</s:iterator>当然key 和value 都可以使java 的 Object
3:遍历数据栈.简单的List类,
List<Attr>
class Attr{String attrName;String getAttrName(){return "123";}}
<s:iterator value="label" id="id">
<s:property value="#id.attrName" />
</s:iterator>当然value 还可以写成 value=”%{label}” label可以有.操作
label的属性List 可以写成value=”%{label.list}” 相当于:getLabel().getList();
4:遍历2个list;
List attrN {color,size,style}
List attrV {red,20,gay}
这2个list的元素是一一对应的,一个attrN对应一个attrV
<s:iterator value="%{attrN }" id="id" status="status">
index is : <s:property value='status.index'/>
attrName is : <s:property value='id'/> or <s:property value='%{id}'/>
attrName is : <s:property value='%{attrV[#status.index]}'/>
</s:iterator> 二、各种遍历用法总结
1.struts2遍历map小结
1)MapAction.java
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport
import com.model.Student
public class MapAction extends ActionSupport
{
private Map<String,String> map;
private Map<String,Student> studentMap;
private Map<String,String[]> arrayMap;
private Map<String,List<Student>> listMap;
public String testMap()
{
map=new HashMap<String,String>();
map.put("1", "one");
map.put("2", "two");
studentMap=new HashMap<String,Student>();
studentMap.put("student1",new Student(new Long(1),"20034140201","张三1","男",25));
studentMap.put("student2",new Student(new Long(2),"20034140202","张三2","女",26));
studentMap.put("student3",new Student(new Long(3),"20034140202","张三3","男",27));
arrayMap=new HashMap<String,String[]>();
arrayMap.put("arr1", new String[]{"1","2003401","leejie","male","20"});
arrayMap.put("arr2", new String[]{"2","2003402","huanglie","male","25"});
arrayMap.put("arr3", new String[]{"3","2003403","lixiaoning","male","21"});
listMap=new HashMap<String,List<Student>>();
List<Student> list1=new ArrayList<Student>();
list1.add(new Student(new Long(1),"20034140201","张三1","男",25));
list1.add(new Student(new Long(2),"20034140202","张三2","男",25));
list1.add(new Student(new Long(3),"20034140203","张三3","男",25));
listMap.put("class1", list1);
List<Student> list2=new ArrayList<Student>();
list2.add(new Student(new Long(1),"20034140301","李四1","男",20));
list2.add(new Student(new Long(2),"20034140302","李四2","男",21));
list2.add(new Student(new Long(3),"20034140303","李四3","男",22));
list2.add(new Student(new Long(4),"20034140304","李四4","男",23));
listMap.put("class2", list2);
return SUCCESS;
}
public Map<String, String> getMap() {
return map;
}
public void setMap(Map<String, String> map) {
this.map = map;
}
public Map<String, Student> getStudentMap() {
return studentMap;
}
public void setStudentMap(Map<String, Student> studentMap) {
this.studentMap = studentMap;
}
public Map<String, String[]> getArrayMap() {
return arrayMap;
}
public void setArrayMap(Map<String, String[]> arrayMap) {
this.arrayMap = arrayMap;
}
public Map<String, List<Student>> getListMap() {
return listMap;
}
public void setListMap(Map<String, List<Student>> listMap) {
this.listMap = listMap;
}
}
2.testMap.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" %>
<%@ taglib prefix="s" uri="/struts-tags" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>struts2中的map遍历总结</title>
</head>
<body>
<b>1.map中的value为String字符串</b><br>
<s:iterator value="map" id="column">
<s:property value="#column"/><br>
key: <s:property value="key"/><br>
value:<s:property value="value"/><br>
******************************************<br>
</s:iterator>
<b>2.map中的value为Student对象</b>
<table border="1" width="50%" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="0">
<tr>
<td>key=value</td>
<td>ID</td>
<td>num</td>
<td>name</td>
<td>sex</td>
<td>age</td>
</tr>
<s:iterator value="studentMap" id="column">
<tr>
<td><s:property value="#column"/></td>
<td><s:property value="value.id"/></td>
<td><s:property value="value.num"/></td>
<td><s:property value="value.name"/></td>
<td><s:property value="value.sex"/></td>
<td><s:property value="value.age"/></td>
</tr>
</s:iterator>
</table>
<p>
<b>3.map中的value为String数组</b>
<table border="1" width="50%" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="0">
<tr>
<td>key=value</td>
<td>ID</td>
<td>num</td>
<td>name</td>
<td>sex</td>
<td>age</td>
</tr>
<s:iterator value="arrayMap" id="column">
<tr>
<td><s:property value="#column"/></td>
<td><s:property value="value[0]"/></td>
<td><s:property value="value[1]"/></td>
<td><s:property value="value[2]"/></td>
<td><s:property value="value[3]"/></td>
<td><s:property value="value[4]"/></td>
</tr>
</s:iterator>
</table>
<p>
<b>4.map中的value为list集合</b>
<table border="1" width="50%" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="0">
<tr>
<td>class</td>
<td>ID</td>
<td>num</td>
<td>name</td>
<td>sex</td>
<td>age</td>
</tr>
<1.<s:iterator value="listHashMap" id="listid">
<s:iterator value="#listid.value" id="listidsub">
<tr>
<td><s:property value="key"/></td>
<td><s:property value="id"/></td>
<td><s:property value="num"/></td>
<td><s:property value="name"/></td>
<td><s:property value="sex"/></td>
<td><s:property value="age"/></td>
</tr>
</s:iterator>
</s:iterator>
</table>
2、普通属性
public String execute(){
username = "zhangsan";
password = "123";
}
<s:property value="username"/><br>
<s:property value="password"/><br>3、自定义对象
public String execute(){
userInfo = new UserInfo();
userInfo.setUsername("hhh");
userInfo.setPassword("111");
}
<s:property value="userInfo.username"/><br>
<s:property value="userInfo.password"/><br>4、List(普通属性)
public String execute(){
list = new ArrayList<String>();
list.add("aaa");
list.add("bbb");
list.add("ccc");
}
<s:iterator value="list" var="var">
<s:property value="var"/><br>
</s:iterator>
或者:
<s:iterator value="list">
<s:property/><br>
</s:iterator>
5、List(自定义对象属性)
public String execute(){
list = new ArrayList<UserInfo>();
UserInfo userInfo = new UserInfo();
userInfo.setUsername("u1");
userInfo.setPassword("p1");
userInfo.setRoleInfo(new RoleInfo("r1"));
list.add(userInfo);
userInfo = new UserInfo();
userInfo.setUsername("u2");
userInfo.setPassword("p2");
userInfo.setRoleInfo(new RoleInfo("r2"));
list.add(userInfo);
}
<s:iterator value="list" var="var">
<s:property value="#var.username"/>
<s:property value="#var.password"/>
<s:property value="#var.roleInfo.rolename"/><br>
</s:iterator>
或者:
<s:iterator value="list">
<s:property value="username"/>
<s:property value="password"/>
<s:property value="roleInfo.rolename"/><br>
</s:iterator>6、数组(普通属性)
public String execute(){
strs = new String[2];
strs[0] = "as";
strs[1] = "asd";
}
<s:iterator value="strs">
<s:property/><br>
</s:iterator>或者:
<s:iterator value="strs" var="var">
<s:property value="var"/><br>
</s:iterator>
7、数组(自定义对象属性)
public String execute(){
strs = new UserInfo[2];
UserInfo userInfo = new UserInfo();
userInfo.setUsername("u11");
userInfo.setPassword("11");
strs[0] = userInfo;
userInfo = new UserInfo();
userInfo.setUsername("u22");
userInfo.setPassword("22");
strs[1] = userInfo;
}
<s:iterator value="strs">
<s:property value="username"/>
<s:property value="password"/><br>
</s:iterator>
或者:
<s:iterator value="strs" var="var">
<s:property value="#var.username"/>
<s:property value="#var.password"/><br>
</s:iterator>8、数组(自定义对象属性)
**public String execute(){
strs = new UserInfo[2];
UserInfo userInfo = new UserInfo();
userInfo.setUsername(“u11”);
userInfo.setPassword(“11”);
userInfo.setRoleInfo(new RoleInfo(“r11”));
strs[0] = userInfo;
userInfo = new UserInfo();
userInfo.setUsername(“u22”);
userInfo.setPassword(“22”);
userInfo.setRoleInfo(new RoleInfo(“r22”));
strs[1] = userInfo;
}
或者:
**
9、Map(普通属性)
public String execute(){
map = new HashMap<String,String>();
map.put("k1", "v1");
map.put("k2", "v2");
}
<s:iterator value="map" var="var">
<s:property value="#var.key"/>
<s:property value="#var.value"/><br>
</s:iterator>
或者:
<s:iterator value="map">
<s:property value="key"/>
<s:property value="value"/><br>
</s:iterator>
8、Map(自定义对象属性)
public String execute(){
map = new HashMap<String,UserInfo>();
UserInfo userInfo = new UserInfo();
userInfo.setUsername("u1");
userInfo.setPassword("p1");
userInfo.setRoleInfo(new RoleInfo("r1"));
map.put("k1", userInfo);
userInfo = new UserInfo();
userInfo.setUsername("u2");
userInfo.setPassword("p2");
userInfo.setRoleInfo(new RoleInfo("r2"));
map.put("k2", userInfo);
}
<s:iterator value="map" var="var">
<s:property value="#var.key"/>
<s:property value="#var.value.username"/>
<s:property value="#var.value.password"/>
<s:property value="#var.value.roleInfo.rolename"/><br>
</s:iterator>
或者
<s:iterator value="map">
<s:property value="key"/>
<s:property value="value.username"/>
<s:property value="value.password"/>
<s:property value="value.roleInfo.rolename"/><br>
</s:iterator>
8、Map嵌套Map(自定义对象属性)
public String execute(){
map = new TreeMap<String,Map<String,UserInfo>>();
Map<String,UserInfo> innerMap = new TreeMap<String,UserInfo>();
UserInfo userInfo = new UserInfo();
userInfo.setUsername("u1");
userInfo.setPassword("p1");
userInfo.setRoleInfo(new RoleInfo("r1"));
userInfo = new UserInfo();
userInfo.setUsername("u11");
userInfo.setPassword("p11");
userInfo.setRoleInfo(new RoleInfo("r11"));
innerMap.put("k1", userInfo);
innerMap.put("k11", userInfo);
map.put("key1", innerMap);
//////////////////////////
innerMap = new TreeMap<String,UserInfo>();
userInfo = new UserInfo();
userInfo.setUsername("u2");
userInfo.setPassword("p2");
userInfo.setRoleInfo(new RoleInfo("r2"));
userInfo = new UserInfo();
userInfo.setUsername("u22");
userInfo.setPassword("p22");
userInfo.setRoleInfo(new RoleInfo("r22"));
innerMap.put("k2", userInfo);
innerMap.put("k22", userInfo);
map.put("key2", innerMap);
}
<s:iterator value="map" var="var">
<s:iterator value="value">
<s:property value="#var.key"/>
<s:property value="key"/>
<s:property value="value.username"/>
<s:property value="value.password"/>
<s:property value="value.roleInfo.rolename"/><br>
</s:iterator>
</s:iterator>