多线程命名管道通信的设计:
命名管道是进程间通信的一种方式,管道分为2种:匿名管道(Anonymous Pipe)和命名管道(Named Pipe)。
这里主要介绍多线程命名管道。
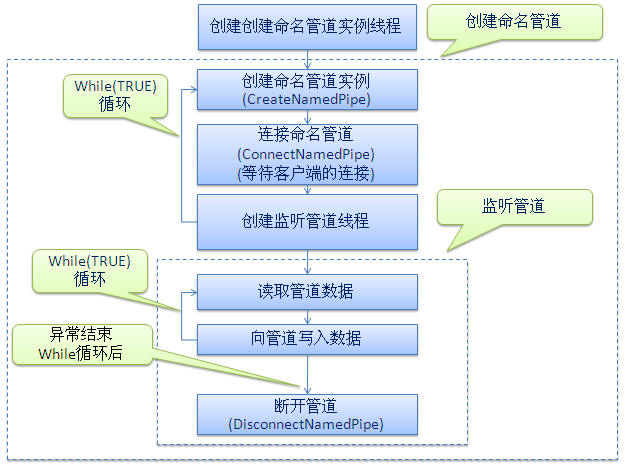
服务端设计如下图:
客户端设计如下图:

服务端采用阻塞模式等待客户端的连接,客户端采用多个线程对管道进行数据读写。
因客户端采用多个线程对管道进行读写,故一个线程读取的数据可能并不是此线程写入数据后,服务端读取此线程刚写入的数据后再写入的数据。也就是客户端多个线程写入与读取的数据可能会串,此理论已经过测试,为解决此问题,可以在客户端写入数据时加标识,服务端读取数据后,再写入的数据带上此标识,客户端读取时可根据此标识来判断是否是写入数据后服务端返回的消息。
以上设计可支持多个客户端多个线程同时对管道进行读写。
此文并没有对命名管道概念进行过多的解释,需要对概念进行了解的,可查看帮助文档。
此文只进行设计,下篇将进行多线程命名管道通信的实现,敬请期待。
(评论:
进程间通信方法很多,Windows Message、msmq、socket(是的,本机socket)、http listener、memory-mapped file、semaphores、mailboxes等等
这里有比较:http://www.codeproject.com/KB/threads/csthreadmsg.aspx
关于named pipe,在这里有:http://www.codeproject.com/KB/threads/dotnetnamedpipespart1.aspx
http://www.codeproject.com/KB/threads/dotnetnamedpipespart2.aspx
我推荐成熟的:http://www.codeproject.com/KB/threads/XDMessaging2.aspx
)
上篇介绍了【多线程命名管道通信的设计】,本篇进行多线程命名管道通信的实现。
服务端实现如下:
创建创建命名管道实例线程
 代码
代码
1 // Handle of create Named Pipe thread.
2 HANDLE hThreadCreatePipes;
3
4 // Create Named Pipe thread .
5 hThreadCreatePipes = CreateThread(
6 NULL, // no security attribute
7 0, // default stack size
8 FUNCreatePipes, // thread proc
9 this, // thread parameter
10 0, // not suspended
11 NULL); // returns thread ID
12 // Close Handle.
13 CloseHandle(hThreadCreatePipes);
14 // Set handle null.
15 hThreadCreatePipes = NULL;
创建命名管道并创建监听管道线程:
 代码
代码
1 DWORD WINAPI FUNCreatePipes(LPVOID lpParameter);
2 DWORD WINAPI FUNCreatePipes(LPVOID lpParameter)
3 {
4 BOOL fConnected = FALSE;
5 LPTSTR lpszPipename = TEXT("\\\\.\\pipe\\MyPipe");
6
7 HANDLE hPipeServer;
8 HANDLE hThreadListenPipes;
9 while(TRUE)
10 {
11 hPipeServer = CreateNamedPipe(
12 lpszPipename, // pipe name
13 PIPE_ACCESS_DUPLEX, // read/write access
14 PIPE_TYPE_MESSAGE | // message type pipe
15 PIPE_READMODE_MESSAGE | // message-read mode
16 PIPE_WAIT, // blocking mode
17 PIPE_UNLIMITED_INSTANCES, // max. instances
18 BUFSIZ, // output buffer size
19 BUFSIZ, // input buffer size
20 0, // client time-out
21 NULL); // default security attribute
22
23 if (hPipeServer == INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE)
24 {
25 AfxMessageBox("Create named pipes failed.");
26 return -1;
27 }
28
29 // Wait for the client to connect; if it succeeds,
30 // the function returns a nonzero value. If the function
31 // returns zero, GetLastError returns ERROR_PIPE_CONNECTED.
32 fConnected = ConnectNamedPipe(hPipeServer, NULL);
33 if (fConnected)
34 {
35 // Create listen pipes thread.
36 hThreadListenPipes = CreateThread(
37 NULL, // no security attribute
38 0, // default stack size
39 FunListenPipes, // thread proc
40 hPipeServer, // thread parameter
41 0, // not suspended
42 NULL); // returns thread ID
43
44 // Close handle.
45 CloseHandle(hThreadListenPipes);
46 // Set handle null.
47 hThreadListenPipes = NULL;
48 }
49 else
50 {
51 // Close handle.
52 CloseHandle(hPipeServer);
53 // Set handle null.
54 hPipeServer = NULL;
55 }
56 }
57 return 0;
58 }
监听管道,对管道数据进行读取与回写:
 代码
代码
1 DWORD WINAPI FunListenPipes(LPVOID lpParameter);
2 DWORD WINAPI FunListenPipes(LPVOID lpParameter)
3 {
4 HANDLE hPipe = (HANDLE)lpParameter;
5
6 HANDLE hHeap = GetProcessHeap();
7 TCHAR* pchRequest = (TCHAR*)HeapAlloc(hHeap, 0, BUFSIZ*sizeof(TCHAR));
8 TCHAR* pchReply = (TCHAR*)HeapAlloc(hHeap, 0, BUFSIZ*sizeof(TCHAR));
9
10 DWORD cbBytesRead = 0, cbReplyBytes = 0, cbWritten = 0;
11 BOOL fSuccess = FALSE;
12
13 CString strRequest = "";
14 CString strReply = "";
15 while (TRUE)
16 {
17 fSuccess = ReadFile(
18 hPipe, // handle to pipe
19 pchRequest, // buffer to receive data
20 BUFSIZ*sizeof(TCHAR), // size of buffer
21 &cbBytesRead, // number of bytes read
22 NULL); // not overlapped I/O
23
24 if (!fSuccess || cbBytesRead == 0)
25 {
26 break;
27 }
28
29 // Process the incoming message.
30 GetAnswerToRequest(pchRequest, pchReply, &cbReplyBytes);
31
32 // Write the reply to the pipe.
33 fSuccess = WriteFile(
34 hPipe, // handle to pipe
35 pchReply, // buffer to write from
36 cbReplyBytes, // number of bytes to write
37 &cbWritten, // number of bytes written
38 NULL); // not overlapped I/O
39
40 if (!fSuccess || cbReplyBytes != cbWritten)
41 {
42 break;
43 }
44
45 strRequest = pchRequest;
46 strReply = pchReply;
47 }
48
49 // Flush the pipe to allow the client to read the pipe's contents
50 // before disconnecting. Then disconnect the pipe, and close the
51 // handle to this pipe instance.
52 FlushFileBuffers(hPipe);
53 DisconnectNamedPipe(hPipe);
54 CloseHandle(hPipe);
55 hPipe = NULL;
56
57 HeapFree(hHeap, 0, pchRequest);
58 HeapFree(hHeap, 0, pchReply);
59
60 return 1;
61 }
62
63 VOID GetAnswerToRequest( LPTSTR pchRequest, LPTSTR pchReply, LPDWORD pchBytes )
64 {
65 // Check the outgoing message to make sure it's not too long for the buffer.
66 if (FAILED(strcpy(pchReply, pchRequest)))
67 {
68 *pchBytes = 0;
69 pchReply[0] = 0;
70 return;
71 }
72 *pchBytes = (lstrlen(pchReply)+1)*sizeof(TCHAR);
73 }
服务端采用阻塞模式等待客户端的连接,客户端连接成功后,立即继续等待下一个客户端的连接
并进行管道的监听、管道数据的读取与写入。
以下为客户端实现:
初始化管道:
 创建文件
创建文件
1 CString strServerIP="This is the server ip";
2 CString lpPipeName="\\\\" + strServerIP + "\\pipe\\MyPipe";
3 LPTSTR lpszPipename = new TCHAR[lpPipeName.GetLength()+1];
4 _tcscpy(lpszPipename, lpPipename);
5 HANDLE m_hPipeClient = CreateFile(
6 lpszPipename,
7 GENERIC_WRITE|GENERIC_READ,
8 0,
9 NULL,
10 OPEN_EXISTING,
11 0,
12 NULL);
13 if(m_hPipeClient == INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE)
14 {
15 CString strLastError;
16 strLastError.Format("%d",GetLastError());
17 AfxMessageBox("Error open pipes, the Last Error number is:"+strLastError);
18 return;
19 }
20 else
21 {
22 AfxMessageBox("Success open pipes");
23 }
24
 设置管道状态
设置管道状态
1 DWORD dwMode = PIPE_READMODE_MESSAGE;
2 BOOL fSuccess = SetNamedPipeHandleState(
3 m_hPipeClient, // pipe handle
4 &dwMode, // new pipe mode
5 NULL, // don't set maximum bytes
6 NULL); // don't set maximum time
7 if ( ! fSuccess)
8 {
9 AfxMessageBox("Failed SetNamedPipeHandleState");
10 }
 创建N个管道线程
创建N个管道线程
1 //Set thread number.
2 int nThreadNumber=10;
3 HANDLE m_hThreadSendReadData;
4 for (int i=0;i<nThreadNumber;++i)
5 {
6 m_hThreadSendReadData = CreateThread(NULL,0,FunSendReadData,this,0,NULL);
7 CloseHandle(m_hThreadSendReadData);
8 m_hThreadSendReadData = NULL;
9 }
 读写管道
读写管道
1 DWORD WINAPI FunSendReadData(LPVOID lpParameter);
2 DWORD WINAPI FunSendReadData(LPVOID lpParameter)
3 {
4 DWORD dwRead,dwWritten;
5 TCHAR chBuf[BUFSIZ];
6 BOOL fSuccess = FALSE;
7 DWORD cbRead, cbToWrite, cbWritten, dwMode;
8 LPTSTR lpvMessage=TEXT("This is the data sent.");
9
10 while(TRUE)
11 {
12 cbToWrite = (lstrlen(lpvMessage)+1)*sizeof(TCHAR);
13 fSuccess = WriteFile(
14 pDlg->m_hPipeClient, // pipe handle
15 lpvMessage, // message
16 cbToWrite, // message length
17 &cbWritten, // bytes written
18 NULL);
19 if (!fSuccess)
20 {
21 break;
22 }
23
24 do
25 {
26 // Read from the pipe.
27 fSuccess = ReadFile(
28 pDlg->m_hPipeClient, // pipe handle
29 chBuf, // buffer to receive reply
30 BUFSIZ*sizeof(TCHAR), // size of buffer
31 &cbRead, // number of bytes read
32 NULL); // not overlapped
33
34 if ( ! fSuccess && GetLastError() != ERROR_MORE_DATA )
35 {
36 break;
37 }
38
39 } while (!fSuccess); // repeat loop if ERROR_MORE_DATA
40 }
41 return 0;
42 }
服务端采用阻塞模式等待客户端的连接,客户端采用多个线程对管道进行数据读写。
因客户端采用多个线程对管道进行读写,故一个线程读取的数据可能并不是此线程写入数据后,服务端读取此线程刚写入的数据后再写入的数据。也就是客户端多个线程写入与读取的数据可能会串,此理论已经过测试,为解决此问题,可以在客户端写入数据时加标识,服务端读取数据后,再写入的数据带上此标识,客户端读取时可根据此标识来判断是否是写入数据后服务端返回的消息。
http://www.cnblogs.com/xinhaijulan/archive/2010/07/31/1789147.html
