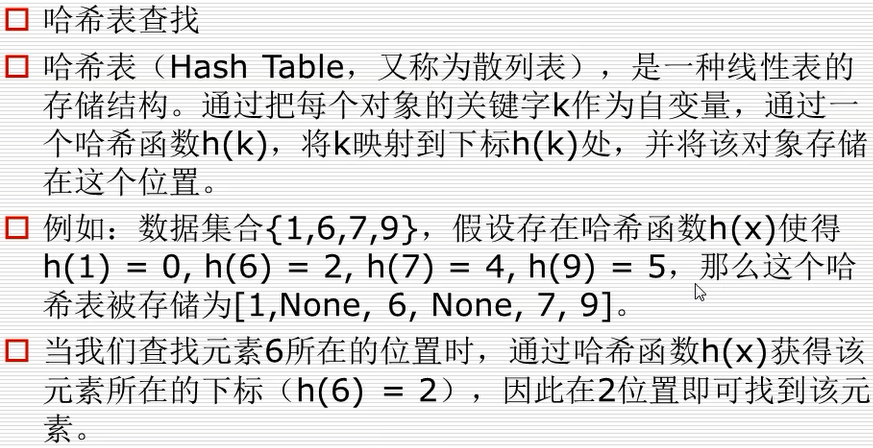
什么是数据结构?

栈

栈的实现

栈的应用


栈的应用
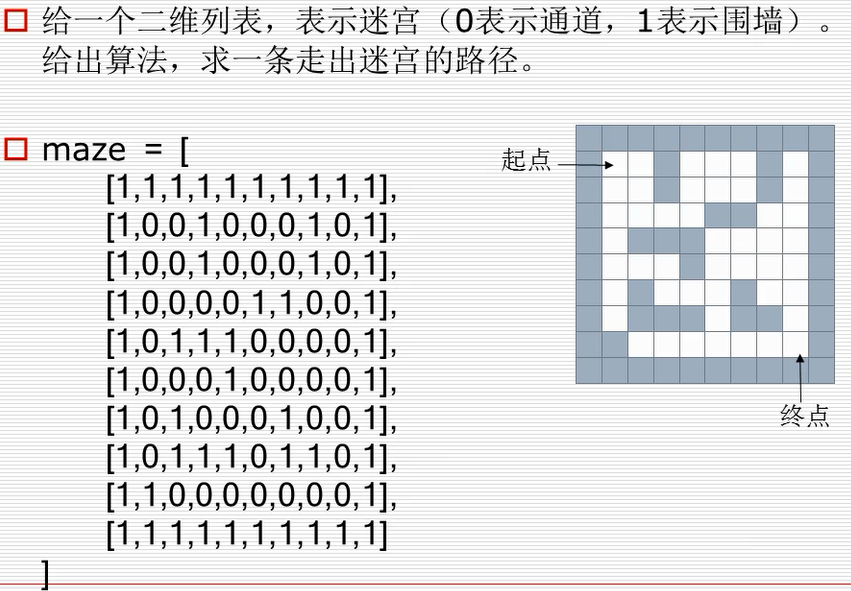
maze = [ # 迷宫
[1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1],
[1,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1],
[1,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1],
[1,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,1],
[1,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,1],
[1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1],
[1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,1],
[1,0,1,1,1,0,1,1,0,1],
[1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1],
[1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1],
]
dirs = [ # 方向
lambda x,y:(x + 1,y), # 右
lambda x,y:(x - 1,y), # 左
lambda x,y:(x,y - 1), # 上
lambda x,y:(x,y + 1), # 下
]
def mpath(x1,y1,x2,y2):
stack = []
stack.append((x1,y1)) # 起点
while len(stack) > 0: # 栈的长度 > 0
curNode = stack[-1] # 当前节点就是栈顶元素
if curNode[0] == x2 and curNode[1] == y2: #如果当前位置就是终点了,就结束了
# 到达终点了
for p in stack:
print(p)
return True
for dir in dirs:
nextNode = dir(curNode[0],curNode[1]) # 找下一个
if maze[nextNode[0]][nextNode[1]] == 0: # maze 找到 0 可以走
# 找到了下一个位置
stack.append(nextNode) # 不管以后能不能走 也要把这步加入到栈中
maze[nextNode[0]][nextNode[1]] = -1 # 标记为已经走过,防止死循环
break
else: # 四个方向 都没有到找
maze[curNode[0]][curNode[1]] = -1 # 死路一条 ,下次别走了
stack.pop() # 回溯
print("没有路!")
return False
mpath(1,1,8,8)
效果显示:
(1, 1)
(2, 1)
(3, 1)
(4, 1)
(5, 1)
(5, 2)
(5, 3)
(6, 3)
(6, 4)
(6, 5)
(7, 5)
(8, 5)
(8, 6)
(8, 7)
(8, 8)
解决思路:

队列
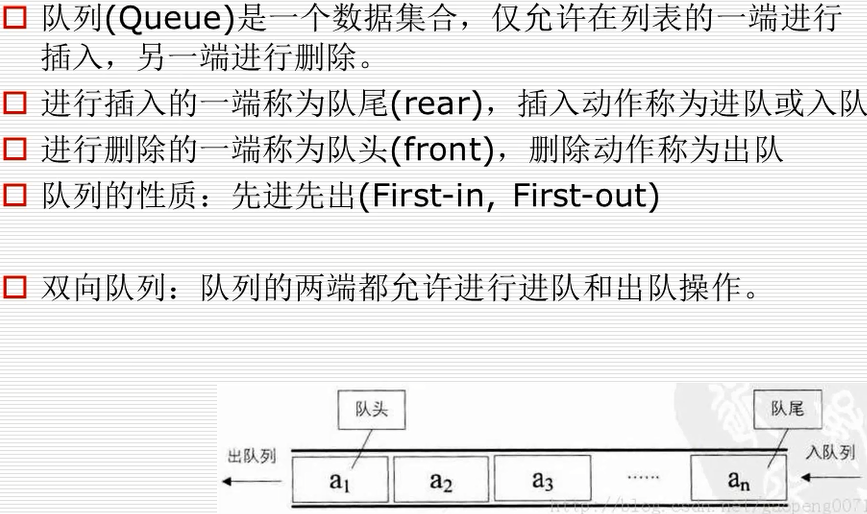
队列的实现

单向队列
from collections import deque queue = deque() queue.append(1) # 进队 queue.append(2) # 进队 print(queue) # 打印此时的队列 print(queue.popleft()) # 打印出队 的 数 print(queue) # 打印剩下的队列
结果显示:
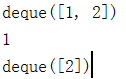
队列的实现原理
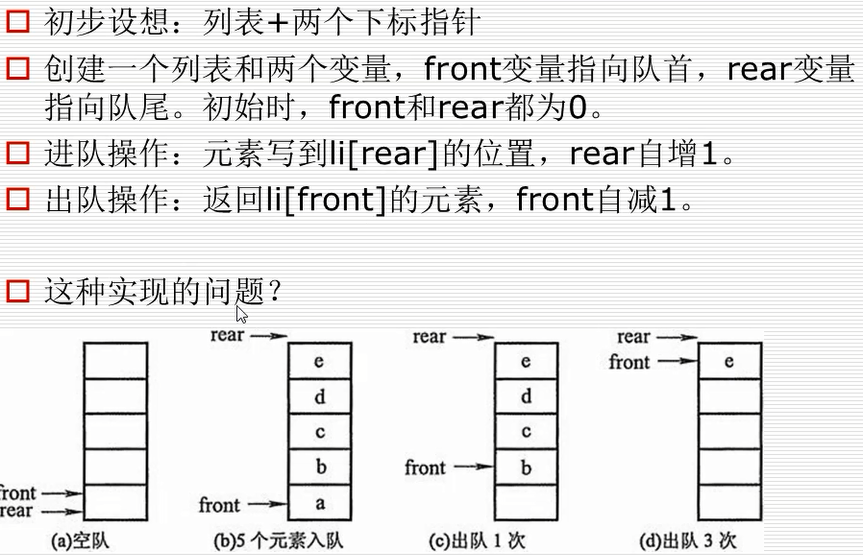
队列的实现原理----环形队列


链表
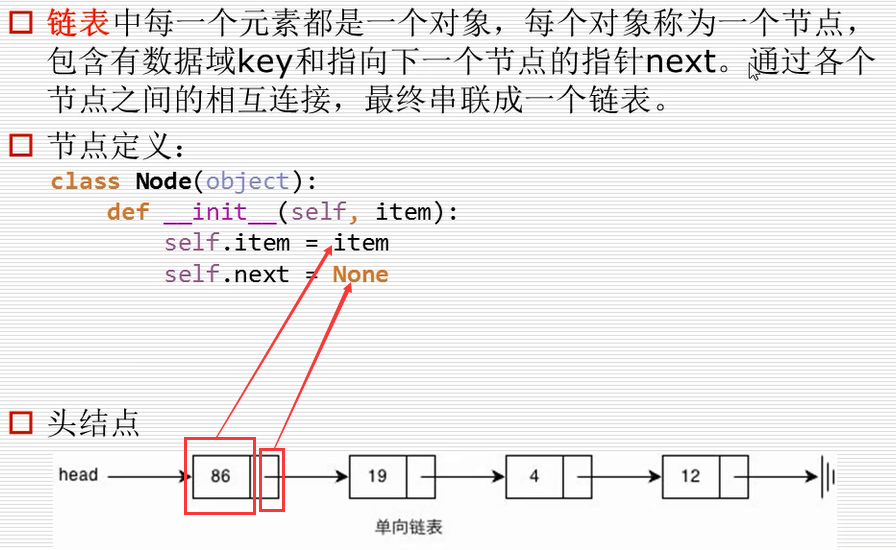
一个很不严谨的链表表示程序:
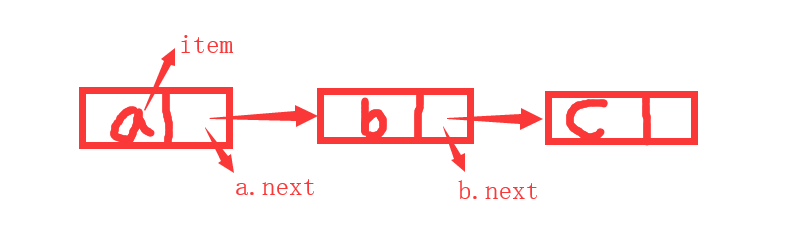
class Node(object):
def __init__(self,item):
self.item = item
self.next = None
a = Node(10)
b = Node(20)
c = Node(30)
a.next = b
b.next = c
print(a.next.item)
print(a.next.next.item)
链表的遍历
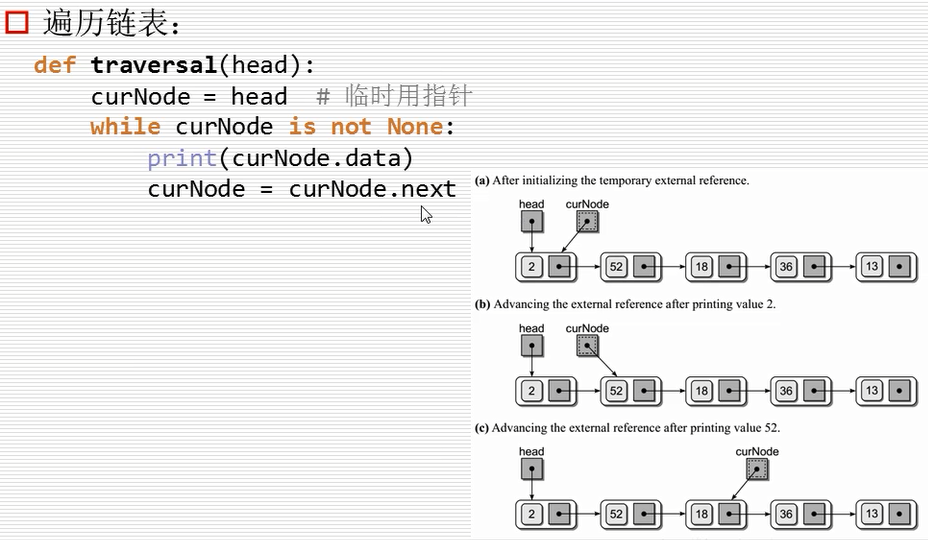
遍历的程序演示:
class Node(object):
def __init__(self,item):
self.item = item
self.next = None
head = Node(10)
head.next = Node(20)
head.next.next = Node(30)
def traversal(head):
curNode = head # 临时用指针
while curNode is not None:
print(curNode.item)
curNode = curNode.next # 指向下一个curNode
traversal(head)
演示的结果为:

链表的插入和删除
单链表
插入:
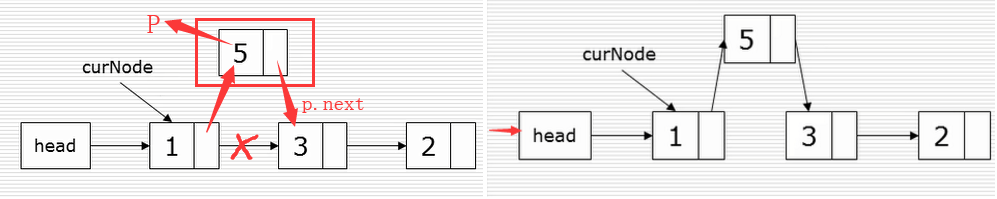

删除:


建立链表
头插法:
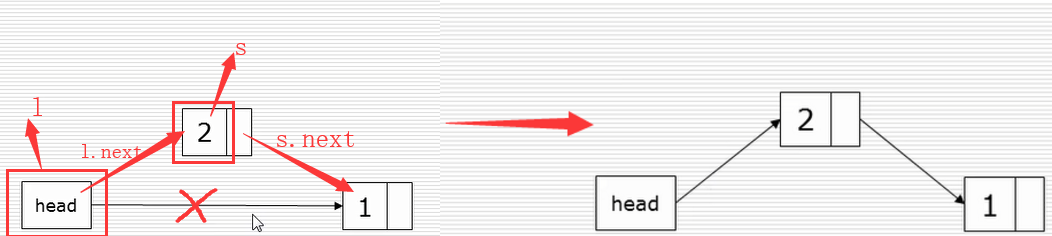

尾插法


双链表

双链表节点的插入和删除
插入
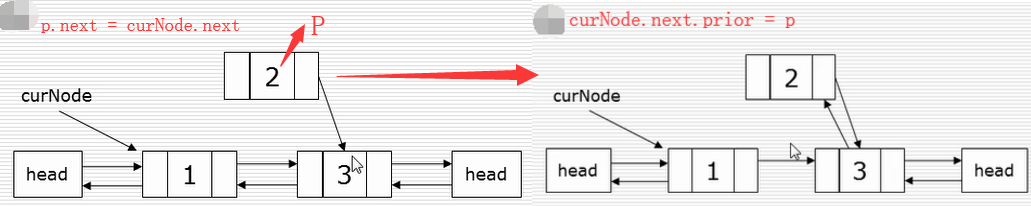


删除

尾插法

链表--分析

Python中的集合与字典(了解)