Queue(队列对象)
Queue是python中的标准库,可以直接import Queue引用;队列是线程间最常用的交换数据的形式
python下多线程的思考
对于资源,加锁是个重要的环节。因为python原生的list,dict等,都是not thread safe的。而Queue,是线程安全的,因此在满足使用条件下,建议使用队列
-
初始化: class Queue.Queue(maxsize) FIFO 先进先出
-
包中的常用方法:
-
Queue.qsize() 返回队列的大小
-
Queue.empty() 如果队列为空,返回True,反之False
-
Queue.full() 如果队列满了,返回True,反之False
-
Queue.full 与 maxsize 大小对应
-
Queue.get([block[, timeout]])获取队列,timeout等待时间
-
-
创建一个“队列”对象
- import Queue
- myqueue = Queue.Queue(maxsize = 10)
-
将一个值放入队列中
- myqueue.put(10)
-
将一个值从队列中取出
- myqueue.get()

多线程示意图
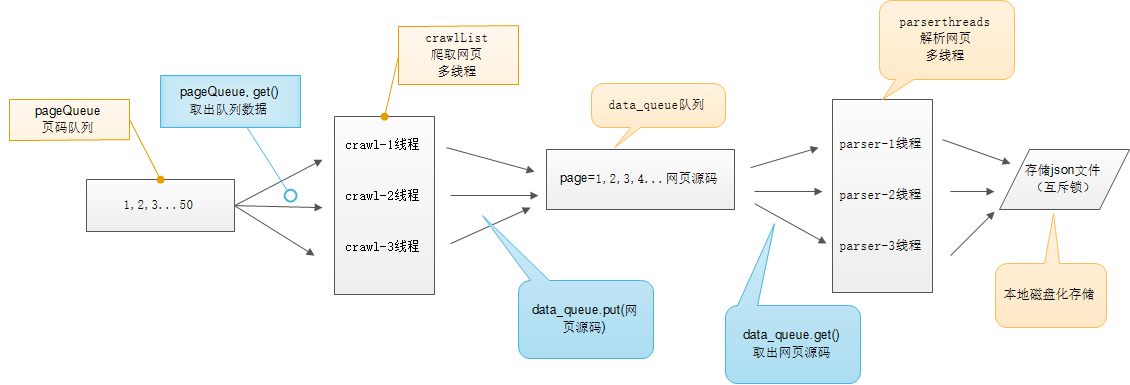
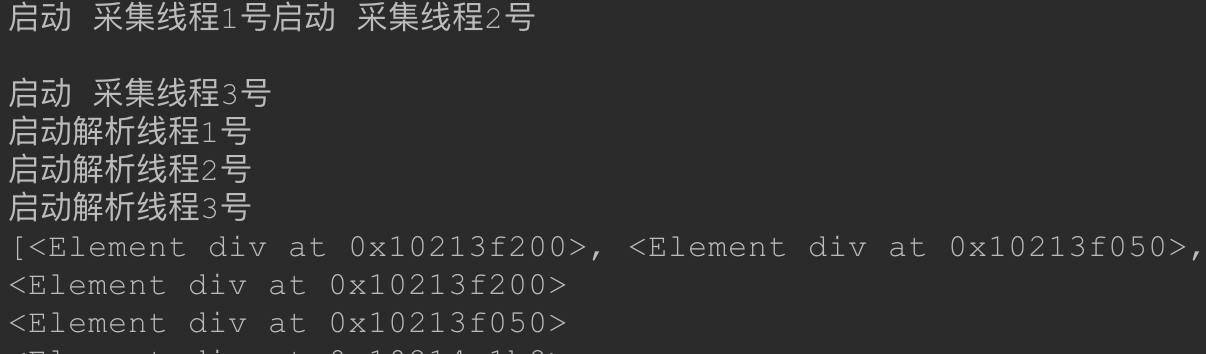
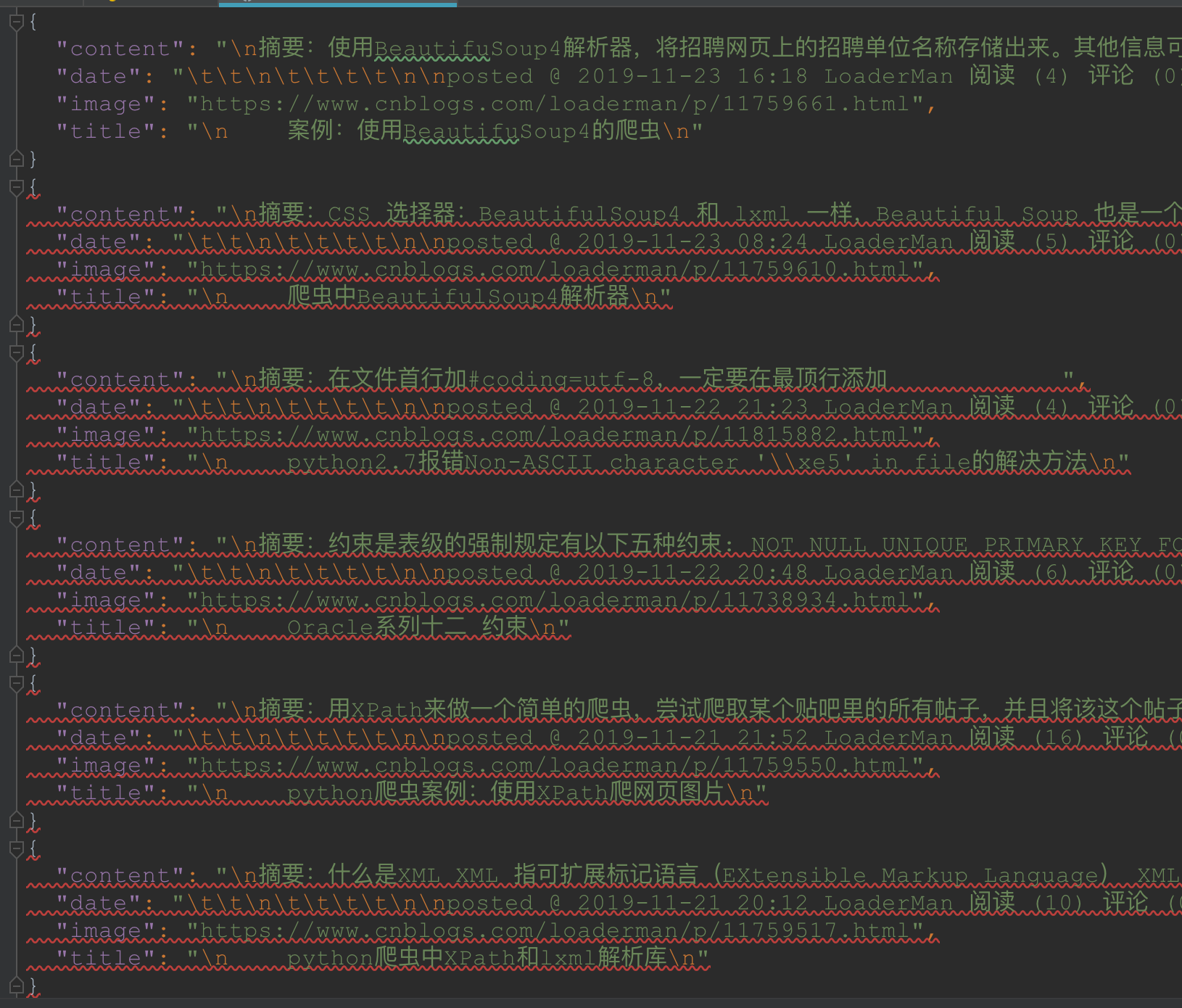
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- # 使用了线程库 import threading # 队列 from Queue import Queue # 解析库 from lxml import etree # 请求处理 import requests # json处理 import json import time class ThreadCrawl(threading.Thread): def __init__(self, threadName, pageQueue, dataQueue): # threading.Thread.__init__(self) # 调用父类初始化方法 super(ThreadCrawl, self).__init__() # 线程名 self.threadName = threadName # 页码队列 self.pageQueue = pageQueue # 数据队列 self.dataQueue = dataQueue # 请求报头 self.headers = {"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; MSIE 9.0; Windows NT 6.1; Trident/5.0;"} def run(self): print "启动 " + self.threadName while not CRAWL_EXIT: try: # 取出一个数字,先进先出 # 可选参数block,默认值为True # 1. 如果对列为空,block为True的话,不会结束,会进入阻塞状态,直到队列有新的数据 # 2. 如果队列为空,block为False的话,就弹出一个Queue.empty()异常, page = self.pageQueue.get(False) url = "https://www.cnblogs.com/loaderman/default.html?page=" + str(page) # print url content = requests.get(url, headers=self.headers).text time.sleep(1) self.dataQueue.put(content) # print len(content) except: pass print "结束 " + self.threadName class ThreadParse(threading.Thread): def __init__(self, threadName, dataQueue, filename, lock): super(ThreadParse, self).__init__() # 线程名 self.threadName = threadName # 数据队列 self.dataQueue = dataQueue # 保存解析后数据的文件名 self.filename = filename # 锁 self.lock = lock def run(self): print "启动" + self.threadName while not PARSE_EXIT: try: html = self.dataQueue.get(False) self.parse(html) except: pass print "退出" + self.threadName def parse(self, html): # 解析为HTML DOM html = etree.HTML(html) node_list = html.xpath('//div[contains(@class, "post")]') print (node_list) items = {} for each in node_list: print (each) title = each.xpath(".//h2/a[@class='postTitle2']/text()")[0] detailUrl = each.xpath(".//a[@class='postTitle2']/@href")[0] content = each.xpath(".//div[@class='c_b_p_desc']/text()")[0] date = each.xpath(".//p[@class='postfoot']/text()")[0] items = { "title": title, "image": detailUrl, "content": content, "date": date, } with open("loadermanThread.json", "a") as f: f.write(json.dumps(items, ensure_ascii=False).encode("utf-8") + " ") CRAWL_EXIT = False PARSE_EXIT = False def main(): # 页码的队列,表示20个页面 pageQueue = Queue(20) # 放入1~10的数字,先进先出 for i in range(1, 21): pageQueue.put(i) # 采集结果(每页的HTML源码)的数据队列,参数为空表示不限制 dataQueue = Queue() filename = open("duanzi.json", "a") # 创建锁 lock = threading.Lock() # 三个采集线程的名字 crawlList = ["采集线程1号", "采集线程2号", "采集线程3号"] # 存储三个采集线程的列表集合 threadcrawl = [] for threadName in crawlList: thread = ThreadCrawl(threadName, pageQueue, dataQueue) thread.start() threadcrawl.append(thread) # 三个解析线程的名字 parseList = ["解析线程1号", "解析线程2号", "解析线程3号"] # 存储三个解析线程 threadparse = [] for threadName in parseList: thread = ThreadParse(threadName, dataQueue, filename, lock) thread.start() threadparse.append(thread) # 等待pageQueue队列为空,也就是等待之前的操作执行完毕 while not pageQueue.empty(): pass # 如果pageQueue为空,采集线程退出循环 global CRAWL_EXIT CRAWL_EXIT = True print "pageQueue为空" for thread in threadcrawl: thread.join() print "1" while not dataQueue.empty(): pass global PARSE_EXIT PARSE_EXIT = True for thread in threadparse: thread.join() print "2" with lock: # 关闭文件 filename.close() print "谢谢使用!" if __name__ == "__main__": main()
效果: